JDBC
advertisement

Advanced Computer Engineering Lab
242-301, Semester 1, 2014-2015
Introduction to Java
Database Connectivity
(JDBC)
•
Objective
– to give some background on JDBC to
help with the lab exercises
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
1
Overview
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
What is JDBC?
The JDBC-ODBC Bridge
Four Types of JDBC Drivers
JDBC Pseudocode
SimpleJDBC.java
Continued
2
6.
7.
8.
Meta Data
Using MS Access
Books.accdb as an ODBC
Data Source
9. Data Source Problems
10. More Information
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
3
1. What is JDBC?
•
JDBC is an interface which allows Java
code to execute SQL statements inside
relational databases
– the databases must follow the ANSI SQL-2
standard
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
4
JDBC in Use
Java
program
Green means
"Java code"
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
JDBC
connectivity
data processing
utilities
jdbc-odbc
bridge
driver
for Oracle
driver
for Sybase
odbc
driver
5
2. The JDBC-ODBC Bridge
•
ODBC (Open Database Connectivity) is a
Microsoft standard from the mid 1990’s.
•
It is an API that allows C/C++ programs to
execute SQL inside databases
•
ODBC is supported by many products.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
6
•
The JDBC-ODBC bridge allows Java code
to use the C/C++ interface of ODBC
– it means that JDBC can access many different
database products
•
The layers of translation (Java --> C -->
SQL) can slow down execution.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
7
•
The JDBC-ODBC bridge comes free with
the JDK:
– called sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver
•
The ODBC driver for Microsoft Access
comes with MS Office
– so it is easy to connect Java and Access
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
8
3. Four Types of JDBC Driver
•
1. JDBC-ODBC Bridge (type 1)
– translate Java to the ODBC API
– used by many Windows-based databases, e.g.
MS-Access
•
2. Database Protocol Driver (type 4)
– Independent from the OS/hardware because the
driver is in Java.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
9
•
3. Native API Connection Driver (type 2)
– connected by a OS native module, dependent
on the OS or hardware
(e.g. DLLs on Windows)
•
4. Net Connection Driver (type 3)
– use Java to access the database via networking
middleware (usually TCP/IP)
– required for networked applications
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
10
JDBC Drivers
•
A very long list of drivers (freeware,
shareware, and commercial) can be found
at:
http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/java/
index-136695.html
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
11
4. JDBC as a Diagram
DriveManager
creates
Connection
creates
Statement
creates
SQL
Green means
"Java code"
make link
to driver
data
Driver
SQL
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
ResultSet
data
12
DriveManager
•
•
It is responsible for establishing the
connection to the database through the
driver.
e.g.
Class.forName(
"sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
Connection conn =
DriveManager.getConnection(url);
name of the database
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
13
Name the Database
•
The name and location of the database is
given as a URL
– the details of the URL vary depending on the
type of database that is being used
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
14
ODBC Database URL
jdbc:odbc: //host.domain.com: 2048 /data/file
The comms
protocol
The machine
holding the
database.
The port
used for the
connection.
The path to
the database
on the machine
e.g. jdbc:odbc:Books
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
15
Statement Object
•
•
The Statement object provides a
‘workspace’ where SQL queries can be
created, executed, and results collected.
e.g.
Statement st =
conn.createStatement():
ResultSet rs = st.executeQuery(
“ select * from Authors” );
:
st.close();
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
16
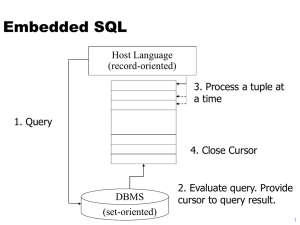
ResultSet Object
•
Stores the results of a SQL query.
•
A ResultSet object is similar to a
‘table’ of answers, which can be
examined by moving a ‘pointer’ (cursor).
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
17
cursor
•
Cursor operations:
23
5
John
Mark
17
98
Paul
Peter
– first(), last(), next(), previous(), etc.
•
Typical code:
while( rs.next() ) {
// process the row;
}
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
18
5. SimpleJDBC.java
// SimpleJDBC.java
// Displays the firstnames and lastnames
// of the Authors table in the Books db.
import java.sql.*;
public class SimpleJDBC {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// The URL for the Books database.
// ’Protected' by a login and password.
String url = "jdbc:odbc:Books";
String username = "anonymous";
String password = "guest";
:
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
19
try {
// load the JDBC-ODBC Bridge driver
Class.forName("sun.jdbc.odbc.JdbcOdbcDriver");
// connect to db using DriverManager
Connection conn =
DriverManager.getConnection( url,
username, password );
// Create a statement object
Statement statement = conn.createStatement();
// Execute the SQL query
ResultSet rs = statement.executeQuery(
"SELECT lastName, firstName FROM Authors" );
:
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
20
// Print the result set
while( rs.next() )
System.out.println(
rs.getString("lastName") + ", " +
rs.getString("firstName") );
// Close down
statement.close();
conn.close();
}
:
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
21
catch ( ClassNotFoundException cnfex ) {
System.err.println(
"Failed to load JDBC/ODBC driver." );
cnfex.printStackTrace();
System.exit( 1 ); // terminate program
}
catch ( SQLException sqlex ) {
System.err.println( sqlex );
sqlex.printStackTrace();
}
} // end of main()
} // end of SimpleJDBC class
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
22
Output
Section 8
not done.
