Titrations
advertisement
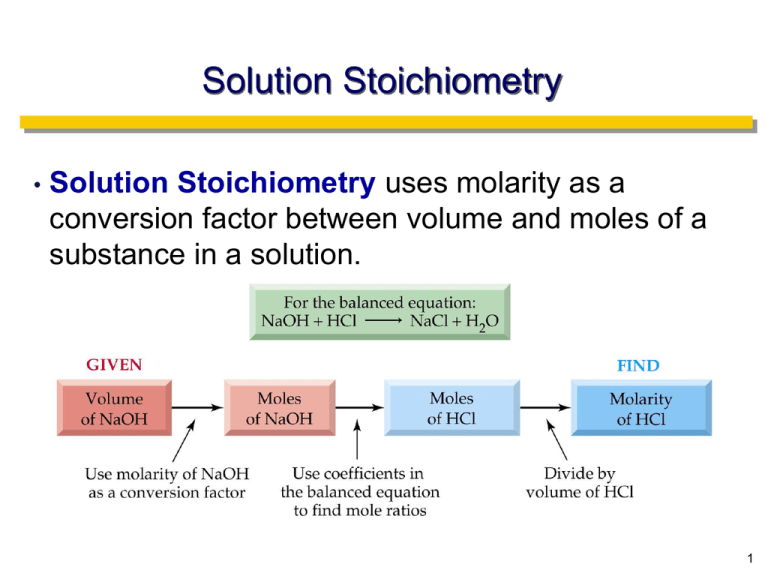
Solution Stoichiometry • Solution Stoichiometry uses molarity as a conversion factor between volume and moles of a substance in a solution. 1 Titrations Titration: A technique for determining the concentration of a solution by measuring the volume of one solution needed to completely react with another solution. This is a special case of a Limiting Reagent! Usually the reaction of an acid with a base. 2 Titrations Analyte: the solution of unknown concentration but known volume. Titrant: the solution of known concentration. Analyte + Titrant → Products Process: Add titrant until all of the analyte has reacted, then record the volume of titrant added. 3 Titrations Equivalence Point: the point at which exactly the right volume of titrant has been added to complete the reaction. Indicator: substance that changes color when an excess of titrant has been added (phenolphthalein, bromocresol green). 4 5 Phenolphthalein 6 Methyl Orange 7 Delivery of Titrant Adding titrant drop-wise. • How many drops fit into 1mL? • • Process: Calibration-hold the pipette in the VERTICAL position and deliver the titrant into a graduated cylinder while counting every drop. 8 Copy the following “Data Tables” Vinegar Measurement Antacid Value Measurement Vinegar Analyte Volume Titrant NaOH Molarity 1.00M Calibration Antacid Analyte 10mL Quantity 1tablet in 20mL H2O Titrant HCl Molarity 3.00M Calibration Volume ____drops ____mL Volume ____drops ____mL Indicator Value phenolphthalein Methyl orange Indicator Acid Colorless Acid Pink Base Pink Base Yellow Reaction Mole Ratio Reaction Mole Ratio 9 Titrations Calculations 1. 2. 3. Find the number of moles of titrant added to reach the endpoint. Determine the moles of analyte that must have been present (use stoichiometric coefficients). Determine the concentration of analyte that must have been present in the flask (use the volume of analyte). • 10 Titrations Example #1: 14.84 mL of an HCl solution of unknown concentration is titrated with standard NaOH solution. At the equivalence point, 25.0 mL of the 0.675 M NaOH has been added. Calculate the concentration of the HCl solution. NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H2O Hints: Titrant = ?moles Analyte = ?moles ?Liters Answer = 1.14 M 11 Stoichiometry Measurement Calculation moles of titrant moles of analyte (use stoichiometric coefficients). concentration of analyte 12