- DairyMD.com

Managing Reproduction in a Modern Dairy Herd
Gregory M. Goodell, DVM
The Dairy Authority, LLC
Transitioning a cow properly through the post partum period
Heat Detection/Timed AI
Pregnancy Diagnosis
Monitoring the reproductive process
Components of Establishing
Pregnancy
Extremely important
Large impact
Multifactorial
Transition through post partum period
Michael W. Overton, DVM, MPVM
University of Georgia-College of Veterinary Medicine, Athens, GA
Heat Detection
◦ Observe for signs of estrous
◦ Advantages:
Less expensive and easier to implement
◦ Disadvantages
Time consuming, more skill required
Heat Detection: How do I find cows that are ready to breed?
Marking Crayons/Chalk
Pressure-sensitive pads
Pedometers
Rumen boluses
Heat Detection Aides
Pressure Sensitive Pads
HeatWatch Pressure Pad
Pedometers
Train personnel on signs of estrous
Cannot cut corners here!
Excellent tools for vets from stud services and breeding companies
Review numbers often as a program starts to evaluate heat detection numbers.
Implementing Heat Detection on a
Dairy
Many different programs
Success depends on management/style of the dairy
Labor intensive
Compliance a must
Timed Artificial Insemination
(TAI)
TAI Programs
CIDRSync Programs with CIDRs
Veterinarian should couple the management ability of the dairy with the
TAI program
A producer will almost always go for the program with the best published rates but demand the most convenient program
In general the more intense the program the better the rates
Which TAI Program is Best?
Same time every day of week and time
(including Christmas day and July 4 th !)
All cows MUST be found.
◦ Missed injections primary cause of compliance failure.
Compliance to TAI Programs
Preg rate = Heat detection X Conception rate
TAI programs force 100% heat detection
If a TAI program requires 6 visits to the cow and we miss 5% of the cows at all visits then we’ve reduced effective heat detection rate from 100 to
70%. If conception rate is 40% then we’ve reduce preg rate by 12%
Example of Compliance
TAI Program
CoSync 72
OvSync 48
OvSync 56
PreSync 12/OvSync 56
PreSync 14/OvSync 56
G6G
Double OvSync
Cow Visits Preg Rate
4
6
3
4
6
6
7
28-33%
28-33%
30-35 %
32-38%
32-38%
40-50%
40-50%
Cost per
Cow
$7.22
$7.38
$7.38
$11.90
$11.90
$11.80
$13.96
Preg Rates and Costs
TAI Program Cow Visits Preg Rate
CoSync 72
OvSync 48 *
OvSync 56 *
PreSync 12/OvSync 56 *
PreSync 14/OvSync 56 *
G6G
Double OvSync
4
6
3
4
6
6
7
* If CIDR used add another $9.00
28-33%
28-33%
30-35 %
32-38%
32-38%
40-50%
40-50%
Preg Rates and Costs
Cost per
Cow
$7.22
$7.38
$7.38
$11.90
$11.90
$11.80
$13.96
Rectal Palpation
Ultrasound
Blood Test
Milk Test
Pregnancy Diagnosis
Most common form of pregnancy diagnosis for cattle
Conducted between 30-50 days after breeding
Sensitivity of 95% and specificity of 96% when conducted between 35 and 45 d post AI
Chronic Trauma to shoulder
Rectal Palpation
Usually performed between 28-35 days
Sensitivity of 97.7% and specificity of
87.7% when conducted between 26 and
33 d post AI (Pieterse et al., 1990)
Skills vary among ultrasonographers
Rechecks still must be done
Reduced shoulder trauma if extension arm used.
