Kagan Training 2
advertisement

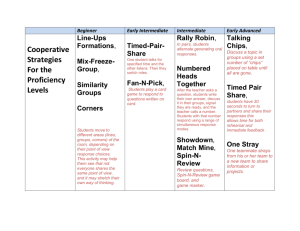
Cooperative learning in the classroom. Session 2 Learning Intentions: 1. To understand the basic principles of Kagan Structures . 2. To generate some practical ideas for effective cooperative learning in the classroom. stand up, hand up, pair up! Key words engagement collaboration Which Kagan strategies have you used since the first session? accountability differentiation HOW TO COACH • Tip • Tip • Tell • Explain Learning Intentions: 1. 2. To understand the basic principles of Kagan. To generate some practical ideas for effective cooperative learning in the classroom. P Positive Interdependence I Individual Accountability E Equal Participation S Simultaneous Interaction Key words engagement collaboration accountability differentiation Numbered Heads Together 1. Divide the students into groups of four and give each one a number from one to four. ( Seating Plan) 2. Pose a question or a problem to the class. 3. Have different numbered students ( 1-4) gather to think about the question and to make sure everyone in their group understands and can give an answer. Students return to original groups. 4. Ask the question and call out a number at random. 5. The students with that number raise their hands, and when called on, the student answers for his or her team. 1. Which formula is used to calculate the area of a circle? A = πr2 2. Who wrote To Kill a Mocking Bird? Harper Lee 3. What is the word equation for photosynthesis? carbon dioxide + water (+ light energy) → glucose + oxygen 4. In which year was the Cuban Missile Crisis? 1962 5. In religion, what is meant by the term ‘natural evil’? Suffering caused by humans acting in a way that is considered morally wrong e.g., bullying, murder, rape, theft or terrorism Review Instant Star 1. Divide the students into groups of four and give each one a number from one to four. 2. Pose a question or a problem to the class. 3. Students write down their answers independently. 4. Ask the question and call out a number at random. 5. The students with that number stand and read out their answer to their team. 6. The teacher reveals the answer. 7. The team praises or coaches. 1. Which three countries in the World Cup finals have the biggest population? USA, Brazil, Nigeria 2. Which coconut-based product is being used for the first time in a World Cup and why? Vanishing spray – stops the wall encroaching on the free kick 3. How many Spanish speaking countries are participating in the World Cup? Nine – Argentina, Chile, Columbia, Costa Rica, Ecuador, Honduras, Mexico, Spain, Uruguay. 4. How many seconds in a World Cup match? 5400 5. ‘Football’s coming home’ was the English World Cup Song in which year? 1998 (was the Euro 1996 song too) Review Rally Coach Partners take turns solving a problem. Whilst one solves the other coaches. 1. Teacher assigns. problems to solve. Partner A solves and partner B coaches (Tip, Tip, Tell, Explain) 2. Partners swap with a new problem to solve. Useful for any process or procedure with a definite right/wrong. E.g. Solve multi-step word problems in maths; change each decimal into a simplified fraction. How do you make a cup of tea? Rally Coach Shoulder partners take turns solving a problem. Whilst one solves the other coaches. 1. Teacher assigns. problems to solve. Partner A solves and partner B coaches (Tip, Tip, Tell, Explain) 2. Partners swap with a new problem to solve. Useful for any process or procedure with a definite right/wrong. E.g. Solve multi-step word problems in maths; change each decimal into a simplified fraction. How do you calculate an average of: 50, 20, 5, 10, 7, 8? Review Centrepiece 1. Creative thinking in a safe environment . 2. Students work with others whilst also being responsible for their own portion of the activity. 3. Students can work at a comfortable pace & also provide help to others in the team by coaching where necessary. Centrepiece Set up – 1. 5 pieces of paper per team of 4 – 1 per person & 1 in the centre. 2. Teacher assigns a topic. 3. Students generate items – 4. Write it, trade it with centrepiece. 5. Goal – to finish all tasks in a collaborative way Review Showdown 1. 2. Each student writes his/her answer on his/her individual response board. When everyone in the group is ready, the leader says "Showdown" and team members compare and discuss their answers before final answer is agreed. Peer support on challenging questions Groups self-correct LA supported by higher achieving pupils YEEEHAAA!!!!! Showdown 1. 2. Each student writes his answer on his individual response board. When everyone in the group is ready, the leader says "Showdown" and team members compare and discuss their answers before final answer is agreed. Peer support on challenging questions Groups self-correct LA supported by higher achieving pupils What can you learn from Elizabeth I’s Rainbow portrait? H H M L M L What does each part of the portrait mean? Angel Wings Flowers and pearls Eyes and Ears Angel Wings • 1. The Angel’s wings show a sign of Elizabeth’s heavenly knowledge • 2. The eyes and ears show that Elizabeth sees and hears everything in her country • 3. The flowers and the pearls represent youth and purity and that she is still young and fit. Review Talking Chips 1. Students are asked to discuss a topic in groups. 2. As each student talks, he/she places his/her chip in the centre of the table(a pen or pencil will work in place of chips). 3. Once a student finishes talking, he/she cannot talk until every other “chip” has been thrown into the centre. 4. If a student doesn’t have anything to share on this particular topic, they can place a chip in the centre at the end. 5. When all chips are down, students retrieve their chips and start over. • Good for ensuring participation in discussion is equal Chips can mean different things• Red- facts • Yellow- supporting point • Blue- Challenge point • White- Question Question: Talking Chips 1. Students are asked to discuss a topic in groups. 2. As each student talks, he/she places his/her chip in the centre of the table (a pen or pencil will work in place of chips). 3. Once a student finishes talking, he/she cannot talk until every other “chip” has been thrown into the centre. 4. If a student doesn’t have anything to share on this particular topic, they can place a chip in the centre at the end. 5. When all chips are down, students retrieve their chips and start over. Chips can mean different things• Red- facts • Yellow- supporting point • Blue- Challenge point • White- Question H H M L M L Evaluation • Please complete the evaluation before you leave • Thanks! All resources are on the Teaching and Learning Blog. • PPT • Templates