Solving Linear Systems
advertisement

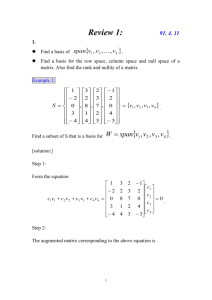
Systems of Linear Equations and Row Echelon Form Motivation • Physical systems typically involve many different quantities. • Relationships between quantities give rise to a system of equations. • Nonlinear equations can be approximated by linear equations. • Linear Algebra is the study of linear systems and efficient methods for solving them. Linear Equations Linear Equations Nonlinear Equations Linear Equations System of Linear Equations Solution Set Solution Set Consistent Linear Systems A linear system is consistent if it has at least one solution. A linear system is inconsistent if it has no solutions. Two Equations, Two Unknowns: Lines in a Plane Three Possible Types of Solutions A unique solution Three Possible Types of Solutions No solution Three Possible Types of Solutions Infinitely many solutions Three Equations, Three Unknowns: Planes in Space Intesections of Planes What type of solution sets are represented? A System of Linear Equations Augmented Matrix Coefficient Matrix Example Write as an augmented matrix: Example Write as a set of linear equations: Solve the System Solve the System Elementary Operations • Multiply any equation by a nonzero number. • Replace any equation with itself added to a multiple of another equation. • Interchange the order in which the equations are listed. Row Operations • Multiply any row by a nonzero number. • Replace any row by a multiple of another row added to it. • Switch two rows. What is the “nicest” form of a reduced matrix? • What happens if the coefficient matrix is reduced to the identity matrix? • Can the coefficient matrix always be reduced to the identity matrix? Reduced Row Echelon Form A rectangular matrix is in reduced row echelon form if it has the following conditions: 1. If a row has nonzero entries, then the first nonzero entry is a 1, called the leading 1 (or pivot) in this row 2. If a column has a leading 1, the all the other entries in that column are 0. 3. If a row contains a leading 1, then each row above it contains a leading 1 further to the left. Note: Condition 3 implies that rows of 0’s, if any, appear at the bottom of the matrix. Reduced Row Echelon Form? Reduced Row Echelon Form? Pivot Positions and Pivot Columns Suppose row operations are used to transform matrix to Reduced Row Echelon form. Then: 1. The positions of the first nonzero entry in each row are called the pivot positions. 2. The columns containing a pivot position are called the pivot columns. What are the pivot positions and pivot columns? Types of Variables The variables corresponding to the columns of a matrix that are not pivot columns are called the free variables. These variables are assigned parameters. The other variables are called basic variables or lead variables and may be solved in terms of the parameters. Solve the System Solve the System Solve the System Types of Solutions Suppose a linear system [A|b] is given where A has m rows and n columns: 1. The system is inconsistent if the augmented column is a pivot column. 2. The system is consistent if the augmented column is not a pivot column. a. There is a unique solution if The number of pivot columns = n b. There are an infinite number of solutions if The number of pivot columns < n