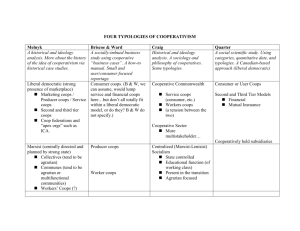
New York Real Estate for
th
Salespersons, 5 e
By Marcia Darvin Spada
Cengage Learning
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
1
Chapter 16
Condominiums and
Cooperatives
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
2
Chapter 16 Key Terms
Alteration agreement
Condominium
Board package
Condop
Bylaws
Cooperative
Common elements
Covenants,
conditions, and
restrictions (CCRs)
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
3
Chapter 16 Key Terms (continued)
Declaration
Maintenance
Flip tax
statement
Proprietary lease
Recognition agreement
Share loan
Sponsor
Offering plan or
Flipping
House rules
Letter of intent
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
4
Condos and Coops
Condo-title transferred by deed
Coop- title transferred through shares
of stock
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
5
Cooperatives
A cooperative corporation usually owns the land,
buildings, and property rights and all interests
The title to the property, as shown on the deed, is
in the name of the corporation
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
6
What are Shares of Stock?
The shareholders do
not own real estate,
but a proportionate
number of shares of
stock in a
cooperative
corporation
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
As lessees, the
shareholders pay
a monthly
maintenance feethe rent
7
Key Issues to Review in a Co-op
Board’s Minutes
Maintenance and
Assessment History
Many cooperative
Reserve
Fund
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Underlying
Mortgage
reserve funds receive
income from the flip
tax, a charge levied
when units change
hands
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
8
Cooperative Board Application and
Interview Preparation
Real Estate Example:
Before
Scheduling
Interview
Consider
Co-op
Interview
Board
Prep
Application
The Role
Of Time
Familiarize
Purchaser
Package for
Discussion
purposes
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Need for total
disclosure
By purchaser
During
Interview
Why?
Dr. Leslie is a single
woman who is paying
cash for a cooperative.
She has sizable and
safe investments and
no debt. The
cooperative board
refuses her. No reason
is given.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
9
CPS1 Phase: Cooperative
Policy Statement
• Sets out New York
Attorney General’s rules
• how a developer may
test market for a new
development before
filing the offering
plan and before
construction is
completed
© 2013 All rights reserved.
• The CPS1 period
• lasts 120 days from
acceptance of the
CPS1 statement by the
Attorney General
• can be extended by
request from the
developer for an
additional 60 days
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
10
Documents Needed for the
Sale/Purchase of Cooperatives
Proprietary
Lease
Alteration
Agreements
House
Rules
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Stock
Certificate
Offering
Plan
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
11
Primary Residency Versus
Subletting Issues In the Cooperative
Primary resident
owner of the cooperative unit
Subletting
allows tenant shareholders more flexibility in ownership
board may limit the length of time a tenant shareholder can
sublet a unit
If the sponsor owns the shares allocated to the
apartment, he may be permitted under bylaws or rules
to sublet or rent a unit even though a unit owner
cannot
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
12
Difference Between a Condop,
Condominium, and Cooperative Apartment
A condop is
Real Estate Example: Why it is created?
a building that
Building owner Sal owns a multi-unit
includes
apartment building that includes a store
the street level. Sal records the
condominium and on
Declaration of Condominium, dividing
the property into two condominium
units: Condo A (the commercial unit) and
cooperative
Condo B (the residential unit). Sal
continues to own fee title to the
ownership
commercial condominium unit and
collects rent from the store. As fee title
in the same
owner to Condo B, Sal deeds the
residential unit to Big City Co-op Corp. in
exchange for the shares of Big City Co-op
structure
Corp. Various blocks of shares are
allocated to the different apartments. Sal
now sells the block of shares allocated to
each unit (together with a proprietary
lease) to individual purchases.
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
13
Condominiums
A structure of two or more units
Interior space is individually owned
Common elements, are owned by owners of
the individual units
To create, the owner/developer of the
property signs a condominium declaration
Shareholder’s rights and obligations are in
the condominium’s bylaws
The sponsor is the owner or developer.
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
14
Offering Plan
Size
of unit
The floor plans
The construction
The size and materials
The plans of recreation buildings
The make and model of appliances
The scope of the landscaping
The land on which condominium is located
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
15
Offering Plan Amendment:
Building Conversion
NYS law
When a developer files an offering plan with the
Attorney General to convert an existing building to
a condo or co-op, the tenants have a 90-day
exclusive right to buy their apartment
During this period sponsor cannot negotiate
separate prices
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
16
Offering Plan Amendment :
New Development
o New building and after
90-day tenant’s
exclusive period in a
converted building
o sponsor can
separately negotiate
the price of a
particular
apartment
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
o The developer can
sell one apartment
for $200,000 and
then sell another
identical
apartment for
$175,000
17
A Condo and Coop Closing Compared
Condominium
Cooperative
Type of
transaction
Transfer
documents
Fee simple
ownership
Deed
Personal property;
shares of stock
Taxes at
closing
NYS transfer
tax
NYS transfer fee;
flip tax
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
Proprietary lease
18
Closing Costs
Real
Estate
Tax
Common
Charges
Tax
Deductions
Mansion
Tax
Mortgage
Recording
Tax
Right of
First
Refusal
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
19
Flipping
Real estate investors
or speculators
believe that they can
turn quick profits by
buying the property
at a certain price and
then immediately
selling the property
at a higher price
© 2013 All rights reserved.
Flipping may be a
problem because it can
drive up prices
The investor attempts
Chapter 16 Condos and Coops
to buy low and sell
high
20