Spinal Cord and Ear - Mrs.Simmons Anatomy & Physiology I Lab IRSC
advertisement

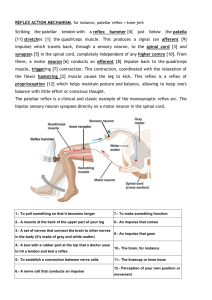
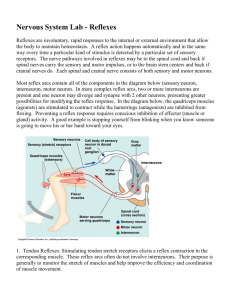
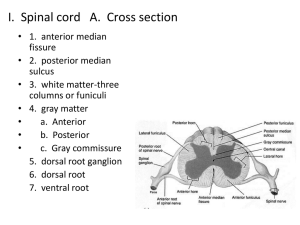
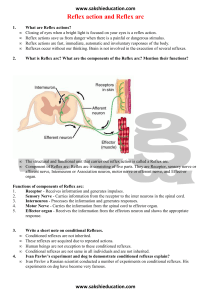
Spinal Cord Spinal Cord • It is continuous with the medulla oblongata • Extends from the foramen magnum of the occipital bone to the upper boarder of L2 • 2 main Functions: – Impulse conduction • Communication to and from the brain through tracts of white matter – Reflex integration • Reflexive movements as opposed to those initiated voluntarily • There are 31 pairs of spinal nerves – C1-C8 – T1-T12 – L1-L5 – 5 sacral nerves Gray & White Matter • Gray Matter: – Nerve cell bodies, neuroglia, axon terminals, and unmyelinated association neurons (interneurons) • White matter – Bundles or tracts of myelinated fibers of sensory and motor neurons Horns • Ventral Horn – Cell bodies and dendrites of the Somatic motor neuron cell bodies and dendrites • Dorsal Horn – Somatic & Autonomic: sensory axons from the sensory nerve roots • Lateral Horn – Present only in thoracic, lumbar, and sacral segments of the cord – Contain cell bodies of the autonomic motor neurons and interneurons Nervous System Figure 11.1 Reflex Arc Spinal cord (in cross-section) Stimulus 2 Sensory neuron 1 3 Integration center Receptor 4 Motor neuron Skin 5 Effector Interneuron Figure 13.14 • Denticulate ligament – Formed by lateral extensions of pia mater – Attaches the spinal cord to the dura mater – Anchors spinal cord in place Reflexes • Fast, predictable, automated responses to changes in the environment • Somatic reflexes involve contraction of skeletal muscles • There are automatic or visceral reflexes which we are not usually conscious of Reflex Arc • Pathway followed by nerve impulses that produce a reflex – 5 functional components 1. Sensory receptor 2. Sensory neuron 3. Integrating center (in gray matter where sensory and motor neuron synapse) 4. Motor neuron 5. Effector (part of body that responds to the motor impulse Reflex Arc Spinal cord (in cross-section) Stimulus 2 Sensory neuron 1 3 Integration center Receptor 4 Motor neuron Skin 5 Effector Interneuron Figure 13.14 Somatic Reflexes • Stretch Reflexes – Involves only two neurons and one synapse (monosynaptic reflex arc) – Stretch reflexes can be elicited at the elbow, wrist, knee and ankle joints – Examples: • Patella or knee-jerk reflex • Achilles or ankle-jerk reflex – (Dorsiflex the ankle and tap the Achilles tendon Stretch Reflex ____ Figure 13.17 • Superficial cord reflexes: – (abdominal, cremaster, and plantar) result from pain and temperature changes – Example: Plantar reflex • Stimulate cutaneous receptors on the sole of the foot • Babinski’s reflex: damage to pyramidal (corticospinal) tract Nervous Physiology Extra Credit • Complete these activities in lab book (listed in your outline) Have to answer questions from the activity to get credit can do all these at home: – Reaction time from a learned stimulus (with the ruler) p.345 Act.9 – Two-point discrimination p356 Act.2 – Adaptation of touch receptors p.357 Act. 5 – Determination of blind spot p. 371 Act. 5 • From Outline- Write a really short paragraph about what happened – “B-r-r-r, That’s Hot” • 2 points for each assignment completed Ear • 2 Important Functions – Hearing • The conversion of sounds waves (mechanical and fluid) into action potentials (electrical) – Equilibrium • Ability to subconsciously detect changes in head position, rotational movement and acceleration/deceleration • Reflexes maintain the body in a stable position in spite of any changes or movements Ear is divided into 3 regions • External Ear – Collect sound waves and channels them • Middle Ear – Conveys sound vibration • Inner Ear – Labyrinth that houses receptors for hearing and equilibrium External Ear • Pinna or auricle – Flap of elastic cartilage • External auditory canal (or meatus) • Ceruminious glands (blue on model) – Secrete earwax (cerumen) • Tympanic membrane (eardrum) Middle Ear • Ear Ossicles – Malleus, Incus, Stapes – (MAiling, INCludes, STAmps) • Auditory tube (phayngotympanic tubes) – Duct connecting middle ear to throat • Oval Window – Creates fluid waves within cochlea • Round window – Equalizes pressure created by vibration of oval window Inner Ear • Bony chambers called osseous or bony labyrinth – Cochlea (hearing) – Vestibule (equilibrium) • Consists of 2 sacs: Utricle & saccule – House equilibrium receptor regions: maculae – Semicircular canals (equilibrium) • Respond to rotational movement in head • Ampulla – Base of semicircular canals – Houses equilibrium receptor (crista ampullaris) Inner Ear Figure 15.27 Cochlea • Scala vestibuli – Provides brain with info concerning position • Scala tympani • Cochlear duct • Tectorial membrane – Where hair cells are embedded Auditory Transduction Video • https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PeTriGTE Noc