Ultrasonography
Current controversy regarding stage to preg check
Research shows no difference in economics when preg check between 32 and 39 days (Silva, et al 2009 )
At 39 days U/S not required and neither is early P2
Ultrasonography
Detection of early pregnancy-associated glycoproteins (PAGs)
Pregnancy-Specific Protein B (PSPB)
Proteins only produced by the placenta of the growing fetus
Blood Tests for Pregnancy
Sensitivity reported to be between 96-99%
Specificity reported to be between 97-99%
Lay personnel can pull the sample
Often combined with other modalities of pregnancy diagnosis allowing for coverage of more animals or larger herds
Decrease physical wear and tear of shoulder
Advantages of Blood Testing
Requires minimum of 24 hours to achieve result
Does not provide any fetal staging
Half life of some PAGs may be as long as
90 day postpartum
Disadvantages of Blood Testing
bioTracking
Idexx
Conception
Commercially Available Tests
Test name is BioPryn
Located in Moscow, Idaho
Characteristics
◦ Se/Sp is 100/87.8 at 30-36 days post breeding
◦ Used as early as 28 days post breeding
◦ Must wait until 90 days postpartum
Cost is $2.50-$3.50 per sample
bioTracking
Idexx Bovine Pregnancy Test
Serum or milk
Located in Westbrook, Maine
Characteristics
◦ Se/Sp is 99.3%/95.1% at 30 days post breeding
◦ Used as early as 28 days post breeding
◦ Must wait 60 days post partum before using
Cost between $2.50 and $3.00 per sample
Idexx
Test name is DG29
Located in Québec, Canada
Characteristics
◦ Se/Sp is 99.4/100 at 29 days post breeding
◦ Used as early as 29 days post breeding
◦ Must wait 90 days post partum before using
Cost between $3.20 and $4.00 per sample
Conception
Reproduction Analysis
Case Definitions!!
Pregnant Cows/Exposed Cows
Pregnancy Rate, DIM, DOPN, etc.
◦ Include cows in EWP?
◦ Include Dead/Sold Cows?
◦ Include Dry Cows?
◦ Frequency of preg checks
Basic Concepts
40-45% of milking herd pregnant
180-200 Average DIM
Cull rate less than 35% (???)
High Production Herd
Characteristics
# milking cows pregnant/total # of cows milking.
30-50% is the goal (moves with DIM)
Dry cows not included
In DC305 …
◦ Sum by rc for rc=1-5 Lact>0\B
% of the Milking Herd Pregnant
Days in milk at first breeding (DIMFB)
Days Open (DOPN)
Days in milk (DIM)
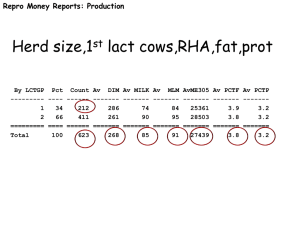
Herd Averages
Days in milk at first breeding (DIMFB)
Days Open (DOPN)
Days in milk (DIM)
Count AvDIMFB Av DOPN Av DIM
------ ------- ------- -------
2851 62 119 180
Herd Averages
Days in milk at first breeding (DIMFB)
Days Open (DOPN)
Days in milk (DIM)
Count AvDIMFB Av DOPN Av DIM
------ ------- ------- -------
2851 62 119 180
4412 63 146 200
Herd Averages
Need to be certain of where CLEANUP parameters are set
Commands like COUNT, SUM and PCT do
NOT look at sold/died cows unless told to
Switches in DC305
◦ \B, \D, \L
Using DC305 for Repro Analysis
# milking cows preg and >150 DIM /
#cows milking and greater than 150 DIM
In DC305…
◦ Sum by RC for DIM>150 RC=1-5 Lact>0
Goal 50-70% (moves with DIM)
Dry cows not included
% Milking Herd Preg and >150
DIM
Calendar Month
Times Bred
Tech
Breeding Code
Interval Analysis
Day of the Week
