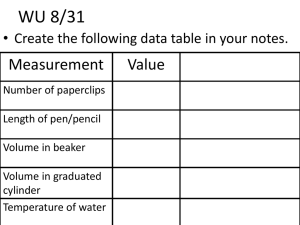
Chemistry: The Study of Change - Chapter 1 Presentation
advertisement

Chemistry: The Study of Change Chapter 1 Copyright © The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. Permission required for reproduction or display. Chemistry: A Science for the 21st Century • Health and Medicine • Sanitation systems • Surgery with anesthesia • Vaccines and antibiotics • Gene therapy •Energy and the Environment • Fossil fuels • Solar energy • Nuclear energy 2 Chemistry: A Science for the 21st Century • Materials and Technology • Polymers, ceramics, liquid crystals • Room-temperature superconductors? • Molecular computing? • Food and Agriculture • Genetically modified crops • “Natural” pesticides • Specialized fertilizers 3 The Study of Chemistry Macroscopic Microscopic 4 Qualitative data consists of general observations about the system The coffee is hot The boy is tall Quantitative data comprises numbers obtained by various measurements of the system. The coffee is heated to 97°C John is 5 ft 6 in tall 5 The scientific method is a systematic approach to research A hypothesis is a tentative explanation for a set of observations tested modified 6 A law is a concise statement of a relationship between phenomena that is always the same under the same conditions. Force = mass x acceleration A theory is a unifying principle that explains a body of facts and/or those laws that are based on them. Atomic Theory 7 Problem 1.3 Classify the following statement as (a) qualitative (b) quantitative 1.The sun is approximately 93 million miles from earth. 2. Leonardo daVinci was a better painter than Michelangelo. 3.Ice is less dense than water. 4.Butter tastes better than margarine. 8 Problem 1.4 (a) Classify the following statement as a (a) hypothesis (b) law (c) theory 1.Beethoven’s contribution to music would have been much greater if he had married. 2. An autumn leaf gravitates toward the ground because there is an attractive force between the leaf and the earth. 3. All matter is composed of very small particles called atoms 9 Chemistry is the study of matter and the changes it undergoes Matter is anything that occupies space and has mass. A substance is a form of matter that has a definite composition and distinct properties. liquid nitrogen gold ingots silicon crystals 10 A mixture is a combination of two or more substances in which the substances retain their distinct identities. 1. Homogenous mixture – composition of the mixture is the same throughout. clear juice (apple, cranberry), bronze, solder 2. Heterogeneous mixture – composition is not uniform throughout. cement, iron filings in sand 11 Physical means can be used to separate a mixture into its pure components. magnet distillation 12 A compound is a substance composed of atoms of two or more elements chemically united in fixed proportions. Compounds can only be separated into their pure components (elements) by chemical means. lithium fluoride quartz dry ice – carbon dioxide 13 An element is a substance that cannot be separated into simpler substances by chemical means. • 114 elements have been identified • 82 elements occur naturally on Earth Element 118 discovered in 2006! gold, aluminum, lead, oxygen, carbon, sulfur • 32 elements have been created by scientists technetium, americium, seaborgium 14 15 Classifications of Matter 16 Problem 1.16(a) Classify the following as a(n) (a) element (c) homogeneous mixture (b) compound (d) heterogeneous mixture filtered sea water Helium gas Kosher salt (sodium chloride) A bottle of soda (capped, unshaken) A milkshake Filtered air in a bottle concrete 17 A Comparison: The Three States of Matter 18 The Three States of Matter: Effect of a Hot Poker on a Block of Ice gas liquid solid 19 Types of Changes A physical change does not alter the composition or identity of a substance. sugar dissolving ice melting in water A chemical change alters the composition or identity of the substance(s) involved. hydrogen burns in air to form water 20 Problem 1.12(a) Does the following describe a (a) chemical change or a (b) physical change? 