Module 10 Notes Part 1
advertisement

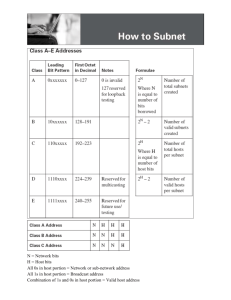
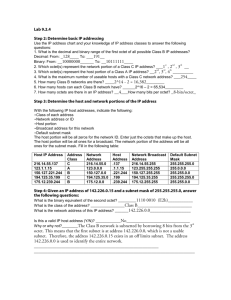
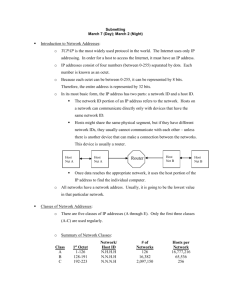
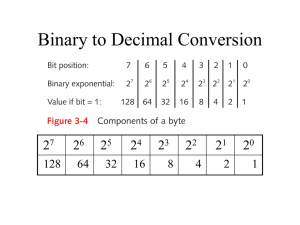
Sem1 - Module 10 Routing Fundamentals and Subnets Network address • Network address provide a convenient way to refer to all of the addresses on a particular network or subnetwork. • Two hosts with differing network address require a device, typically a router, in order to communicate. • An IP address that ends with binary 0s in all host bits is reserved for the network address. Broadcast address • Broadcast goes to every host with a particular network ID number. • An IP address that ends with binary 1s in all host bits is reserved for the directed broadcast address. • An IP address with binary 1s in all network bits and host bits is reserved for the local broadcast address. Local broadcast address STOP 255.255.255.255 Directed broadcast address 192.168.20.0 192.168.20.255 Broadcast address Example: 172.16.20.200 • 172.16.20.200 is Class: – B address • Network portion: – 172.16 • Host portion: – 20.200 • Network address: – 172.16.0.0 • Broadcast address: – 172.16.255.255 1. What is the decimal and binary range of the first octet of class B IP addresses? – – Decimal: 128 – 191 Binary: 10000000 – 10111111 2. Which octet(s) represent the network portion of a class C IP address? – The first three octets 3. Which octet(s) represent the host portion of a class A IP address? – The last three octets IP Addresses Host IP Address Address Class Network Address Portion Host Address Portion Broadcast Address 216.14.55.137 C 216.14.55 137 216.14.55.255 123.1.1.15 A 123 1.1.15 123.255.255.255 150.127.221.244 B 150.127 221.244 150.127.255.255 194.125.35.199 C 194.125.35 199 194.125.35.255 175.12.239.244 B 175.12 239.244 175.12.255.255 Valid IP Address? 150.100.255.255 – This is a Class B – This is the Broadcast Address: NO - not valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 175.100.255.185 – This is a Class B – The Host Bits are not all 0s or 1s: Yes - valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 195.234.253.0 – This is a Class C – This is the Network Address: NO - not valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 100.0.0.23 – This is a Class A – The Host Bits are not all 0s or 1s: Yes - valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 188.256.221.176 – This would be a Class B – BUT the 2nd Octet is greater than 255 NO - not valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 127.34.25.189 – This would be a Class A – BUT is invalid since 127 cannot be used in the first Octet – reserved for diagnostic testing NO - not valid IP Address Valid IP Address? 224.156.217.73 – This is a Class D network – Class D is reserved for multicasting & cannot be used as a commercial IP address NO - not valid IP Address SubNet Mask Notation: Class C: Class B: Class A: 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.0 255.255.255.0 192.168.100.0/24 (24 Bits in the Network part) 255.255.0.0 172.16.0.0 172.16.0.0/16 255.255.0.0 (16 Bits in the Network part) 255.0.0.0 10.0.0.0 10.0.0.0/8 255.0.0.0 (8 Bits in the Network part) SubNet Mask Notation: Not Valid for Class C (MUST borrow at least 2 Bits) The last two bits in the last octet, regardless of the IP address class, may never be assigned to the subnetwork. These bits are referred to as the last two significant bits. Host Subnet Schemes The number of lost IP addresses with a Class C network depends on the number of bits borrowed for subnetting. SubNet Mask Notation: Consider Network: 192.168.23.0/24 Subnet with a SNM: 255.255.255.224 3 Bits Borrowed /27 Fourth Octet Position Value 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 Bit 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 SubNet Host Bits Bits SubNet Mask Notation: Network: 192.168.23.0/27 SNM 255.255.255.224 SubNet # ID Host Range Start Host Range End Broadcast 0 192.168.23.0 192.168.23.1 192.168.23.30 192.168.23.31 1 192.168.23.32 192.168.23.33 192.168.23.62 192.168.23.63 2 192.168.23.64 192.168.23.65 192.168.23.94 192.168.23.95 3 192.168.23.96 192.168.23.97 192.168.23.126 192.168.23.127 4 192.168.23.128 192.168.23.129 192.168.23.158 192.168.23.159 5 192.168.23.160 192.168.23.161 192.168.23.190 192.168.23.191 6 192.168.23.192 192.168.23.193 192.168.23.222 192.168.23.223 7 192.168.23.224 192.168.23.225 192.168.23.254 192.168.23.255 Review • Classes of IP address and range of IP on each class. • Determine network portion and host portion in a IP address. • Understand about broadcast addresses. • Understand about valid host address. • Binary and Decimal conversion. • Subnetting Chapter #10 Labs: – – – – – 10.3.5a (Basic Subnetting) 10.3.5b (Subnetting a Class A Network) 10.3.5c (Subnetting a Class B Network) 10.3.5d (Subnetting a Class C Network) 10.2.9 (Small Router Purchase) – Homework • See Web Page for Extra Practice