Specific Areas of Monitoring
By Calendar Month for past 12 months
Month 95% CI %Conc #Preg #Open Other Abort Total %Tot SPC
==================== ====== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ==== ====
2012 January 35-45 40 142 214 72 41 428 4 2.5
2012 February 35-44 40 179 271 79 46 529 5 2.5
2012 March 35-43 39 204 319 108 47 631 6 2.6
2012 April 37-45 41 251 358 134 62 743 8 2.4
2012 May 36-44 40 220 336 110 47 666 7 2.5
2012 June 28-35 31 178 392 74 46 644 7 3.2
2012 July 13-19 16 100 531 117 20 748 8 6.3
2012 August 8-12 10 83 742 134 8 959 10 9.9
2012 September 14-18 16 158 837 203 11 1198 12 6.3
2012 October 27-32 29 314 754 310 19 1378 14 3.4
2012 November 37-44 41 333 487 166 6 986 10 2.5
2012 December 30-38 34 192 373 * 144 2 709 7 2.9
2013 January 0 0 93 * 141 0 234 2
TOTALS 28-30 29 2354 5707 1792 355 9853 100 3.4
1002 non-AI breedings were omitted
By Times Bred
Bred Number 95% CI %Conc #Preg #Open Other Abort Total %Tot SPC
==================== ====== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ==== ====
1 27-40 33 62 124 4 0 190 32 3.0
2 30-46 37 51 86 0 1 137 23 2.7
3 22-42 31 25 55 4 1 84 14 3.2
4 18-40 27 17 45 2 1 64 11 3.6
5 18-47 31 11 25 1 0 37 6 3.3
6 22-56 37 10 17 1 0 28 5 2.7
7 12-55 29 4 10 2 0 16 3 3.5
8 15-58 33 5 10 1 0 16 3 3.0
OTHERS 6-38 16 3 16 3 0 22 4 6.3
TOTALS 29-37 33 188 388 18 3 594 100 3.1
35 non-AI breedings were omitted
By Technician
Technician 95% CI %Conc #Preg #Open Other Abort Total %Tot SPC
==================== ====== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ==== ====
Efrain 19-31 25 50 153 5 1 208 35 4.1
Luis 17-35 25 21 64 4 0 89 15 4.0
Alfonso 35-46 41 117 171 11 2 299 50 2.5
TOTALS 29-37 33 188 388 20 3 596 100 3.1
35 non-AI breedings were omitted
By Breeding Code
Breeding Code 95% CI %Conc #Preg #Open Other Abort Total %Tot SPC
==================== ====== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ==== ====
CIDR 12-49 26 5 14 0 1 19 3 3.8
Thur PM 40-63 52 33 31 3 1 67 11 1.9
Normal 31-44 37 85 142 8 1 235 39 2.7
TAI 20-30 25 65 199 9 0 273 46 4.1
OTHERS 0-66 0 0 2 0 0 2 0
TOTALS 29-37 33 188 388 20 3 596 100 3.1
35 non-AI breedings were omitted
By Day of the Week
Week Day 95% CI %Conc #Preg #Open Other Abort Total %Tot SPC
==================== ====== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ===== ==== ====
Monday 24-55 38 13 21 0 0 34 6 2.6
Tuesday 36-70 54 15 13 0 1 28 5 1.9
Wednesday 25-51 37 17 29 5 0 51 9 2.7
Thursday 33-52 42 45 62 3 1 110 18 2.4
Friday 22-32 26 81 225 11 1 317 53 3.8
Saturday 14-44 27 8 22 0 0 30 5 3.8
Sunday 20-55 36 9 16 1 0 26 4 2.8
TOTALS 29-37 33 188 388 20 3 596 100 3.1
35 non-AI breedings were omitted
Survival Analysis on DOPN
DC305 command…
◦ Graph DOPN for Lact>0 RC=1-5\S
◦ Survival Curve
DIM for 25, 50 and 75% Preg.
Rate
GRAPH DOPN\S
GRAPH DOPN FOR TID=3 WITH
TID<>3\S
Caveats
◦ Interpret results with other repro parameters
◦ There is a lag in reproduction data equal to days till preg check post breeding
◦ Should also apply monitoring techniques to parity groups
DOPN Cohort Analysis
Know the case definition
Record the data often
Look at the data often
Check data against other criteria