Coordinates - Alston Publishing House
advertisement

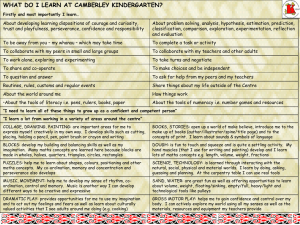
Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 8-point compass Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd 8-point compass Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Acute angle Angles smaller than 90 are called acute angles. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Acute angle Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Approximately equal to () The sign means ‘approximately equal to’. Example: 3468 3470 (when rounded to the nearest ten) Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Approximately equal to () Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Centre mark Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Centre mark Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Common factors Example: 1 and 2 are common factors of 6 and 10. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Common factors Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Common multiples Example: 6, 12 and 18 are some common multiples of 2 and 3. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Common multiples Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinates Example: The strawberry is located at the point (2, 4). The point (2, 4) is a pair of coordinates. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinates Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinate grid Example: This is a coordinate grid. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Coordinate grid Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Degree () We measure the size of an angle in degrees. We can also write for degree(s). Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Degree () Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd East Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd East Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Factors The factors of a number are the numbers that it can be divided exactly by. Example: The factors of 40 are 1, 2, 4, 5, 8, 10, 20 and 40. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Factors Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Heptagon A heptagon has 7 straight sides and 7 vertices. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Heptagon Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Hundreds Example: 2 hundreds = 200 We can say that the value of 2 hundreds is the same as 200. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Hundreds Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Inner scale Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Inner scale Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Irregular polygon An irregular polygon has sides and angles that are not all equal. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Irregular polygon Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Multiples A multiple of a number is the product of that number and any number. A number is a factor of all its multiples. Example: 3, 6, 9 and 12 are the first four multiples of 3. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Multiples Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Net A figure which can be folded to form a solid is called the net of the solid. Example: This is a net of a cuboid. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Net Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North-east Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North-east Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North-west Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd North-west Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Obtuse angle Angles greater than 90 but smaller than 180 are called obtuse angles. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Obtuse angle Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Octagon An octagon has 8 straight sides and 8 vertices. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Octagon Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Origin The pair of coordinates (0, 0) is called the origin. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Origin Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outer scale Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Outer scale Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Polygon A polygon is a closed figure. Its sides are formed by straight lines that do not cross one another. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Polygon Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Prime numbers A prime number has only two factors, 1 and the number itself. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Prime numbers Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Product When we multiply numbers, the answer is called the product. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Product Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Protractor We can find the size of an angle by measuring it with a protractor. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Protractor Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quadrilateral A quadrilateral has 4 straight sides and 4 vertices. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quadrilateral Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quotient When we divide a number by another, the answer we get is called the quotient. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Quotient Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Regroup We need to regroup in a place value when - we get more than 9 after adding or multiplying; or - we subtract a greater number from a smaller number; or - we get a remainder in place values other than the ones place when dividing Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Regroup Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Regular polygon A regular polygon has all equal sides and all equal angles. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Regular polygon Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Remainder Remainder is the amount that is left over when a number is divided by another number. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Remainder Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Right angle A right angle is 90. Example: Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Right angle Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Round to the nearest hundred When we round a number to the nearest hundred, we look at the digit in the tens place. (a) If the digit < 5, we round it to the smaller hundred. (b) If the digit > 5, we round it to the bigger hundred. (c) If the digit = 5, we round it to the bigger hundred. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Round to the nearest hundred Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Round to the nearest thousand When we round a number to the nearest thousand, we look at the digit in the hundreds place. (a) If the digit < 5, we round it to the smaller thousand. (b) If the digit > 5, we round it to the bigger thousand. (c) If the digit = 5, we round it to the bigger thousand. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Round to the nearest thousand Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South-east Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South-east Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South-west Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd South-west Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Thousands Example: 5 thousands = 5000 We can say that the value of 5 thousands is the same as 5000. Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Thousands Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Unit Each in a bar model stands for 1 unit. Example: 1 unit 29 5 units 29 × 5 = 145 Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Unit Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd West Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd West Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-axis Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-axis Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-coordinate Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd X-coordinate Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-axis Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-axis Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-coordinate Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Y-coordinate Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Zero line Maths Smart Grade 4 © 2012 Alston Publishing House Pte Ltd Zero line