Section 8
now done.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
23
•
If you've done section 8, but still getting
error messages, then check out section 9.
•
If you're still having problems, please come
to see Aj. Andrew.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
24
5.1. Username & Password
•
The database’s link to the outside (e.g. its
ODBC interface) must be configured to
have a login and password
– details for ODBC are given later
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
25
5.2. Accessing a ResultSet
•
The ResultSet class contains many
methods for accessing the value of a column
of the current row
– can use the column name or position
– e.g. get the value in the lastName column:
rs.getString("lastName")
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
26
•
The ‘tricky’ aspect is that the values are
SQL data, and so must be converted to Java
types/objects.
•
There are many methods for
accessing/converting the data, e.g.
– getString(), getDate(), getInt(),
getFloat(), getObject()
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
27
6. Meta Data
•
Meta data is the information about the
database:
– e.g. the number of columns, the types of the
columns
– meta data is the schema information
ID
Name
Course
Mark
007
008
James Bond
Aj. Andrew
Shooting
Kung Fu
99
1
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
meta data
28
•
One important use for metadata is for
formatting result set data
– e.g. instead of displaying the results as text,
display them in a Java table with headers, rows,
columns
•
see TableDisplay.java in the Exercises
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
29
6.1. Accessing Meta Data
•
•
The getMetaData() method can be used
on a ResultSet object to create its meta
data object.
e.g.
ResultSetMetaData md =
rs.getMetaData();
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
30
6.2. Using Meta Data
int numCols = md.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 0; i <= numCols; i++) {
if (md.getColumnType(i) ==
Types.CHAR)
System.out.println(
md.getColumnName(i) )
}
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
31
6.3. More Meta Data Methods
•
getTableName()
getPrecision()
•
– number of decimal digits in the column
isSigned()
•
– returns true if column has signed numbers
isCurrency()
•
etc.
•
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
32
7. Using MS Access
•
MS Access changed its file formats when
Access 2007 was released:
– for Access 2003 (and earlier) you should use
Books.mdb
– for Access 2007 or 2010, you should use
Books.accdb
– both versions are in the lab's website.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
33
Access and SQL
•
How to use SQL in Access is described at:
– http://www.jaffainc.com/SQLStatementsInAccess.htm
And on the
website, in
sqlAccess2007
.txt and
sql_intr.pdf
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
34
TableRelationships in Books.accdb
(and Books.mdb)
Under Database Tools > Relationships
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
35
8. Books.accdb as an ODBC Data Source
•
1. Click on
“Data Sources
(ODBC)” in
“Administrative
Tools” folder in
the Control
Panel.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
36
•
Select the MS Access Data Source.
Press “Add’ to add a data source.
If you don't find
MS Access here,
then go to
Section 9.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
37
•
Select the English
Microsoft Access
Driver (*.mdb,
*.accdb).
Press “Finish”.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
38
•
3. Type in the
"Books"
source name,
any description,
and press “Select”
to browse to set
the path to the
Books.accdb or
Books.mdb file.
Click on
“Advanced”.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
39
•
4. Type in a username
and password (guest).
Click “Ok” repeatedly
until all the dialog
boxes are gone.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
40
9. Data Source Problems
•
Two problems may occur when using JDBC
with the data source set up in Section 8:
– "No suitable driver found for jdbc: odbc:
driver={Microsoft Access Driver (*.mdb)};...
– "The specified DSN contains an architecture mismatch
between the Driver and Application"
•
These problems are usually due to you
using the 64-bit version of Windows 7.
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
41
•
Check your version of Windows by
following the steps listed at:
– http://support.microsoft.com/kb/827218
means
32-bit
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
42
Which Version of Access?
•
Check whether you are using the 32-bit or
64-bit version of Access:
– look at the "Help" dialog
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
43
Win7 64-bit & Access 64-bit
•
You may need to download the 64-bit
Access drivers from:
– http://www.microsoft.com/
en-us/download/details.aspx?id=13255
– execute AccessDatabaseEngine_x64.exe
•
You should also be using the 64-bit version
of Java for Windows. get it from:
– http://www.java.com/en/download/
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
44
Win 7 64-bit & Access 32-bit
•
Set up the data source using the 32-bit
ODBC control panel at:
– c:\windows\sysWOW64\odbcad32.exe
•
You should also be using the 32-bit version
of Java for Windows. Get it from:
– http://www.java.com/en/download/
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
45
10. More Information
•
Ivor Horton’s Beginning Java 2, JDK 5
Edition, Wiley Publishing, 2005
Chapters 24 and 25 (starts on p.1306)
•
Advanced Java 2 Platform: How to Program
Deitel & Deitel, Prentice-Hall, 2001
Chapter 8
http://java.coe.psu.ac.th/ForMember/
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
Continued
46
•
JDBC Wikipaedia page:
• http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/JDBC_driver
•
The Java Documentation and tutorial
– http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/
– the JDBC Database Access ‘trail’ is very good
– http://docs.oracle.com/javase/tutorial/
jdbc/index.html
242-301 Adv. CoE Lab: JDBC
47