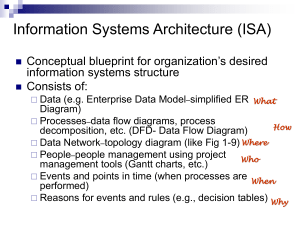
Aluminium – a Key Research Area at NML
advertisement

Thermal decomposition kinetics of biomass wastes used in energy co-generation C.SASIKUMAR & K.K.S. GAUTAM Department of MSME, MANIT, Bhopal T.C.ALEX & S.SRIKANTH National Metallurgical Laboratory, (CSIR), Jamshedpur Kinetics studies of biomass materials and its complexity Rate at which a chemical process occurs. Besides information about the speed at which reactions occur, kinetics also sheds light on the reaction mechanism (exactly how the reaction occurs). d dt E A . exp . f ( ). k ( T ) f ( ) Nk B T Biomass wastes - hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin Possibility of change in reaction mechanism with temperature Complex multiple reactions - series, parallel or independent overlapping reactions Program on decomposition Studies of biomass Materials Rise Husk Groundnut Shell Coffee Husk Bagasse Cotton Flower Wood - chips Various conditions of Thermal decomposition of sugarcane bagasse Argon Atmospheric air Oxygen Biomass Biomass + Coal Atmosphere Fuel mix 0.5 to 100 0C/min Isothermal Non-isothermal • Linear heating • Non-linear heating Heating rate Heating method Thermogravimetric Studies of Sugarcane bagasse S.NO 1. 2. 3. Material Sugar cane bagasse E.I.D. Parry (India) Limited, Nellikuppam, Tamil Nadu, India. Sugar cane bagasse Sugar cane bagasse Atmosphere Argon Atmospheric Air Oxygen Heating Rate (0C/min) 2 5 10 30 2 5 10 30 2 5 10 30 TG/DTA analyzer (Seiko, Japan, Model No. A320) chemical composition (%w/w) of the bagasse Constituent of sugarcane S.No bagasse in dry Condition Weight percentage (Initial) 1 Hemi-Cellulose 33% 2 Cellulose 38% 3 Lignin 22% 4. Ash 2.3% 5. Moisture content 4.7% By murugappa groups R&D, Chennai, India. TG-DTG Results of Sugarcane bagasse at Argon atmosphere 1600 Bagasse Argon atm 0.0 1400 -0.2 DTG (g/min) Mass loss () 1200 0 30 C/min -0.4 0 2 C/min Bagasse Argon atm 0 2 C/min 0 5 C/min 0 10 C/min 0 30 C/min 1000 800 600 400 -0.6 200 0 5 C/min -0.8 0 0 10 C/min -1.0 400 400 600 800 0 Temperature ( K) 1000 600 800 0 Temperature ( K) 1000 DTA -Sugarcane bagasse Argon atmosphere 40 30 Bagasse Argon atm T 20 10 0 30 C/min 0 0 10 C/min -10 0 2 C/min -20 400 600 800 0 Temperature ( K/min) 0 5 C/min 1000 TG & DTG Results of Sugarcane bagasse in static air Bagasse Static air atm 0.0 1000 Bagasse Static air atm 900 -0.2 800 -0.4 DTG (g/min) mass loss 700 0 30 C/min -0.6 0 5 C/min 600 500 0 30 C/min 0 10 C/min 400 300 0 5 C/min 200 -0.8 100 0 2 C/min -1.0 200 400 0 0 10 C/min 600 0 Temperature ( C) 800 -100 0 2 C/min 200 400 600 0 Temperature ( C) 800 TG & DTG Results of Sugarcane bagasse in Oxygen atmosphere Bagasse Oxygen atm -0.2 -0.4 0 30 C/min -0.6 0 -0.8 0 30 C/min 600 DTG, g/min Fraction of mass loss, 0.0 Bagasse Oxygen atm 800 2 C/min 0 5 C/min 400 0 5 C/min 200 0 10 C/min 0 10 C/min -1.0 200 400 600 0 Tempearure ( C) 800 0 0 2 C/min 200 400 600 0 Tempearure ( C) 800 The integral and differential from of various reaction models S.No 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. 13. Reaction Model f(α) g(α) Reaction order and geometrical contraction models Mampel (first order) 1- α -ln(1- α) nth Second Order (1- α)n 1-(1- α) 1-n /(1-n) Contracting cylinder 2(1- α)1/2 1- (1- α) 1/2 Contracting Sphere 3(1- α)2/3 1- (1- α) 1/3 Diffusion models One dimensional Diffusion 1/2 α-1 α2 2(1- α)2/3[1-(1Diffusion control (Janders) -1 [1-(1- α) 1/3]2 1/3 α) ] Diffusion control (Crank) 3/2[(1- α) -1/3 -1] -1 1-2/3 α – (1- α) 2/3 Nucleation models Power Law 4α3/4 α1/4 Power Law 3 α2/3 α 1/3 Power Law 2 α1/2 α 1/2 Avrami-Erofeev 4(1- α)[-ln(1- α)]3/4 [-ln(1- α)]1/4 Avrami-Erofeev 3(1- α)[-ln(1- α)]2/3 [-ln(1- α)]1/3 Avrami-Erofeev 2(1- α)[-ln(1- α)]1/2 [-ln(1- α)]1/2 Decomposition of sugarcane bagasse - Reaction Mechanism T E g ( ) exp 0 RT A g ( ) A RT E 2 .dT 2 RT