Digital Circuit Implementation
Wafers and Chips
Integrated circuit (IC) chips are manufactured on
silicon wafers
Transistors are placed on the wafers through a
chemical etching process
Each wafer is cut into chips (dies)
which are then packaged individually
Chip Manufacturing Process
COPYRIGHT 1998 MORGAN KAUFMANN PUBLISHERS, INC. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
IC Cost
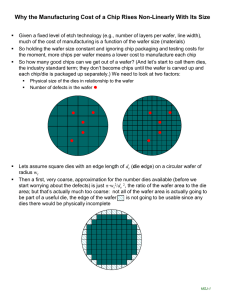
Cost of an integrated circuit (IC) can be modeled
with three equations
Cost per die = (cost per wafer) / ((dies per wafer) * yield)
Dies per wafer (wafer area) / (die area)
Yield = fraction of dies on a wafer that pass testing
Ignores border of the circular wafer that cannot accommodate
a rectangular die
Yield = 1 / (1 + (defects per area * die area) / 2)2
Based on many years of empirical observations
Basic IC Chip Types
Logic circuits may be implemented …
on single chip, or
using many chips interconnected on a printed circuit board
(PCB)
Main types of IC chips are:
Standard chips
Programmable Logic Devices (PLD)
Custom chips
Standard Chips
Small number of transistors (< 100)
Simple and fixed functions
Logic designer must decide how to interconnect
multiple chips for desired function
Agreed upon / standard functionality
Popular in the 1980s – too large in physical size for
much industry use now (good for teaching though!)
7400 Series TTL Logic Chips
Gnd
The 7400 NAND Chip: pin layout
1
14
2
13
3
12
4
11
5
10
6
9
7
8
7400
The equivalent logic layout
Vcc = +5V
00
1
2
3
4
5
6
9
10
8
12
13
11
7400 Series Implementation
Implementing f = x1x2 + x2'x3 using 7400 series ICs
DD
V
7404
7408
7432
1
x2
x3
x
f
Why TTL is Only Used For Small Systems
PLDs
Programmable chips – functionality determined by
the designer
Can handle more complex functions than standard
chips (approx 100 million transistors per PLD)
Can even be reprogrammed
FPGA: Field Programmable Gate Arrays
CPLD: Complex Programmable Logic Devices
PAL: Programmable Array Logic
PLA: Programmable Logic Arrays
These are used very extensively in industry
Custom Chips
Programmable chips have two major drawbacks:
Custom chips
Consume space due to large number of switches for
programmability
Slow speed also limited by excessive switches
(resistance/capacitance)
Logic designer builds a custom chip
Manufactured by a special fabrication facility ($$$!)
ASIC: Application Specific Integrated Circuit
Fast, small
Expensive! And takes time to build and manufacture
Digital Design Process
Design Loop for Digital Hardware
The basic design loop:
Design concept
Initial design takes
creativity and
experience
CAD tools are used
for simulation and to
work out details
Initial design
Simulation
Design correct?
Yes
Successful design
Redesign
No
The Entire Development Process
Required product
Design is only one part
Design specifications
Verification and testing
are also important – this
is called design verification
Initial design
Simulation
Design correct?
Errors may not be uncovered
until after the prototype is made
Errors may not be uncovered
until after “release”!
Pentium bug
Redesign
No
Yes
Implement prototype
Make corrections
Yes
Testing
Minor errors?
No
Meets specs?
Yes
Finished product
No
Simulation Phase
Functional simulation
Timing simulation
Test the circuit to determine if it correctly performs all the
functions that are required
Test the circuit to determine if it meets the timing
requirements
Correct functionality does not necessarily lead to fast speed
The physical design / layout will affect the timing
Inherent gate delays
Physical wiring leaves metal traces that have resistance
CAD Tools
There are a number of commonly used industry
standard CAD tools
CAD = Computer Aided Design
Altera, Cadence, Mentor Graphics, Synopsys, Synplicity,
Xilinx
We have Altera products
Tools are used for multiple purposes
Synthesis, timing simulation, functional simulation, layout
Can even download the design onto a PCB
CAD Tools vs Theory
Why learn any theory if the CAD tools do the work?
Initial design must be provided by the designer
Tools implement the theory
Quality of final design is a function of the quality of the initial
design
Designers need to understand how the tools work in order to
be effective in using them
Tools have many options
Knowing which to select requires knowing what they do and
how they do it