2011_Poster_Foereid_F_140_7
advertisement

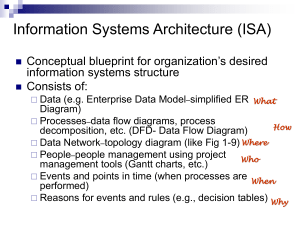
Major J, B, Nguyen Lehmann Lehmann J, Rondon J, Hockaday M, Goodale WC, Joseph C (2010a) S, Masiello Fate ofCA soil-applied (2010) Temperature black carbon: sensitivity downward of black migration, carbonleaching decomposition and soiland respiration. oxidation. Glob Environ Change SciBiol Tech16:1366-1379 DOI: 10.1021/es903016y Modeling black carbon in the environment Bente Foereid, Johannes Lehmann, Julie Major Crop and Soil Sciences, Cornell University •Black carbon (BC) is produced in fires and is assumed to be stable in the environment •“Biochar” is BC intentionally produced for soil amendment •BC has not yet been explicitly introduced into carbon turnover models •Here we make a simple model accounting for loss of BC by decomposition and horizontal as well as vertical movement out of the area Results Lab data for decomposition 2000 1800 -1 day ) 1600 Measured Simulated 0.5 1400 -2 2 y=1.452ln(x)-2.4599 r2=0.7094 1 2200 0 Model structure Field data for leaching 1000 0.4 RMSD=0.24 20 40 0.2 0.1 0.0 Decomposition CO2 600 400 30 Simulated Measured 25 20 15-30 cm 15 10 60 Temperature (oC) 800 -2 0.3 -1 0 0-15 cm 1200 Black carbon in layer (g m ) 3 CO2 production from BC (g CO 2-C m Temperature modifier 4 2400 0.6 Nguyen et al., 2010 Environ Sci Tech 44, 3324–3331 Whitman , 2010 M.Sc. thesis, Cornell University 5 2600 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 5 Time since BC application (days) Predicted and measured CO2 production. Data from Major et al. 2010 0 0 Added black carbon 2500 0-15 cm 2000 standard stable pool decomposition rate erosion rate moisture modifier temperature modifier 1500 CO2 Labile Erosion -1 15 cm Major et al., 2010 Glob Change Biol 16:1366-1379 Stable CO2 Labile 1000 Time since BC application (days) Predicted and measure BC in topand sub-soil. Data from Major et al. 2010 500 0.3 30 cm 100 y 0.1 standard erosion rate slow pool decomposition rate temperature sensitivity 400 0.2 Conclusions 600 0 15-30 cm Leaching 400 500 BC in 0-30 cm soil (gm-2) Stable BC in soil layer (g m ) Erosion 200 300 2000 y 200 100 •Erosion is poorly quantified, but probably Effect of changing parameter values, erosion the largest flux of BC out of a given area rate ± 50%, slow pool turnover rate 500-5000 •A two pool model can adequately y, alternative values for temperature and moisture modifier describe BC decomposition dynamics Next step – earth system model, CLM •Decomposition rate of the slowest carbon pool is unimportant on time-scales < 100 y •Downwards movement is small as a mass flux, but not the only downward flux of BC 0.0 0 0 20 40 60 Time since BC application (years) 80 100 0 500 1000 Time (years) 1500 2000