E 1 . exp E RT AR E g ( ) ln ln 2 T E RT The plot of ln[g(α)/T2] and 1/T yields a straight line with a slope of –E/R. Selection of suitable reaction model for overall decomposition reaction of sugarcane bagasse at 2 K/min. 0 Bagasse, Argon atm, 2 C/min 2.72 overall decomposition CR -Integral Method 2 ln [g()/T ] 0.37 Stage II 0.05 0.01 0.00 con.sphr con.cylin sec.order DC Crank DC jander 1D diff Avrami power law Mample (I rst order) 0.0012 0.0014 Stage I 0.0016 0.0018 -1 1/T (K ) 0.0020 0.0022 Separation of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin decomposition reactions 0.012 Bagasse Argon,5 K/min 0.008 I I Overall I I I d/dT I I 0.000 I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I Hemi-cellulose I Cellulose I I I I I I I I I I I I Lignin I I I I I I I I II I II II II II IIII IIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIII 500 I I I I I I II I I II I III I I IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII II II III I I II II I II II I II III I I I II I II I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I II II II II I I II II II III IIII IIII IIIII IIIIII IIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII IIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIIII 400 I I I 0.004 Experimental IIII II II I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I I 600 700 800 Tempearture (K) d dT Sugarcane Bagasse AH wH 2 (T TCH . Exp 2 wH 2 2 (T TCC ) 2 (T TCL ) ) AC AL . Exp . Exp 2 2 wC wL w w C L 2 2 Mass loss reactions of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin of sugarcane Bagasse Argon, 5 K/min n Lig in Cellulose 0.4 i-cell ulose 0.6 Hem Fraction decomposed, 0.8 0.2 0.0 400 500 600 700 Temperature (K) 800 Selection of suitable reaction model after resolution - decomposition reaction of hemi cellulose in sugarcane bagasse at 2 K/min. 0.006 g()=1- (1- ) n=1.5 0.1 (1-n) /(1-n) Diffusion control-Jander g()=-1 [1-(1- ) Power law 0.04 1/3 2 ] 1/3 g()= 0.003 0.02 th n order 0.000 ln (g())/T 2 0.01 0.00 0.12 0.08 0.006 contracting cylinder g()=1- (1- ) 1/2 Diffusion Control- Crank 0.004 0.04 0.002 0.00 0.000 Avarami 0.4 (2/3) 1/3 g() = [-ln(1- )] 0.2 0.0 0.08 0.06 g()=1-2/3 - (1- ) 0.24 Mample (1 rst order) contracting sphere g()=1- (1- ) 1/3 0.6 ID diffusion g()=-ln(1- ) 0.16 0.04 0.4 2 g()= 0.08 0.02 0.2 0.00 0.00 0.0019 0.0020 0.0021 0.0019 0.0020 0.0021 -1 1/T(K ) 0.0019 0.0020 0.0021 Comparison of experimental and reconstructed α-T plots of hemi-cellulose decomposition at 2 K/min. Fraction decomposed, 1.2 Sugarcane bagasse - Hemi-cellulose 0 1.0 Argon atm, 2 C/min 0.8 ln A = 22.98 E = 134.17 1-n g()= 1-(1-) /(1-n) n=1.5 0.6 0.4 0.2 Reconstructed Experimental 0.0 300 400 500 Temperature (K) 600 700 The kinetic parameters of overall decomposition & hemi-cellulose decomposition derived with different reaction models. Overall decomposition- Stage II E (kJ/ Ln A R2 mol) Hemi-cellulose decomposition E (kJ/ Ln A R2 mol) Reaction order and geometrical contraction models Contracting Sphere Contracting Cylinder 6.12 54.68 1.00 18.65 108.73 0.88 6.11 53.04 1.00 18.39 106.04 0.87 nth Order n=1.5 Mample First Order Diffusion Models Diffusion Control (Crank) Diffusion Control (Janders) One Dimensional Diffusion Nucleation Models 10.94 69.39 0.99 22.98 134.17 0.98 8.10 58.09 1.00 21.15 114.43 0.89 17.29 114.21 1.00 41.01 220.32 0.87 18.35 118.55 1.00 42.56 226.57 0.88 17.46 105.94 0.99 39.86 206.36 0.85 Avrami-Erofeev 0.42 24.45 1.00 7.51 52.66 0.87 Power Law -4.06 9.98 0.97 1.18 26.76 0.77 MODEL FREE METHODS – HEMI CELLULOSE, CELLULOSE & LIGNIN 2.5 0 1.0 Flynn, Wall and Ozawa method - Bagasse - Argon atm - 2, 5, 30 c/min Friedman method - Bagasse - Argon atm - hemicellulose fraction of decomposition () - Hemicellulose fraction of decomposition () - Hemicellulose 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 0.05 