1. The helium gas inside of a balloon tends to leak out after a few hours. 2. Frozen orange juice is reconstituted by adding water to it. 3. The growth of plants depends on the sun’s energy in a process called photosynthesis. 4. A spoonful of table salt dissolves in a bowl of soup. 21 Extensive and Intensive Properties An extensive property of a material depends upon how much matter is is being considered. • mass • length • volume An intensive property of a material does not depend upon how much matter is is being considered. • density • temperature • color 22 Matter - anything that occupies space and has mass. mass – measure of the quantity of matter SI unit of mass is the kilogram (kg) 1 kg = 1000 g = 1 x 103 g weight – force that gravity exerts on an object W=mxa SI unit of force is the Newton (N) 1 N = 1 kg∙m/s2 Interestingly, the process of measuring mass is called weighing! 23 Mass is constant, while weight is dependent on location On the moon, a = 1.67 m/s2 W = m x a = 1 kg x 1.67 m/s2 1.67 Newton On earth, a = 9.81 m/s2 W = 1 kg x 9.81 m/s2 = 9.81 kg∙m/s2 9.81 Newton 9.81 Newton/1.67 Newton = 5.87 A 1 kg mass weighs almost 6 times more on earth than on the moon! 24 International System of Units (SI) 25 26 Volume – SI derived unit for volume is cubic meter (m3) 1 cm3 = (1 x 10-2 m)3 = 1 x 10-6 m3 1 dm3 = (1 x 10-1 m)3 = 1 x 10-3 m3 1 L = 1000 mL = 1000 cm3 = 1 dm3 1 mL = 1 cm3 27 Density – SI derived unit for density is kg/m3 1 g/cm3 = 1 g/mL = 1000 kg/m3 mass density = volume m d= V A piece of platinum metal with a density of 21.5 g/cm3 has a volume of 4.49 cm3. What is its mass? 28 Problem 1.22 The density of ethanol, a colorless liquid that is commonly known as grain alcohol, is 0.798 g/mL. Calculate the mass of 17.4 mL of the liquid. 29 30 A Comparison of Temperature Scales K= ( 0C + 273.15 0C) 1K 1 0C 273 K = 0 0C 373 K = 100 0C 0F 9 0F = 0C + 32 0F x 0 5 C 32 0F = 0 0C 212 0F = 100 0C 31 Convert 327.5 0C to degrees Fahrenheit. Convert 172.9 0F to degrees Celsius. Convert 77 K, the boiling point of liquid nitrogen to degrees Celsius. 32 Problem 1.24(a) Normally the human body can endure a temperature of 105 °F for only short periods of time without permanent damage to the brain and other vital organs. What is the temperature in °C? 33 Problem 1.24(b) Ethylene glycol is a liquid organic compound that is used as an antifreeze in car radiators. It freezes at -11.5 °C. Calculate the freezing point in °F. 34 Problem 1.24(c) The temperature of the surface of the sun is about 6300 °C. What is this temperature is °F? 35 Problem 1.24(d) The ignition temperature of paper is 451 °F. What is the temperature in K? 36 Scientific Notation The number of atoms in 12 g of carbon: 602,200,000,000,000,000,000,000 6.022 x 1023 The mass of a single carbon atom in grams: 0.0000000000000000000000199 1.99 x 10-23 N x 10n N is a number between 1 and 10 n is a positive or negative integer 37 Scientific Notation 568.762 0.00000772 move decimal left move decimal right n>0 n<0 568.762 = 5.68762 x 102 0.00000772 = 7.72 x 10-6 Addition or Subtraction 1. Write each quantity with the same exponent n 2. Combine N1 and N2 3. The exponent, n, remains the same 4.31 x 104 + 3.9 x 103 = 4.31 x 104 + 0.39 x 104 = 4.70 x 104 38 Scientific Notation Multiplication 1. Multiply N1 and N2 2. Add exponents n1 and n2 Division 1. Divide N1 and N2 2. Subtract exponents n1 and n2 (4.0 x 10-5) x (7.0 x 103) = (4.0 x 7.0) x (10-5+3) = 28 x 10-2 = 2.8 x 10-1 8.5 x 104 ÷ (5.0 x 109)= (8.5 ÷ 5.0) x 104-9 = 1.7 x 10-5 39 Significant Figures • Any digit that is not zero is significant 1.234 kg 4 significant figures • Zeros between nonzero digits are significant 606 m 3 significant figures • Zeros to the left of the first nonzero digit are not significant 0.08 L 1 significant figure • If a number is greater than 1, then all zeros to the right of the decimal point are significant 2.0 mg 2 significant figures • If a number is less than 1, then only the zeros that are at the end and in the middle of the number are significant 0.00420 g 3 significant figures 40 How many significant figures are in each of the following measurements? 