C - Sweatt lab
advertisement

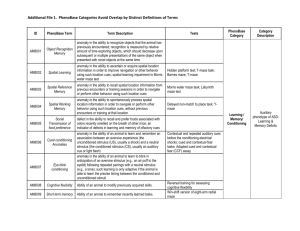
Chapter 4: Rodent Behavioral Learning Memory Models From Mechanisms of Memory, second edition By J. David Sweatt, Ph.D. Hippocampal Pyramidal Neuron Of Mice and Rats Blue Box 1 Open Field Apparatus Figure 1 Open Field Behavior Center/total distance A 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0 0 2 4 6 8 10 Time (min) 400 30 C Vertical activity Total distance (cm) B 300 200 100 0 20 10 0 0 2 4 6 Time (min) Figure 2 8 10 0 2 4 6 Time (min) 8 10 Elevated Plus Maze Figure 3 Roto Rod Figure 4 Rotating Rod Behavior Time (sec) 150 100 50 0 0 1 2 Trial Figure 5 3 Acoustic Startle and Prepulse Inhibition 2000 % Inhibition Acoustic startle reflex to 120 dB noise 75 1500 1000 50 25 500 0 0 74 78 82 dB A Figure 6 B 86 90 Nociception Behavior 20 10 0 +/+ n=26 -/- n=20 Stimulus Intensity (mA) Hind Paw Lick Latency (s) Hot Plate Test 0.35 0.30 0.25 Shock Threshold -/- n=6 +/+ n=6 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 Flinching Figure 7 Jumping Vocalizing Visual Cliff Figure 8 Fear Conditioning Chamber Figure 9 Variants of Fear Conditioning in Rodents A. Cue-plus-contextual Fear Conditioning TRAINING CUED TEST CONTEXTUAL TEST B. C. TRAINING Context Discrimination Train Context 1 Figure 10 Context Alone Conditioning Test Context 1 Context 2 CONTEXTUAL TEST Cued-Plus-Contextual Fear Conditioning Freezing (%) 100 Training 75 50 25 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Time (min) Cued 100 Contextual 75 Freezing (%) Freezing (%) 100 50 25 50 25 0 0 1 2 3 Time (min) Figure 11 75 4 5 6 0 0 1 2 3 Time (min) 4 5 Contextual Fear Conditioning in Rats Figure 12 Passive Avoidance Paradigms Step-Through Passive Avoidance Train Test: measure time to step through Figure 13 Step-Down Passive Avoidance Train Test: measure time to step down Active Avoidance Shuttle Box Active Avoidance Train Figure 13, continued Test: Can the animal avoid the shock? Passive Avoidance Data Figure 14 Bar Press Operant and/ or Conditioned Place Preference Figure 15 Eyeblink Conditioning in Rabbits Corneal Air Puff Elicits Eyeblink Response Figure 16 Corneal Air Puff Given with Tone Tone Given Alone Elicits Eyeblink Response Types of Mazes Lashley Maze 4 Arm Radial (Plus) Maze 8 Arm Radial Maze Finish Start Triangle Maze Figure 17 “T” Maze “Y” Maze The Morris Water Maze Distal Visual Cues Platform Figure 18 Camera A Probe Test Escape Latency (sec) Morris Water Maze – Experimental Results 60.0 Hidden Platform 50.0 40.0 30.0 20.0 10.0 0.0 1 B C Right Trained 3 4 5 6 7 8 Blocks of 4 trials 9 Right Trained 40.0 30.0 20.0 10.0 4.0 Opposite Left 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 0.0 1 129/SvImJ D Escape Latency (sec) Opposite Left 50.0 60.0 50.0 40.0 30.0 20.0 10.0 0.0 Visible Platform 1 2 3 4 Blocks of 4 trials Figure 19 10 5.0 Platform Crossings Quadrant Search Time (%) 60.0 2 5 6 Path Tracking in the Probe Test A Subject #66 Path Length = 1154.2 cm Vehicle B Subject #57 Path Length = 1278.2 cm 30 mg/kg SL327 Figure 20 The Barnes Maze Escape Chamber Spatial Cues Search strategy A Search strategy B Figure 21 Conditioned Taste Aversion A DAY 1 B 1.0 Injection of LiCl or NaCl DAY 2 grams blueberry bar 1st Exposure to Food Item 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 LiCl NaCl Grams Ingested on 2nd Exposure 2nd Exposure to Food Item Figure 22 (LiCl treated group compared to NaCl treated control) Neophobia DAY 1 1st Exposure to Food Item DAY 2 2nd Exposure to Food Item B 0.8 grams blueberry bar A 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 1st intake 2nd intake Grams Ingested Figure 23 (1st exposure compared to second exposure) Novel Object Recognition Figure 24 Memory Reconsolidation Figure 25 The Four Basic Types of Experiments Four Types of Experiments Hypothesis: A→B→C Prediction Experiment • Determine • None (A makes C happen) • Block • Blocking B should block A causing C • Mimic • Activating B should cause C • Measure • A makes B happen Figure 26 Behavioral Tests Commonly Used in Rodents Test Name Open Field Analysis Elevated Plus Maze Rotating-rod Acoustic Startle Pre-pulse Inhibition Hot Plate Hargreave’s Apparatus Light-Dark Exploration Visual Cliff Fear Conditioning: Cued Fear Conditioning: Contextual Passive Avoidance Active Avoidance Lever Press Conditioned Place Preference Eye-blink Conditioning Simple Maze Learning Morris Water Maze Barnes Maze Conditioned Taste Aversion Novel Taste Learning Novel Object Recognition Measurement Distance Moved Over Time Time Spent in Open Arms Time to Fall Off Force of Jump Suppression of Startle Time to Lick Paw Time to Lift Paw Time in Lit Chamber Suppression of Movement Freezing or Startle Freezing or Startle Time Spent in Lit Chamber Time Spent in Cued Chamber Number of Bar Presses Time Spent in One Chamber Blink in Response to Cue Errors or Time to Completion Quadrant Time, Platform Crossings Errors Food or Taste Avoidance Attenuation of Neophobia Time Spent with Object Index Of: Activity Anxiety Coordination and Motor Learning Hearing Sensorimotor Gating Nociception Nociception Vision Vision Auditory Associative Learning Spatial Associative Learning Spatial Associative Learning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning Operant Conditioning Associative Conditioning Spatial Learning, Working Memory Spatial Memory Spatial Memory Taste Learning Taste Learning Recognition Memory