Chapter 29 Review
advertisement

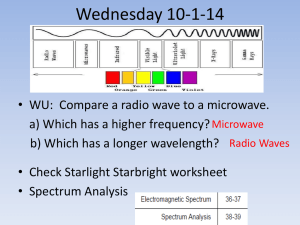
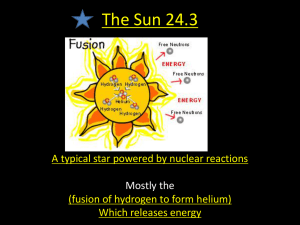
Chapter 29 Review Stars Which correctly lists objects in order of decreasing mass? A. Solar System, Jupiter, Earth, Sun B. Solar System, Jupiter, Sun, Earth C. Sun, Solar System, Jupiter, Earth D. Solar System, Sun, Jupiter, Earth 0% A. 0% 0% B. C. 0% D. Which line on the graph best represents the way in which the number of sunspots changes over time? 1. 2. 3. 4. A B C D 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which planet has composition and density most similar to the Sun? 1. 2. 3. 4. Saturn Mars Mercury Venus 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 A scientist comparing the properties of a large number of different stars could expect to find the most variation in the data describing the stars’ 1. 2. 3. 4. luminosity diameter composition temperature 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The line on this graph best describes the relationship between 1. the temperature of a star and its luminosity 2. the temperature of a star and its distance from Earth 3. the temperature of a star and its composition 4. the temperature of a star and its location in the universe 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The timeline shows the sequence of events that occurs during the formation of a star. What is the correct label for the blank in the diagram? 1. 2. 3. 4. nuclear fusion begins internal temperature drops gravity ceases to act rotation begins 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Which point on the timeline most correctly identifies the Sun’s current point in its lifecycle? 1. 2. 3. 4. A B C D 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Use the table to calculate which of the following units represents the greatest distance. 1. 2. 3. 4. meter parsec light year kilometer 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 A scientist using parallax to determine the distance to a star will notice the greatest shift in a star’s apparent position when measured 1. at 6-month intervals 2. during Earth’s coldest weather 3. at the midpoint of the star’s rotation 4. at the peak of the star’s blueshift 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Most of the light emitted by the Sun comes from the 1. 2. 3. 4. chromosphere corona photosphere prominence 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 When the polarity of the Sun's magnetic field is taken into account, the solar activity cycle lasts 1. 2. 3. 4. 22.4 years 22.2 years 11.2 years 11.4 years 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 What causes the dark bands observed in a solar spectrum? 1. the emission of specific elements 2. different chemical elements which absorb light at specific wavelengths 3. highly compressed, glowing gas 4. warmer gas in front of a source that emits a continuous spectrum 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The apparent shift in a star’s position caused by the motion of the observer is called 1. 2. 3. 4. luminosity apparent magnitude absolute magnitude parallax 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 A star that is gravitationally bound to another star can either be part of a star cluster or a ____ star. 1. 2. 3. 4. constellation white dwarf binary red giant 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 All stars, including the Sun, have the following identical composition: 1. 25 percent hydrogen; 73 percent helium; and 2 percent oxygen 2. 25 percent helium; 73 percent hydrogen; and 2 percent other 3. 25 percent helium; 73 percent hydrogen; and 2 percent oxygen 4. 25 percent hydrogen; 73 percent helium; and 2 percent other 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 The ____ of a star determines its temperature, luminosity, and diameter. 1. 2. 3. 4. mass composition energy output density 0% 1 0% 0% 2 3 0% 4 Combining of lightweight nuclei into heavier nuclei, such as four hydrogen nuclei combining to form a helium nucleus 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Cloud of interstellar gas and dust that collapses on itself to form a new star 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Visible light arranged according to wavelengths 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Group of bright stars named for an animal, a mythological character, or an everyday object 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Minimum to maximum sunspots, a reversal of polarity, and minimum to maximum sunspots over a period of 22.4 years 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Lowest layer of the Sun’s surface from which most of the light emitted by the Sun comes 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Section of the H-R diagram into which about 90 percent of stars fall 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 Small, massive, dense object that has a gravity so immense that nothing—not even light—can escape it 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. black hole photosphere fusion constellation main sequence nebula solar activity cycle spectrum 0% 0% 1 2 0% 0% 0% 3 4 5 0% 0% 0% 6 7 8 The density of gas in coronal holes is greater than the density of the entire corona. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The Sun is almost entirely composed of hydrogen and helium. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 A parsec is a greater distance than a light year. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The shaded area of the graph correctly represents the percentage of stars that are in the main sequence of an HR diagram. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Stars more massive than the Sun use up their fuel at a slower rate. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The corona is visible only during eclipses because it is the coolest layer of the Sun’s atmosphere. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 When hydrogen nuclei fuse, they produce helium. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The state of matter found in the Sun’s interior is plasma. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The greatest proportion of elements in the universe are those with the smallest masses. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Scientists gather evidence about the Sun’s composition by directly sampling material from the Sun. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Other than the use of special instruments, the chromosphere is only visible during a solar eclipse when the photosphere is blocked. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 In the modern classification of apparent magnitude, a difference of 5 magnitudes corresponds to a factor of 100 in brightness. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 When the core of a star collapses forever, the extremely dense object that remains is called a(n) neutron star. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 As a star ages, its internal composition changes as nuclear reactions in the star’s core convert one element into another. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Astronomers can sometimes identify binary stars even if only one star is visible. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Absolute magnitude takes distance into account when indicating the surface temperature of a star. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Using the parallax technique, astronomers can accurately measure the distance of stars up to 300 pc away. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The Hertzsprung-Russell diagram (H-R) diagram, first plotted in the nineteenth century, demonstrates the relationship of luminosity and temperature. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 Stars are assigned a spectral type, with M being the hottest stars. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2 The mass of a star determines the star’s temperature, luminosity, and constellation. 1. True 2. False 0% 1 0% 2