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.30 0.35 0.40 0.45 0.50 0.55 0.60 0.65 0.70 0.75 0.80 0.85 0.90 0.95 2.0 0.5 0.0 1 1 A a a 3 C 3 log (.d/dT) c log () 1.5 A 1.0 C -0.5 c -1.0 2 B b -1.5 1 b B A 2 a -2.0 0.5 a A 1 -2.5 0.00165 0.0 0.00165 0.00170 0.00175 0.00180 0.00185 0.00190 0.00170 0.00175 0.00195 0.00180 0.00185 0.00190 0.00195 -1 1/T (k ) 1/T 0.04 Cellulose Bagasse, Argon atm Friedman 350 Cellulose 300 Activation energy (kJ/mol) d/dT 0.03 0.02 0 = 2 C/min 0.01 0 = 5 C/min e 250 200 Hem ulos i-cell r all er Ov on cti ea 150 nin Lig 100 0 = 30 C/min 50 0.00 0.2 0.0 0.2 0.4 0.6 Fraction reacted, 0.8 1.0 0.4 0.6 0.8 Fraction reacted, Variation of activation energy with fraction reacted for hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin decomposition reactions and overall decomposition reaction of sugarcane bagasse. The kinetic parameters of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin derived with model free iso-conversional methods. α Ln A* E(kJ/mo l) R2 0.1 43.81 207.13 0.99 Flyn, Wall and Ozawa Method E(kJ/mo Ln A* R2 l) 54.41 221.63 0.99 0.2 51.43 242.28 0.99 57.80 234.82 0.99 0.3 54.38 256.45 0.99 62.53 248.11 0.99 0.4 55.78 263.71 0.99 67.89 255.23 0.99 0.5 57.95 274.52 0.99 72.13 265.17 0.99 0.7 59.83 283.95 0.99 81.83 270.24 0.99 Constituent Hemicellulose cellulose Lignin Friedman Method 0.1 68.68 349.55 0.99 80.40 385.90 0.99 0.2 62.86 320.52 0.99 73.24 352.87 0.99 0.3 60.60 308.97 0.99 70.32 339.36 0.99 0.4 58.34 297.40 0.99 67.77 327.08 0.99 0.5 56.61 288.27 0.99 65.93 317.69 0.99 0.7 55.37 281.55 0.99 64.86 311.84 0.99 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 38.38 50.11 81.86 99.10 119.38 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 10.41 13.22 16.19 19.49 24.65 38.90 55.86 73.63 94.41 118.83 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.99 0.5 16.94 19.04 11.12 14.27 17.73 0.7 22.52 147.38 0.99 26.24 150.25 0.99 * - Derived by assuming f(α) =(1-α)1.5 0.99 Kissinger method Ln A* E(kJ/mo l) R2 55.50 255.54 0.99 64.65 322.71 0.99 18.36 109.23 0.98 NON-LINEAR LEAST SQUARE MINIMZATION METHOD M OF N j (( d j 1 exp t / dT ) ij ( d / dT ) ij calc 2 ) /N j i 1 ( d / dT ) calc EH d A H . Exp 1 a H dT RT AC EC . Exp 1 a C RT n 1 E . exp . f ( ) RT A AL EL . Exp 1 a L RT n 2 n 3 The derivation of kinetic parameters of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin in sugarcane bagasse using a non-linear least square minimization method. 0.012 Non-linear least square minimization 0 2 C/min 0 5 C/min 0 30 C/min Calculated da/dT 0.008 0.004 Suagarcane bagasse Argon atm 0.000 400 500 600 700 Temperature (K) 800 900 Reconstruction of fraction reacted (α) vs temperature plot using the kinetic parameters derived from integral method for hemi-cellulose decomposition 0.004 0.20 Least square minimization Experimental Reconstructed Kissinger 0.15 0.10 0.002 0.05 0.00 da/dT 0.000 0.004 KD Differential 80000 0.002 40000 0.000 0 0.004 CR Integral 0.04 0.002 0.02 0.000 0.00 450 500 550 600 650 Ozawa, Flynn, Wall Friedman 500 Temperatute (K) 550 600 650 Conclusions About 70-80 percent mass loss was occurred at argon atmosphere. The separation of overall reaction showed about 92-96% of hemi-cellulose, 91-95.5% cellulose and 94-97% lignin decomposition. The decomposition of cellulose and hemi-cellulose occurred rapidly while decomposition of lignin was sluggish in nature. The selection of suitable reaction model was possible after separation of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin decomposition reactions. The reaction order model f(α) = (1- α)1.5, better described the kinetics of hemi-cellulose, cellulose and lignin decomposition. The activation energy of hemi-cellulose and lignin increased with heating rate, while the activation energy of cellulose decreased with heating rate. The non-linear least square minimization method showed better results