24 mL 3001 g 0.0320 m3 6.4 x 104 molecules 560 kg 41 Problem 1.34 How many significant figures are in each of the following measurements? a) 0.006 L b) 0.0605 dm c) 60.5 mg d) 605.5 cm2 e) 960 x 10-3 g f) 6 kg g) 60 m 42 Significant Figures Addition or Subtraction The answer cannot have more digits to the right of the decimal point than any of the original numbers. 89.332 +1.1 90.432 3.70 -2.9133 0.7867 one significant figure after decimal point round off to 90.4 two significant figures after decimal point round off to 0.79 43 Significant Figures Multiplication or Division The number of significant figures in the result is set by the original number that has the smallest number of significant figures 4.51 x 3.6666 = 16.536366 = 16.5 3 sig figs round to 3 sig figs 6.8 ÷ 112.04 = 0.0606926 = 0.061 2 sig figs round to 2 sig figs 44 Significant Figures Exact Numbers Numbers from definitions or counted numbers of objects are considered to have an infinite number of significant figures The average of three measured lengths; 6.64, 6.68 and 6.70? 6.64 + 6.68 + 6.70 = 6.67333 = 6.67 = 7 3 Because 3 is an exact number 45 Carry out the following arithmetic operations to the correct number of significant figures. 11,254.1 g + 0.1983 g 66.59 L – 3.113 L 8.16 m x 5.1355 0.0154 kg ÷ 88.3 mL 2.64x103 cm + 3.27x102 cm 46 Carry out the following arithmetic operations to the correct number of significant figures. 26.5862 L+ 0.17 L 9.1 g – 4.682 g 7.1x104 dm x 2.2654x102 dm 6.54 g ÷ 86.5542 mL 7.55x104 m – 8.62x103 m 47 Problem 1.36 Carry out the following operations as if they were calculations of experimental results, and express each answer in the correct units with the correct number of significant figures a) b) c) d) 7.310 km ÷ 5.70 km (3.26 x 10-3 mg) – (7.88 x 10-5) mg (4.02 x 106 dm) + (7.74 x 107 dm) (7.8 m – 0.34 m)/(1.15 s + 0.82 s) 48 Accuracy – how close a measurement is to the true value Precision – how close a set of measurements are to each other accurate & precise precise but not accurate not accurate & not precise 49 Problem 1.38 Three apprentice tailors (X,Y, and Z) are assigned to the task of measuring the seam of a pair of trousers. The results in inches are: X (31.5, 31.6, 31.4) Y (32.8, 32.3, 32.7) Z (31.9, 32.2, 32.1) The true length is 32.0 in. Comment on the precision and accuracy of each tailor’s measurements. 50 Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems 1. Determine which unit conversion factor(s) are needed 2. Carry units through calculation 3. If all units cancel except for the desired unit(s), then the problem was solved correctly. given quantity x conversion factor = desired quantity given unit x desired unit given unit = desired unit 51 Dimensional Analysis Method of Solving Problems How many mL are in 1.63 L? Conversion Unit 1 L = 1000 mL 1000 mL 1.63 L x = 1630 mL 1L 2 1L L 1.63 L x = 0.001630 1000 mL mL 52 The speed of sound in air is about 343 m/s. What is this speed in miles per hour? conversion units meters to miles seconds to hours 1 mi = 1609 m 1 min = 60 s 1 mi 60 s m x x 343 s 1609 m 1 min 1 hour = 60 min 60 min mi x = 767 hour 1 hour 53 Problem 1.46 The current speed limit in some states in the US is 55 miles per hour. What is the speed limit in km/hr? (1 mi = 1609 m) 54 Problem 1.66 Vanillin is the substance whose aroma the human nose detects in the smallest amount. The threshold limit is 2.0 x 10-11g per liter of air. If the current price of 50 g of vanillin is $112, determine the cost (in cents) to supply enough vanillin so that the aroma could be detected in a large aircraft hanger with a volume of 5.0 x 107 ft3 55