Jaringan Komputer Lanjut
advertisement

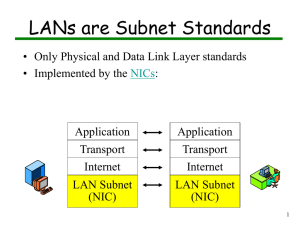
Jaringan Komputer Lanjut Ethernet dan IEEE 802.3 LAN Standard -Aurelio Rahmadian- Pemodelan Lapisan Jaringan Physical Layer Physical Layer Media is the actual physical environment through which data travels as it moves from one component to another, and it connects network devices. The most common types of net-work media are twisted-pair cable, coaxial cable, fiberoptic cable, and wireless. Each media type has specific capabilities and serves specific purposes. Understanding the types of connections that can be used within a network provides a better understanding of how networks function in transmitting data from one point to another. Physical Layer Jenis-jenis Media Jenis-jenis Media Jenis-jenis Media Jenis-jenis Media Type Max Segment Length Speed Cost Advantages Disadvantages UTP 100 m 10 Mbps 100 Mbps Least expensive Easy to install, widely available, widely used Susceptible to interference; can cover only a limited distance STP 100 m 10-100 Mbps More expensive than UTP Reduced crosstalk, less susceptible to EMI than UTP or Thinnet Difficult to work with; can cover only a limited distance Coaxial 500 meters (Thicknet) 10-100 Mbps Relatively inexpensive but more costly than UTP Less susceptible to EMI than other types of copper media Difficult to work with (Thicknet); limited bandwidth; limited application (Thinnet); damage to cable can bring down entire network 185 meters (Thinnet) Type Max Segment Length Speed Cost Advantages FO 3 km and further (singlemode) 10-1000 Mbps (singlemode) Expensive Cannot be Difficult to tapped easily; terminate great distances; not susceptible to EMI; higher data rate Expensive Does not require installation of media 2 km and further (multimode) Wireless 50 km - global 100 Mbps-9.92 Gbps (multimode) 1-54 Mbps Disadvantages Susceptible to atmospheric conditions Ethernet Logical Link Control (LLC) Makes the connection with the upper layers. Frames the Network layer packet. Identifies the Network layer protocol. Remains relatively independent of the physical equipment. Uses IEEE 802.2 standard. Media Access Control (MAC) Data Encapsulation: Includes frame assembly before transmission, frame parsing upon reception of a frame, data link layer MAC addressing, and error detection. Media Access Control: Because Ethernet is a shared media and all devices can transmit at any time, media access is controlled by a method called Carrier Sense Multiple Access with Collision Detection (CSMA/CD). Alasan Penggunaan Ethernet Simplicity and ease of maintenance Ability to incorporate new technologies Reliability Low cost of installation and upgrade Sejarah Ethernet Coaxial -10BASE5 (Thicknet) -10BASE2 (Thinnet) Sejarah Ethernet UTP -10BASE-T -Half-duplex communication Sejarah Ethernet UTP -100BASE-TX -Full-duplex communication Struktur Frame Ethernet Struktur Frame Ethernet Header ◦ ◦ ◦ ◦ Preamble Start of Frame Delimiter Address Length Data (Packet) Trailer Struktur Frame Ethernet Preamble ◦ 7 octet of 10101010 Start of Frame Delimiter ◦ 1 octet of 10101011 Address ◦ Source MAC Address ◦ Destination MAC Address Length/Ethertype Data (Packet-Segment-Data) Frame Check Sequence ◦ Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC) Interframe Gap ◦ 12 octet of idle-line state MAC Address MAC Address