chapter four risk and term structure of interest rate
advertisement

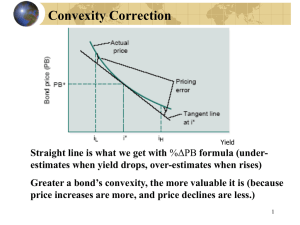
Chapter Four Risk and Term Structure of Interest Rate ⅠRisk Structure of Interest Rate Discussion: What do you find from the following table? table 1 Interest rate of U.S. 1.Default risk 2.Liquidity 3.Income tax considerations default risk: the risk of unable to make interest payments or pay off the face vale when the bond mature. Risk premium= interest rate on default risk bonds﹣interest rate on default risk free bonds Please calculate the risk premium of Moody’s Baa corporation bonds. 4.91-2.77=2.04 The Risk Structure of Interest Rate Default risk liquidity Interest rate positive negative Tax exempt low ⅡTerm Structure of Interest Rates Introduction: Yield Curve A plot of the yields on bonds with differing terms to maturity but the same risk, liquidity, and tax considerations is called a yield curve. It describes the term structure of interest rates for particular types of bonds. The shape of yield curve Ascending Yield Curve This is the common shape in developed countries. It shows that yield rises for longer maturities. Descending Yield Curve This shape shows that short term interest rates are higher than long term rates. This shape is often seen when the market expects interest rates to fall. Flat Yield Curve Short term rates are the same as long term rates. Humped Yield Curve Shape often seen when the market expects that interest rates will first rise (fall) during a period and fall (rise) during another. Please draft the yield curve of government security of U.S. ,what can you find from the curves. 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 i of AUG 2012 i of AUG 1999 30 20 10 7 5 3 2 1 5 0. 25 0. 1.interest rates on bonds of different maturities move together over time. 2.the yield curves of U.S. government security are upward slope. How to explain the different shape of yield curve? 1.Expectation Theory 2. Segmented market theory 3.liqudity premium theory 1.Expectation Theory (1)The key assumption buyers of bonds do not prefer bonds of one maturity over another, so they will not hold any quantity of a bond if its expected return is less than that of another bond with a different maturity. (2) basic proposition: The interest rate on a long-term bond will equal an average of short-term interest rates that people expect to occur over the life of the long-term bond. i i i i t nt e e t 1 t 2 it n e n int=n-period interest rate i t e today’s interest rate on a one-period bond interest rate on a one year bond expected for next period i This equation means that n period interest rate equals the average of the one period interest rate to occur over the n period life of the bond. t 1 (3)Analyze A.When short term interest rates are low, people generally expected them to rise to some normal level in the future, and the average future expected short term interest rate is high relative to current short term interest rate. Therefore long term interest rate will be above current short term rates, the yield curve would be an upward slope. B.If short term interest rate are high, people usually expected them to come back down, long term interest rate would drop below short term interest rates because the average of expected future short term would be below the current short rates and the yield curve would slope down ward and become inverted. C.Short term interest rates have had a characteristic that if they increase today, they will tend to be higher in the future. Hence a rise in short term rates will raise people’s expectations of future short term rates. Because long term interest rates are the average of expected future short term interest rates, a rise in short term interest rates will also raise long term interest rates, causing short term and long term rates to move together. (4)Summary of Expectation Theory A. The interest rate on long term bonds will equal an average of short term interest rate that people expected to occur over the life of the long term bond. B. The difference of interest rate on bonds of different maturities is attributing that short term interest rates are expected to have different values at future dates. 2. Segmented market theory (1)Assumption bonds of different maturities are not substitutes at all. (2)Key point: Sees markets for different –maturity bonds as completely separate and segmented. The interest rate for each bonds with different maturity is determined by the supply and demand for that bond with no effects from expected returns on other bonds with other maturity. 3. Liquidity premium theory (1)Introduction most widely accepted theory of term structure of interest rates, it combines the features of both the expectations theory and segmented market theory by asserting that a long term interest rate will be the sum of a liquidity (term) premium and average of short term interest rates that are expected to occur over the life of bonds (2)Abstract Interest rate on a long term bond will equal an average of short term interest rates expected to occur over the life of the long term bonds plus a liquidity premium (also refer to as a term premium) (3)Assumption bonds of different maturity are substitutes, which mean that the expected return on one bonds dose influence the expected return on bond of a different maturity. But it allows investors to prefer one maturity over another. In other words, bond of different maturity are assume to substitutes but not perfect substitute. (4)Analyze in iat pnt n is period , t at time t iat average short term interest rates. pntliquidity premium When short term interest rates rise, then long term interest rate will also rise with it, therefore interest rates on bonds of different maturity move together. When short term interest rates are low, investor expect them will rise to some normal level, therefore, the average of future expected short term interest rates will be high relative to current short term interest rates, with additional positive interest rate premium, long term interest rates will higher than short term interest rates, therefore ,yield curve will be upward slope. If short term interest rates are high , and investor expect short rates will come back down, the average expected short term interest rates would below short current short term interest rates, therefore long term rates will drop fairly below short term interest rates and overwhelm positive liquidity premiums, the yield curve will be invert to downward slope. The theory also helps us predict the movement of short-term interest rates in the future. A steeply upward slope of yield curve means that future short term rates are expected to rise, a mildly upward slope curve indicates that short term interest rates are expected to stay on the same, a flat slope means that short term rates are expected to fall moderately, and an invert curve means that short term rates are expected to fall sharply. Summary Bonds with same maturity will have different interest rates because of three factors: default risk, liquidity, and tax consideration. The greater default risk the higher the interest rates, the greater the bond’s liquidity, the lower the interest rate, and bonds with tax exempt have lower interest rate. Interest rates of different maturity are different which can be explained by three term structure theory. the expectation theory views the interest rate on long term bonds equal an average of short term interest rate that people expected to occur over the life of the long term bond. The difference of interest rate on bonds of different maturities is attributing that short term interest rates are expected to have different values at future dates. Segmented market theory states that The interest rate for each bonds with different maturity is determined by the supply and demand for that bond with no effects from expected returns on other bonds with other maturity. Liquidity premium theory combines the features of both the expectations theory and segmented market theory by asserting that a long term interest rate will be the sum of a liquidity(term) premium and average of short term interest rates that are expected to occur over the life of bonds. questions 1.please use the theory you learned to explain why different bonds with same maturity have different interest rate? 2.please use the theory you learned to explain why the same bond with different maturity have different interest rate? 3.please sketch the expectation theory. 4.please sketch the segmented market theory. 5.please sketch the Liquidity premium theory . 6.key words: default risk Default free bonds Expectations theory liquidity premium theory Risk premium Segmented market theory Yield curve