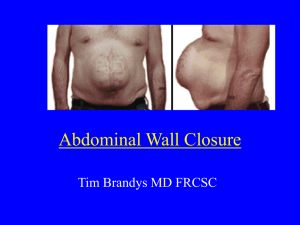
BASIC SUTURING 1:
advertisement
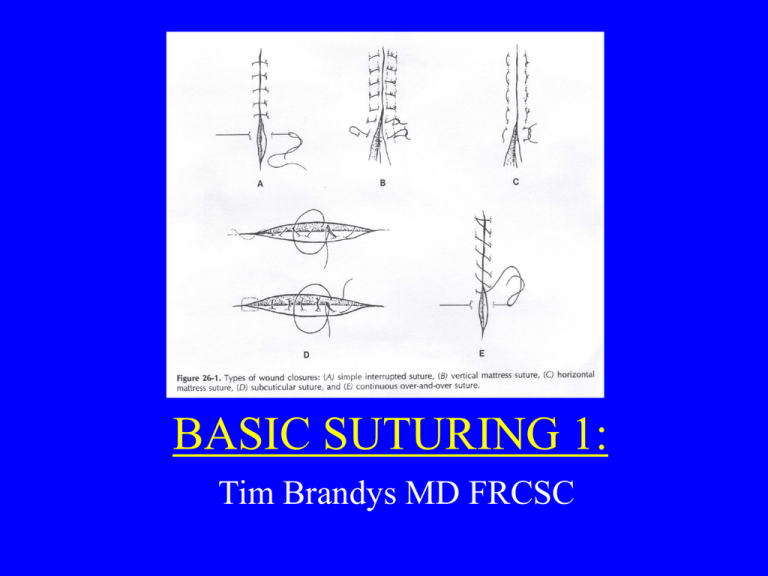
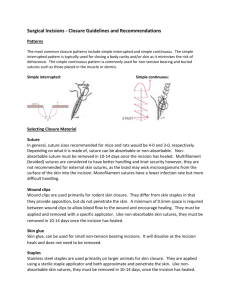
BASIC SUTURING 1: Tim Brandys MD FRCSC Principles of Wound Closure: 1.Equal Bites on each side of the wound 2.Distance between sutures = distance suture is from wound edge 3.Apposition,Eversion (skin),or Inversion(bowel)of wound edges depends on tissues being closed Principles of Wound Closure: 4.Follow curve of Needle,levering causes damage 5.Approximation not Strangulation:avoid excessive stitches placed too close together,be careful of post-op swelling with running and running locking sutures. Principles of Wound Closure: 6.Principle of Halving: 1st suture placed centrally.Next suture placed halfway between end of wound and 1st suture.And so on. Avoids mismatch of wound edges with “Dog Ear” HEMOSTATIC SUTURES: SUTURE LIGATURE (STICK TIE,TRANSFIXION SUTURE): Purpose:Secure control of a vessel Technique:Suture passes thru vessel to anchor the knot Uses: 1. One chance to ligate vessel may retract ex: mesentery,amputation, pelvis 2.Large Vessel FIGURE OF EIGHT: Purpose: Secure ligation of vessel surrounded by other tissue(not readily controlled by a hemostat) Technique:Two parallel simple running sutures in same direction Uses:1. Any recessed vessel in other tissue 2. Lumbar vessels in the aorta Purse-String Suture: Purpose: To invert or secure an opening in a structure Technique: Encircle an opening or tube with simple running sutures Uses: 1.Secure and prevent leaks around a drain. 2. Secure Aorta cannulation catheter 3. Invaginate stump of the appendix WOUND CLOSURES: Interrupted Closure: A new knot every 1 or2 stitches Advantages: Less interference with vascular supply to wound edges M ore secure,if one breaks others will hold incision together Disadvantage: Time consuming RUNNING/CONTINUOUS CLOSURE: Definition: Many stitches between knots Advantages: Faster Temporary seal against fluid loss Tension distributed along entire suture line Disadvantages: Too much tension makes entire suture line ischemic Integrity can be broken at any point INTERRUPTED SUTURES: SIMPLE INTERRUPTED: Definition: Equal full thickness bites thru skin and subcutaneous layers Vertical Mattress: Definition: Far-Far Reverse,Near-Near Purpose: Everts skin edges with precise approximation and little tension Uses: Any setting where you want good approx. with no tissue ischemia ex. Amputation stump Horizontal Mattress: Definition: Simple interrupted ,but additional parallel bites are taken in reverse Purpose: Everts skin edges in wounds under tension Running: Simple(Baseball) Vertical Horizontal Subcuticular: Running Horizontal in the intradermal level SUBCUTICULAR Agenda: 1.Proper needle placement on the driver 2.Simple Interrupted, Vertical Mattress,Horizontal mattress 3.Running Subcuticular 4.Stick Tie 5.Purse String 6.Figure of Eight