IEEE 802.3
Carrier Sense Multiple Access with
Collision Detection (CSMA/CD)
All rights reserved. No part of this publication and file may be reproduced, stored in a retrieval system,
or transmitted in any form or by any means, electronic, mechanical, photocopying, recording or otherwise,
without prior written permission of Professor Nen-Fu Huang (E-mail: nfhuang@cs.nthu.edu.tw).
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Typical CSMA/CD Network
B
收發器
D
F
終端器
同軸電纜
收發器電纜
A
C
E
終端器
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
IEEE 802.3 Architecture
OSI參考模式
CSMA/CD
應用層
表達層
高層通訊協定
會議層
傳輸層
網路層
邏輯鏈結控制
LLC (IEEE 802.2)
媒介擷取控制
MAC
實體層訊號處理 PLS
鏈結層
實體層
PMA
AUI
MAU
MDI
傳輸媒介
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
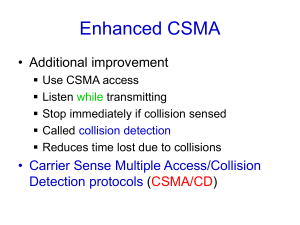
CSMA/CD Protocol
Carrier Sense before transmission
Carrier Sense while transmission
Collision: Two or more stations transmitting
simultaneously
Backoff: Random delay after collision
Deference: Defers transmission if channel is
sensed busy
Collision Window (Slot time): Round-trip
propagation delay time plus some carrier sense
time. In IEEE 802.3, this value is defined to be
51.2 us.
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
CSMA/CD Collision Handling
Collision Signal is generated by Physical
layer.
Jam signal (collision enforcement): To make
sure that all stations involved in the collision
will detect collision. A pattern of 32 bits.
Collision backoff and retransmission method
(Truncated Binary Exponential Backoff
Algorithm, BEBA):
n : number of collisions experienced (n <= 16)
k : Min (n,10) -- Truncation
r : Random delay time (unit: slot time) between 0
<= r < 2k
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
CSMA/CD Collision Handling
Slot time = 51.2 us.
Disadvantage of BEBA:
Last-in-First-out effect: Stations with no
or few collisions will have a better chance
to transmit before stations that have
waited longer.
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
IEEE 802.3 Frame Format
7
1
Preamble SFD
2, 6
DA
2, 6
SA
2
LEN
4
LLC
PAD
位元組
FCS
Preamble: (101010...1010) for Synchronization
I/G
15-位元地址
SFD: Start Frame Delimiter (10101011)
DA: Destination Address
I/G U/L
46-位元地址
SA: Source Address
Length: Length of LLC-Frame
I/G = 0 Individual Address (個別地址)
LLC-Frame: Up to 1500 bytes
I/G = 1 Group Address (群體地址)
PAD: Padding when LLC-Frame < 46 bytes
U/L = 0 Globally Administered Address (整體性地址)
U/L = 1 Locally Administered Address (區域性地址)
FCS: Frame Check Sequence (CRC-32)
MAC-frame size -- from DA to FCS
Min 64 bytes to distinguish from collision
Max 1518 bytes to prevent dominating bandwidth
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Cyclic Redundancy Check
(CRC32) Hardware
Implementation
X0
X1
X8 X9
X7
17
X 16 X
X 18 X19 X20 X 21
X 26 X 27 X 28 X
29
MUX
B
X4
X5 X6
X 10
X 11
X 12 X 13 X 14 X 15
X 22
X 23 X24 X 25
.
X 30 X 31
.
