addresses - SCN Wiki
advertisement

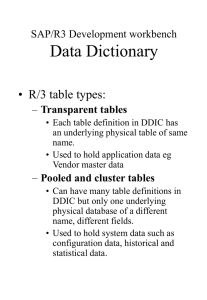
& Address Cleansing Integration of REST web services Chris Twirbutt & Forrest Horner 2010 November 1 Melissadata REST & SAP Integration • • • • Background of Sacramento County Address cleansing choices Architecture to facilitate REST web services Example SAP screens 2 Background Sacramento County CA • Sacramento County, California – About 1.3 million citizens – Multiple jurisdictions, Cities, Districts, etc • SAP IS-U/CCS Utility Billing System (aka: “FOCUS”) – – – – Implemented in July 1999 (on v1.1b)…now vECC6 Bill for ~300K customers, ~$300m revenue Waste Water, Solid Waste, Drainage, Potable Water …have a SAP tech support staff of: ~8 3 Address Cleansing Choices #1 – Load Postal CD’s to SAP Regional Structure …but alas, it doesn’t fix “bad” addresses…only flags address is not good. #2 – Periodic Batch Cleansing Is re-active management…and bad addresses percolate through downstream data systems. #3 – Web Service Address Cleansing Is pro-active,but must put in a technical architecture. 4 Postal CD Data – Does Not “Fix” Postal CD comes from the Post Master The USPS web site http://www.usps.com/ncsc/addressinfo/addressinfomenu.htm The web site has the postal AIS technical guide in PDF format and order forms for ordering the postal CD. Note: RSADRLSM02 is the program that loads the data Connection Object Note: SAP function module ADDR_CHECK is what SAP uses for verifying if an BP or CO address is valid against the postal structures Business Partner 5 Periodic Batch Cleanse (Monthly) ADRC table File dump Data Extract SAP Production Cleansing Service Address Corrections File Data Upload and update This fixes after the fact…after bad mail has already gone out…and after other downstream data systems have already consumed the bad address 6 Melissadata – Web Service Has many different address cleansing products Meldata provides back a ‘corrected’ address. SAP Production / SYSID:“PPW” Web Service FOCUS RFC Web Hit Counter Dev / Test Systems Address Cache An “architecture” had to be built in SAP. The SAP production system acts as a “service buss”. 7 Overview of MelData Web Services Mellisadata (Henceforth referred to as “Meldata”) offers numerous services and Suites of Services. Sac County procured the “Data Quality Web Services Suite” , which is a “Multiplatform toolkit to verify, correct and standardize address, phone, email and names at point-of-entry.” This Suite consists of 7 services, 5 of which we have enabled ( And two of which we are currently using ( ): • Address Check • RBDI (Residential/Business Delivery Indicator) • GeoCode • IP Location • Email • Name Check • Phone Check ) 8 Usage allowance We subscribed to 600K hits per year for each enabled service. The following is a screen-print from MelData’s side which tracks our usage: 9 Technical Implementation SOAP vs. REST Overall, more companies such as Google and Amazon are using REST-based Web Services. REST stands for “Representational State Transfer”. We won’t go into fine detail of SOAP vs. REST but rather, why we chose REST. A nice robust link on the technical differences between SOAP and REST: http://www.taranfx.com/rest-vs-soap-using-http-choosing-the-right-webservice-protocol We utilize the REST-based Web Service Interface because: • SOAP required more JAVA skills than were available in-house, for example: • SOAP had many data-type binding issues which had to be worked out by contacting MelData tech support and having them make changes to the WSDL, etc. • REST was 10 times easier to code for in ABAP as it didn’t have to deal with Proxy generation (data binding issues), and other JAVA-related issues. • Developers who simply understand HTTP and XML can start building Web services right away, without needing any toolkits beyond what they normally use for Internet application development. 