presentation
advertisement
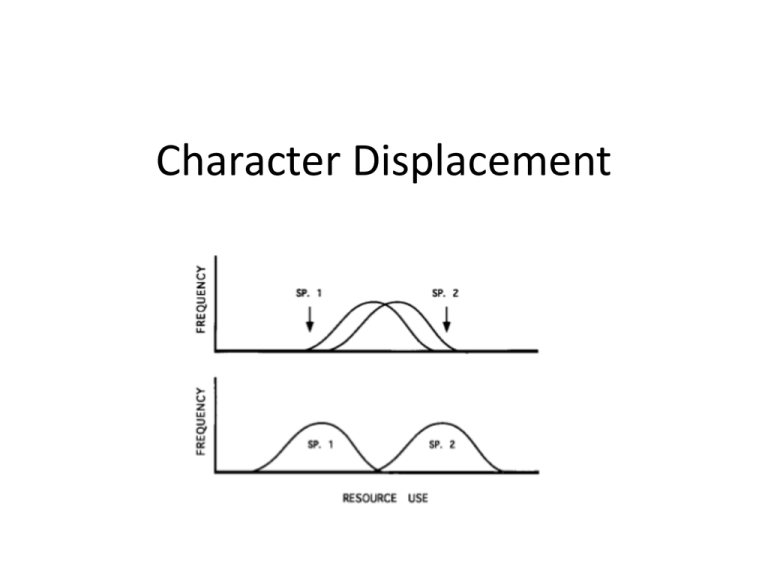
Character Displacement Brown & Wilson’s Definition: Two closely related species have overlapping ranges. In the parts of the ranges where one species occurs alone, the populations of that species are similar to the other species and may even be very difficult to distinguish from it. In the area of overlap, where the two species occur together, the populations are more divergent and easily distinguished, i.e., they "displace" one another in one or more characters. The characters involved can be morphological, ecological, behavioral, or physiological; they are assumed to be genetically based. Lack’s Work Beak size similar where allopatric, but G. fulginosa has smaller beak than G. fortis when sympatric The Pattern What else could cause this? • Competitive exclusion (character sorting) • Environmental gradients (sympatry happens to correspond with largest differences) • Random • Phenotypic plasticity Character displacement = just so story! How can we improve observations? 1) Know what to look for 2) Null models 3) Do experiments instead! Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 1) Differences between sympatric taxa are greater than expected by chance How?: Null models for comparison Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 2) Differences in character states are related to differences in resource use How?: Correlate resource use with character. Duh. Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 3) Resources are limiting, and interspecific competition for these resources is a function of character similarity. How?: Demonstrate competition is occurring (e.g. fewer prey consumed in sympatry vs. allopatry); Experiments help here. Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 4) Resource distributions are the same in sympatry and allopatry such that differences in character states do not simply reflect differences in resource availability How?: Show that environment is sufficiently similar in both places. Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 5) Differences must have evolved in situ How?: Trait differences in sympatry should exceed whole range in allopatry; use population genetics/phylogenetics to model past events Six Criteria for Character Displacement (know what to look for) 6) Differences must be genetically based How?: Reciprocal transplants, experimental rearing, genetics. Criteria Met? Meta-analysis of 61 studies; from Schluter 2000 Is character displacement biased? Meta-analysis of 61 studies; from Schluter 2000 Types of Character Displacement • Ecological Character Displacement: Competition over resources causes divergence • Reproductive Character Displacement: “Competition” over correct gamete causes divergence Case study: Grant & Grant 2006 Green = Invader Red = Invaded Case study: Grant & Grant 2006 Severe drought Severe drought G. magniostris arrives Case study: Grant & Grant 2006 Case study : Grant & Grant 2006 Case study: Grant & Grant 2006 Which criteria are met? 1) Change greater than chance? 2) Character states related to resource use? 3) Demonstrated resources are limiting? 4) Resource distributions same in sympatry and allopatry? 5) Differences evolved in situ? 6) Characters heritable? Case study: Schluter 1994 Uses experiments! Case study: Schluter 1994 White = Intermediates only Black = Intermediates plus limnetic specialist Benthic Limnetic Paper choices for discussion • Option 1: Losos 1990 – Uses phylogenetics and various models to determine why Anolis species pairs on Antilles islands are large/small, but single species are intermediate: character displacement or character sorting? Paper choices for discussion • Option 2: Muchhala and Potts 2007 – Looks at reproductive character displacement in batpollinated flowers; looks at nature of pollination mechanisms experimentally and observationally. Paper choices for discussion • Option 3: Pfennig and Pfennig 2005 – Examines character displacement in spade foot toads to test if displacement may lead to a ‘winner’ and ‘loser’; is character displacement the best of a bad situation? Paper choices for discussion • Potential 4th option – If you liked the case studies, we could read Grant & Grant 2006, plus Schluter 2000, which reviews his labs work, including the experiment presented today. Both are pretty short.