A
C
X2 X3
= AND
= XOR
= NOT
MUX
O = A, C = 0
輸出
O = B, C = 1
控制訊號
輸入
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Flow
Chart
Y
傳送訊框
接收訊框
組成訊框, i=1
開始接收
線上有
訊號
接收完畢
Y
N
傳送訊框
發生衝撞
訊框過短
(衝撞)
送出擾亂訊號
N
傳送完畢
Y
N
Y
Y
N
N
i=i+1
位址辨識
成功
N
Y
Y
i > 16
N
N
尚有多餘
位元
Y
計算延遲時間
檢查碼
正確
Y
長度欄位
內容正確
N
Y
刪除訊框頭尾
等待延遲時間
傳送成功
傳送失敗
訊框錯誤
對齊錯誤
接收成功
長度錯誤
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Collision Detection Window
for Baseband CSMA/CD (=2a)
a = 0.5, 傳輸時間 = 1
t0
A
B
A 開始傳送訊框
t0+a-e
A
B 開始傳送訊框
B
衝撞
t0+0.5
A
B 偵測出衝撞
B
t0+1-e
A
A 偵測出衝撞
B
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Cable Signaling
(Manchester Encoding)
Idle
1
0
1 ... 0
Idle
Data
Preamble
1
1
1 ... 0
0
Coaxial Cable
0V
-0.225V
-1.825V
Idle
1
0
1 ... 0
Idle
Data
Preamble
1
1
1 ... 0
0
Transceiver Cable
+0.7V
0V
-0.7V
100ns
50ns
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Network Configuration
Example 1 (Single segment)
同軸電纜區段(最長 500 公尺)
C
B
E
終端器
同軸電纜
(最長 50 公尺)
收發器電纜
A
(每區段最多接 100 個)
收發器
D
終端器
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Network Configuration
Example 2 (Two segments)
同軸電纜區段(最長 500 公尺)
B
A
C
第一段同軸電纜
收發器電纜(最長 50 公尺)
D
訊號增益器
E
F
第二段同軸電纜
G
H
I
同軸電纜區段(最長 500 公尺)
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Network Configuration Example
3 (Five segments, maximum)
A
1
D
區段 1
區段 2
B
E
C
F
訊號增益器
2
H
G
3
區段 3
4
L
半訊號增益器
5
I
J
區段 4
K
半訊號增益器間電纜
(最長 1000 公尺)
區段 5
M
N
6
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Architecture, Functions, and
Implementation
工作站界面
高層通訊協定
網路控制卡
訊框包裝
鏈結管理
鏈結層
編碼及解碼
實體層
收發器電纜
收發器
傳送及接收
銅軸電纜
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Calculation
of Slot time
(Example 3)
元件
元件
穩定延遲
編碼器
0.1us
收發器電纜
前進路徑 回程路徑
元件
元件數
元件數
啟動延遲
0.1us
整體延遲
5
5
2.0us
5.13ns/公尺 0
300公尺
300公尺
3.08us
收發器(傳送路徑)
0.05us
0.3us
3
3
2.10us
收發器(接收路徑)
0.05us
0.6us
3
0
1.95us
收發器(衝撞路徑)
0
0.9us
0
3
2.70us
同軸電纜
4.33ns/公尺 0
1500公尺
1500公尺
12.99us
半訊號增益器間電纜
5.13ns/公尺 0
1000公尺
1000公尺
10.26us
電纜驅動器
0.1us
0
2
2
0.40us
電纜接收器
0.1us
0
2
2
0.40us
訊號增益器(增益路徑)
0.2us
0.4us
2
0
1.20us
訊號增益器(衝撞路徑)
0.2us
0.2us
0
2
0.80us
載波感測
0
0.2us
5
0
1.00us
衝撞偵測
0
0.2us
0
5
1.00us
訊號上升時間
0
0.1us
3
0
0.30us
0
2.0us
0
3
6.00us
0
0.2us
0
1
0.20us
(至 70% 於500公尺處)
訊號上升時間(由 50%
至 94% 於 500公尺處)
衝撞分割
訊號來回傳遞最長延遲
46.38us
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
10BaseT Ethernet Examples
10BASE5 界面 10BASE2 界面
10BASE5 界面 10BASE2 界面
10BASET
集線器(HUB)
10BASET
集線器 (HUB)
H
A
B
F
D
C
G
串聯線
A
B
D
C
E
無遮蔽式雙絞線(UTP)
最長 100 公尺
E
F
G
H
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Half-duplex MAC
Ethernets have always used a half-duplex MAC.
Efficient bidirectional communications is effected by
rapidly changing the direction of communication on
half-duplex channel.
For Ethernet, this is not a problem due to stations can
quickly arbitrate for the ability to send their frames.
However, the extension of the Ethernet MAC algorithm
to gigabit data rates does strain the ability to efficiently
operate in this mode.
When the arbitration time (equal to the round-trip
delay, in the worst-case) approaches or exceeds the time
to transmit a typical frame, the efficiency of the
algorithm suffers.
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Limitations of Half-duplex
Operation
CSMA/CD implies an intimate relationship between the
minimum length of a frame (L, measured in bit-times,
not absolute time) and the maximum round-trip
propagation delay (2a) of the network:
L > 2a
If we want to allow very long networks, we can make
the minimum frame very long. Padding needs if a
station wishes to send less data than this minimum
frame. Reduces the transmission efficiency.
If we want to avoid the overhead of padding, we must
reduce the extent of the network so that collision can be
detected in all cases.
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Limitations of Half-duplex
Operation
For the original 10 Mbps Ethernet, a compromise was struck.
Minimum frame = 512 bits (64 bytes), not including the preamble and
Physical Layer overhead.
Minimum data field = 46 bytes rarely imposes a significant padding
overhead (IP header + TCP header = 40 bytes).
At 10 Mbps, 512 bit-times is 51.2us. Depends on the type of cable used
and the network configuration, the extent of a 10 Mbps Ethernet can be
on the order of from 2-3 Km.
7
1
Preamble SFD
6
6
2
DA
SA
LEN
46
4
Data
FCS
bytes
Minimum Frame Length (512 bits)
Ethernet - ‹#›/21
Network Extent
For a given minimum-length frame, the extent of a
network scales inversely with data rate.
10,000 m
~ 2800m
1,000 m
~ 205m
100 m
~ 20m
10m
10Mbps
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
Ethernet - ‹#›/21