10 BASIS/Config. Requirement (for SAP to communicate with the Web Service) -Using SSL (https) to access external web site recommended. - Public web servers have SSL certificates signed by known public Certificate Authority - Web browsers come with built-in store of known public CA’s to verify certificate server is presenting. -The SAP Web Application Server (Web AS) ships with very few CAs, so it won’t know the CA the remote site had its SSL cert signed by. For example, Melissadata uses “GoDaddy”. -Navigate to the secure URL using a web browser, not SAP initially. -While there, click the “lock” icon and download the security certificates in base 64 format. This incl. both the root and class 2 certificates. -There may be multiple cert’s, called a chain. Download cert for each part of chain. -Load the security certificate into SAP (STRUST) -Import certificates into SAP anonymous &client standard PSE’s (Personal Security Environment) -Still In STRUST, export the certificates (to load them into the db). -Restart ICM. -Set up a “hosts file” entry, if needed (i.e. DNS is turned off, which it is in PPW) to Melissadata so the SAP server “knows” who Melissadata is. 11 Architecture Overview Custom(‘Z’) Naming Convention Begin all Web-Service-related Z-table names with “ZWS_” 12 Architecture Overview (cont’d) • All requests for address scrubs are done thru PPW (Production), regardless of source system. This is done by RFC and ensures that all hits are tracked in one place (Production). • PPW architected with several control & tracking tables: • A master table(ZWS_MELDATA) which stores/caches all detailed request history • A table to configure how many hits allowed per day (ZWS_HITS_MAX) • A table to store actual hits per day counts (ZWS_HITS_DAILY) 13 Architecture (Cont’d) PPW contains (cont’d): • table (ZWS_MELDATACODES) stores all possible return codes (and descriptions) Note on Return Codes: • 1st Char: •Address Scrub return Codes begin with “A” •and GeoCoding Return Codes begin with “G”. • 2nd Char: •“S” (Success – Corrected address returned) •or “E” (Error – Not able to return a fully corrected address) 14 Architecture (Cont’d) • Communication to PPW from all systems: -An RFC interface was added (By BASIS) to all the systems that "points to" PPW. This interface is named "PPW_SCRUB". -A user and role was created in PPW to perform the scrub function. The user is "adrscrub", and the role is "z_address_scrub". • Communication to Web Service from SAP/ABAP: A user-friendly wrapper/RFC/FM was developed called: ZMELISSADATA_ADDRESS_CLEANSE This FM/RFC currently performs both Address Check and Geocoding. This FM uses SAP’s OO methods contained in Class/Interface “IF_HTTP_CLIENT”, For example: CALL METHOD http_client=>create_by_url (sets up the URL to be called) CALL METHOD http_client->send (makes a call to the URL) CALL METHOD http_client->receive (receives data back from URL) The result comes back in XML format and is parsed by the FM (could have been done using XLST Transformation, but in our case using custom code to parse the XML result into Z-Table fields (this was prior to our knowledge of XLST Transformations). 15 Example of how to call the RFC IN OUT Note: Input has incorrect Street name (“AVE” vs. “RD”) and incorrect zip (95826 Instead of 95827) Output has corrected Street Name And Zip Code (+4). “Address Key” required for GeoCoding (see next slide) 16 Example of Geo-Coding IN OUT 17 Table Entry Created (in ZWS_MELDATA) MANDT COUNTER ALL TIME 020 9910 SOURCE SYSTEM PPW SOURCE USER TWIRBUTTC CALLING PROGRAM SAPLSEUJ CALLING TXN SE37 CALLED ON DATE 06/14/2010 CALLED ON TIME 14:06:45 CALLED BY ADRSCRUB URL CALLED https://addresscheck.melissadata.net/v2/REST/Service.svc/doAddressCheck?id=1234567890&a1=9700%20GOETHE%20AVE&ctry=US&opt=true&a2=&ste=C&city=SA CRAMENTO&state=CA&zip=95826 RETURN CODE AS01,AS12 BACKGROUND FLAG IN HOUSE NUM 9700 IN STREET GOETHE AVE IN SUITE C IN CITY SACRAMENTO IN STATE CA IN ZIP 95826 OUT PARSED HOUSE 9700 OUT PARSED STR Goethe OUT PARSED STSUF Rd OUT PARSED SUIT1 Ste OUT PARSED SUIT2 C OUT ADDRESS1 9700 Goethe Rd OUT ADDRESS2 OUT SUITE Ste C OUT CITY Sacramento OUT STATE CA OUT ZIP 95827 OUT PLUS4 3558 OUT RESULT CODES AS01,AS12 HOUSESTREETMATCH CITY MATCH X STATE MATCH X ZIP MATCH ADRC NUM OUT ADDRESSKEY 95827355875 GEO RESULT CODES GS01 GEO LAT 38.554697 GEO LONG -121.335972 18 ZWS_MELDATA: Field Definitions MANDT COUNTER_ALL_TIME 020 9910 # of hits made to the Web Service (all-time) SOURCE_SYSTEM PPW Calling System SOURCE_USER TWIRBUTTC Self-explanatory CALLING_PROGRAM SAPLSEUJ “ CALLING_TXN SE37 “ CALLED_ON_DATE 06/14/2010 “ CALLED_ON_TIME 14:06:45 “ CALLED_BY ADRSCRUB RFC User id (set up by BASIS) URL_CALLED https://addresscheck.melissadata.net/v2/REST/Service.svc/doAddressCheck?id=1234567890&a1=0970%20GOETHE%20AVE&ctry =US&opt=true&a2=&ste=C&city=SACRAMENTO&state=CA&zip=95826 RETURN_CODE AS01,AS12 MelData Return Codes BACKGROUND_FLAG Background/Foreground indicator IN_HOUSE_NUM 9700 Input House # IN_STREET GOETHE AVE Input Street IN_SUITE C Input Suite (opt’l) IN_CITY SACRAMENTO Input City IN_STATE CA Input State IN_ZIP 95826 Input Zip Note: Key fields are MANDT & COUNTER_ALL_TIME Index exists on URL_CALLED since we CACHE based on this one field (each unique URL represents a unique AddressCheck). Continued on next Slide… 19 Field Definitions (cont’d) OUT PARSED HOUSE OUT PARSED STR OUT PARSED STSUF OUT PARSED SUIT1 OUT PARSED SUIT2 OUT ADDRESS1 OUT ADDRESS2 OUT SUITE OUT CITY OUT STATE OUT ZIP OUT PLUS4 OUT RESULT CODES HOUSESTREETMATCH CITY MATCH STATE MATCH ZIP MATCH ADRC NUM OUT ADDRESSKEY GEO RESULT CODES GEO LAT GEO LONG 9700 Goethe Rd Ste C 9700 Goethe Rd Ste C Sacramento CA 95827 3558 AS01,AS12 X X 95827355875 GS01 38.554697 -121.335972 Parsed Address fields returned from MelData “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ “ MelData Return Code(s) Did INPUT House # and Street match the OUTPUT House # and Street ? Did INPUT City match the OUTPUT City ? Did INPUT State match the OUTPUT State? Did INPUT Zip match the OUTPUT Zip ? ADRC Record # scrubbed (if applicable) Meldata address key returned (needed to GeoCode) GeoCode Return Code(s) GeoCode Lat Result GeoCode Long Result 20 Find Billing Account by Address lookup Via GeoCoding Step 1 – Meldata address check -- Cache result in table ZWS_MELDATA Step 2- Update sap address if necessary and possible (if address scrub was successful) Step 3 – Using MelData Address key (from Successful scrub only), get lat long Step 4 – Using haversine formula, get nearest parcel (ZPSD_APN) and VKONT (ZGIS_APN_DATA) (Using FM “Z_RFC_LAT_LONG_IN_PARCEL_OUT”) IN OUT Since Geo-Coding is not always down to the rooftop level, enter As much info of the Address as possible (in this case House # and 1st letter of Street) 21 Secret Sauce: HAVERSINE Formula http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Haversine_formula SAP ABAP program code: Assume that U = North Pole, and V and W are our pair of X,Y coordinates (note the variable names above do not match that of the program code in this presentation) a,b, and c are the “Great Circle”* distances between U,V and W. * A great circle of a sphere is a circle that runs along the surface of that sphere so as to cut it into two equal halves. The great circle therefore has both the same circumference and the same center as the sphere. It is the largest circle that can be drawn on a given sphere. Great circles serve as the analogue of "straight lines" in spherical geometry. 22 Other FOCUS Applications: This stand alone screen demonstrates the architecture. Link to Youtube demo of this screen: http://www.youtube.com/watc h?v=7txYpWmKWCg Link to SAP Developer Network (SDN) SAP/Meldata WiKi: http://wiki.sdn.sap.com/wiki/di splay/stage/Address%20Cleansi ng%20via%20REST%20Web%20 Service%20Consumption 23 Other FOCUS Applications: E.g. Lifeline Entry (for Non-FOCUS Accts.) New Button New Sub-screen For scrubbed address Results. 24 Future Integration • Managed update, with clerical review of suggested Address fixes. •Fully Automated update of our Address from Mel-Data. • Business Partner mailing address update • Physical location addresses • To be continued…… A myriad of other opportunities will present themselves: Finding duplicate customers, locations. Finding missing locations: address exists, but we aren’t billing. Geocoding & Work Order proximity based routing. •Regional MADD (Master Address Database) Effort by Cities, and public safety, police, fire, etc to standardize addresses. Lessons Learned: •Must have an architecture to facilitate & manage the web service “hits” •Must involve your BASIS team to “open up” the interface •Mass cleansing (thousands at a time) needs “404” error handling •Melissadata tech team were great to collaborate with!...an essential aspect. 25