Attacks on Computer Systems
advertisement

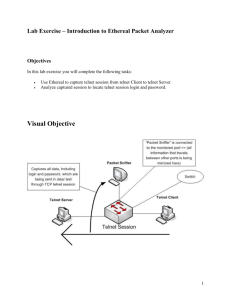
Attacks on Computer Systems Hans Hedbom Attacks “Non-Technical” attacks Example Social engineering Phishing Cause Low user awareness or missing policies/routines Technical attacks Example See following slides Cause 2 Transitive trust Bugs and configuration errors in apps and OS Vulnerabilities in protocols and Network Infrastructure Threats to confidentiality Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010 NETWORK ATTACKS SYN-Attacks The attacker sends a large amount of SYN-packets to the server fills-up the SYN-buffer server is unable to accept more connections Denial of Service Client SYN Server SYN,ACK ACK TCP event diagram 5 Timeout ~4 min. IP Fragmentation Attack Intentional fragmentation of IP-packets may confuse routers, firewalls and servers IP-packet Data Header Fragment 1 Header Offset 0 Fragment 2 Data H Data Offset 20 Offset 16 Original Fragmented IP-packet Data Header 6 Overlap! Assembled Sniffer Attacks Eavesdropping on a network segment. Telnet (password in the clear) Telnet Client Telnet Server IP Network Telnet Attacker 7 Passwords over the Net Telnet FTP Rlogin Rexec POP SNMP NFS SMB HTTP 8 IP-Spoofing Counterfeiting of IP-sender-addresses when using UDP and TCP NFS-request NFS Client NFS-response SYN-attack Attacker 9 NFS Server IP Network Session Hijacking Attacker hijacks a session between a client and a server it could for example be an administrator using telnet for remote login Telnet traffic Telnet client IP Network SYN-attack IP-Spoofing Attacker 10 Telnet server DNS Cache Poisoning DNS = Domain Name Service is primarily used to translate names into IP-addresses e.g. ”www.sunet.se” to ”192.36.125.18” data injection into the DNS server cross checking an address might help 11 OS (SOFTWARE) ATTACKS Race Condition Attacks Explores software that performs operations in an improper sequence. e.g. psrace (Solaris 2.x). Application /usr/bin/ps Create file Store data Set SUID Use data Remove file 13 /tmp/sh Create link /tmp/ps_data Buffer overflows Buffer overflow accounts for 50 % of the security bugs (Viega and McGraw) Data is stored in allocated memory called buffer. If too much data need to be stored the additional bytes have to go somewhere. The buffer overflows and data are written past the bounds. WEB ATTACKS Browser Vulnerabillities Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010 Window of Exposure Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010 Phishing Phishing (only works with predictable or time invariant values) Trick the user to access a forged web page. SSL/TLS 1. Username 2. Ask for login credentials 3. Give login credentials 4.Ok alt Deny (error code) Forged Web Page Phishing Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010 Phishing Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010 Pharming 5.Chalange 6. Responce 1.Username 4.Chalange 7 .Responce 9.Ok alt Deny 2.Username 3.Chalange 8.Responce 9.Ok alt Deny XSS What is SQL Injection? $name = $HTTP_POST_VARS["name"]; $passwd = $HTTP_POST_VARS[“passwd"]; $query = “select name from users where name = ‘”.$name.”’ and passwd = ‘”.$passwd.”’” ; $result = mysql_query($query); What is SQL Injection? BOT-NETS Bot-nets A bot-net is a large collection of compromised computers under the control of a command and control server. A bot-net consists of bots (the malicious program), drones (the hijacked computers) and (one or more) C&C server. A bot is usually a combination of a worm and a backdoor. IRC and HTTP are the primary communication protocols in today's bot-nets. Bots are usually self spreding and modular. 26 Uses of bot-nets Bot-nets could be used for the following: Click Fraud Making drones click on specific advertisements on the web. DDoS For financial gain or blackmail. Keyloging For financial gain and identity theft. Warez Collecting, spreading and storing Spam For financial gain. And of course as a private communication network. 27 Detecting and preventing bot-nets Detection is all about finding the C&C server. Look for suspicious traffic patterns in firewall logs and other logs. Take note of servers whit a high number of incoming connections. Monitor the suspicious C&C and inform the owner and the authorities when you are sure that it is a bot-net controller. Prevention All the usual rules apply: patch and protect. Do egress filtering in firewalls as well as ingress. This will stop infections from spreading and could block outgoing traffic from drones within the intranet. Problems Some bot-nets are encrypted. Tracking the C&C to the real bot-net owner can be hard. 28 Bot activity Table from: Symantec Global Internet Security Threat Report Trends for 2009 Volume XV, Published April 2010