lab 9
advertisement

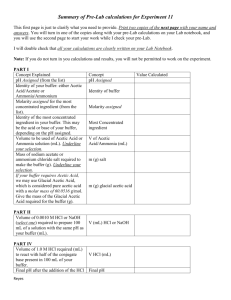
BUFFER SOLUTIONS LAB 9 INTRODUCTION Adding trace amount of acid to water will result in increase in H+ concentration. In the same manner, adding trace amount of alkali eg. NaOH to pure water will result in increase of OH− So we can say that water has no ability to resist change in H+ concentration or pH. (pH = − log [H+]) WHAT IS A BUFFER SOLUTION? Buffer solution: Is a system that possesses the property of resisting change in the pH with the addition of small amount of strong acid or base. The efficiency of the system called buffer capacity. COMPOSITION Buffer solution is usually composed of a weak acid and a salt of the acid eg. Acetic acid and sodium acetate, or weak base and a salt of the base eg. Ammonium hydroxide and ammonium chloride. WEAK ACID BUFFER Weak acids do not completely dissociate when in solution, instead an equilibrium is set up; HA ⇌ H+ + A− The dissociation constant or 𝑲𝒂 value is calculated by the following equation: 𝑲𝒂 = Where 𝐀− = salt 𝐇𝐀 = acid 𝐇 + 𝐀− (𝐇𝐀) WEAK ACID BUFFER Dissociation constants of some weak acids at 25 °C ACID 𝑲𝒂 Acetic acid 1.75 x 10-5 Benzoic acid 6.4 x 10-5 Formic acid 1.76 x 10-4 Lactic acid 1.38 x 10-4 Salicylic 1.06 x 10-3 WEAK ACID BUFFER 𝐇 + 𝐀− 𝑲𝒂 = (𝐇𝐀) …… (1) Since most 𝑲𝒂 values are small numbers its more convenient to express them as negative logarithm p𝑲𝒂 = − log 𝑲𝒂 So equation (1) will be 𝐩𝑲𝒂 = −𝒍𝒐𝒈 𝐇 + − 𝐥𝐨𝐠 𝐬𝐚𝐥𝐭 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 and because pH = −𝒍𝒐𝒈 H + Then and 𝐩𝑲𝒂 = pH − 𝐥𝐨𝐠 pH = 𝐩𝑲𝒂 + 𝐥𝐨𝐠 Weak acid buffer pH is ˂ 7 𝐬𝐚𝐥𝐭 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 𝐬𝐚𝐥𝐭 𝐚𝐜𝐢𝐝 WEAK BASE BUFFER BOH ⇌ B+ + OH− Similary, the dissociation constant, or Kb value of weak base is given by the equation: 𝑲𝒃 = 𝐁 + 𝐎𝐇− (𝐁𝐎𝐇) Where B+ = salt and 𝐁𝐎𝐇 = base pH = 𝐩𝑲𝒘 − p Kb + 𝐥𝐨𝐠 𝑲𝒘 = 10−𝟏𝟒 𝐩𝑲𝒘 = 14 𝒃𝒂𝒔𝒆 𝒔𝒂𝒍𝒕 PRACTICE PROBLEMS 1. the dissociation constant Ka of acetic acid is 1.75 x 10-5 at 25 °C. Calculate its pKa value. 2. What is the pH of a buffer solution prepared with 0.05 M sodium borate and 0.005 M boric acid? The pKa of boric acid is 9.24 at 25 °C. 3. What is the pH of a buffer solution prepared with 0.05 M ammonia and 0.05 M ammonium chloride? The Kb of ammonia is 1.8 x 10-5 at 25 °C. 4. What molar ratio of salt/acid is required to prepare a sodium acetate-acetic acid buffer solution with a pH of 5.76? pKa of acetic acid is 4.76 at 25 °C. PRACTICE PROBLEMS 5. The molar ratio of sodium acetate to acetic acid in a buffer solution with a pH of 5.76 is 10:1. Assuming the total buffer concentration is 2.2 x 10-5 mol/L, how many grams of sodium acetate (m.w. 82) and how many grams of acetic acid (m.w. 60) should be used in preparing a liter of the solution? 6. Calculate the change in pH after adding 0.04 mol of sodium hydroxide to a liter of buffer solution containing 0.2 M concentration of sodium acetate and acetic acid. The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76 at 25 °C. 7. What is the pH of buffer solution prepared with 0.055 M sodium acetate and 0.01 M acetic acid? The pKa of acetic acid is 4.76 at 25 °C. HOME WORK 1. What is the change in pH with addition of 0.01 hydrochloric acid to a liter of buffer solution containing 0.05 M of ammonia and 0.05 M ammonium chloride? Kb of ammonia is 1.8 x 10-5 at 25 °C. 2. The dissociation constant of ethanolamine is 2.77 x 10-5 at 25 °C. Calculate pKb