Fluid and Electrolytes
advertisement

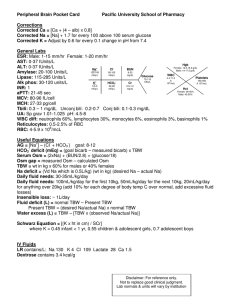
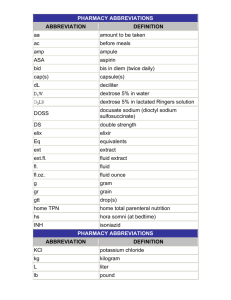
Fluid and Electrolytes Zach Gregg Zachary_Gregg@brown.edu Total Body Water 60% body weight (50% in women) ECW- 20% body weight 33% TBW ICW- 40% body weight 67% TBW Interstitial – 15% body weight Intravascular – 5% body weight 8% TBW 25% TBW ECW Intravascular Water supplies the blood Maintenance essential to survival Interstitial Equilibrated rapidly with intravascular compartment Increases in size after an operation, burn, trauma, or severe illness (3rd Spacing) Plasma is separated from interstitium by an endothelial cell layer and basement membrane Electrolytes ECW Na+ 142 K+ 4 Cl110 HCO324 Inorg. Phos12 ICW Na+ K+ ClHCO3Org. Phos- 10 140 3 10 137 Na+/K+ ATPase • Actively pumps 3 Na+ out of cell and 2K+ inside cell • Energy from ATP • Regulated by – Insulin – Aldosterone Daily Requirements • • • • Water – 30-35 cc/kg Sodium – 1mEq/kg Potassium – 0.5-1mEq/kg Chloride – 1.5 mEq/kg Fluid Loss • Urine Output – Highest daily water loss – 0.5cc/kg/hr • Sufficient UO to excrete the daily solute load • 70kg pt = 35cc/hr Fluid Loss • Insensible – Skin - 300-400 ml/day – Breathing – 400 ml/day – Feces – 100-200 ml/day • Potential – – – – – Saliva – 1000 ml/day Bile – 500-1000 ml/day Gastric – 1000 ml/day Pacreatic – 1000 ml/day Small intestine – 3000 ml/day Maintenance Fluid • 100/50/20 per 24 hrs for 70kg – First 10 kg x 100cc/kg = 1000 cc – Second 10 kg x 50cc/kg = 500 cc – Remaining 50 kg x 20cc/kg = 1000 cc 2500 cc/day Maintenance Fluid • 4/2/1 per hr for 70kg – First 10 kg x 4cc/kg = 40 cc – Second 10 kg x 2cc/kg = 20 cc – Remaining 50 kg x 1cc/kg = 50 cc 110 cc/hr Fluid Components per Liter • Resuscitative Fluids + - – NS (0.9%) 154mEq Na , 154mEq Cl + + – LR 130mEq Na , 110mEq Cl , 4mEq K , 28mEq HCO3 , 3mEq Ca • Maintenance Fluids + – ½ NS (0.45%) 77mEq Na , 77mEq Cl • Colloid - Fluid Pearls • Resuscitation – isotonic fluid (LR or NS), no dextrose, if ongoing losses consider using colloid • Post-op – LR or NS until pt euvolemic, then switch to maintenance • Bolus – Isotonic, no dextrose • Mobilization – movement of fluid from 3rd space into intravascular space Hypovolemia • Acute volume loss – Tachycardia – Hypotension – Decreased UO • Gradual volume loss • • • • – Loss of skin turgor, dry mucus membranes – Thirst – Changes in mental status Low CVP Hemoconcentration (Increased HCT) BUN:Cr > 20:1 Metabolic acidosis due to hypoperfusion Hypervolemia • • • • • • Large UO Pitting edema JVD Crackles on lung exam Hypoxia CXR – cephalization of vessels, pulm edema Hyponatremia • Serum Na+ < 130mEq/L • Sx- Nausea, emesis, weakness, MS changes, seizure • Hypovolemic – Causes – Na+ and water are lost and replaced with hypotonic solutions • • • • • Renal – salt wasting nephropathy GI – diarrhea, vomiting, fistulas Excessive sweating 3rd spacing – ascites, peritonitis, pancreatitis, burns Hypoaldosteronism – Tx – replete with NS, no faster than 0.5 mEq/L/hr to avoid central pontine myelinolysis Hyponatremia • Euvolemic – Causes – SIADH, psychogenic polydipsia – Tx – free water restrict • Hypervolemic – Causes - Renal failure, nephrosis, CHF, cirrhosis Hypernatremia • Serum Na+ > 145 • Sx – altered level of consciousness, seizure, coma, signs of dehydration • Causes – DI, hyperosmolar diuresis, EtOH suppresses Vasopressin release • Tx – Calculate free water deficit = 0.6 x wt(kg) x (measured Na+ - 140)/140 – Replace first ½ in 24hrs, then 2nd ½ in 24 hrs. No faster then 10mEq/day to avoid cerebral edema – Use D5W, ½ NS or ¼ NS Hypokalemia • K+ < 3.5 • Sx – fatigue, weakness, ileus, N/V, arrhythmia, rhabdomylosis, flaccid paralysis, resp compromise – EKG - long QT, depressed ST, low T waves, U waves • Causes – vomiting, NGT drainage, diarrhea, high output enteric/pancreatic fistula, hyperaldo, loop diuretics • Tx – replete 10 mEq KCl for every 0.1 below 4.0, if persistent hypoK+, may also need Mg 2+ replacement Hypokalemia QuickTime™ and a decompressor are needed to see this picture. EKG - long QT, depressed ST, low T waves, U waves Hyperkalemia • K+ > 5.0 • Sx – weakness, N/V, abdominal cramping, diarrhea, arrhythmias – EKG – peaked T waves, prolonged PR, widened QRS, V-fib, arrest • Causes – lab error, iatrogenic, renal failure, acidosis, hemolysis, crush injury, reperfusion after 4hrs ischemia • Tx – cardiac monitoring – 1 amp calcium gluconate (stabilizes myocardium) – 1 amp glucose, 10units IV insulin (shifts K+ intracellular) – Kayexalate, dialysis Hyperkalemia EKG – peaked T waves, prolonged PR, widened QRS, Vfib, arrest Hypocalcemia • Ca2+ < 8.5 • Sx – parasthesias, muscle spasms, tetany, seizures, Chvostek, Trousseau’s – EKG – prolonged QT, can progress to complete heart block or V-fib • Causes – pancreatitis, tumor lysis syndrome, blood transfusion, renal failure, thyroid or parathyroid surgery, diet deficient in Vit D or Ca, inability to absorb fat soluble viatmins • Tx – For chronic hypoCa give supplemental Ca and Vit D. For symptomatic give IV Ca Hypercalcemia • Ca2+ > 10.5 • Sx – stones, moans, groans, psychologic overtones • Causes – CHIMPANZEES • Tx – Identify cause and treat, severe/symptomatic hyperCa tx with IVF, bisphosphonates if due to release of Ca from bone