PWM Control - Louisiana State University
advertisement

Robotics Research Laboratory
Louisiana State University
Digital Output
◦ 8 * 8 LED matrix
◦ Techniques for LEDs control on LED matrix
Basic I/O operation
◦ Define pins on PORTas either input or output (DDRx)
◦ Output control ( PORTx)
◦ Input read (PINx)
Digital input
◦ Button
◦ Button Flag
Ex) bitwise operations
Let’s assume that we add 4 buttons on PINA4 ~ 7 and 4 LEDs on
PINA0~3
LED0 PIN0, LED1 1, LED2 2, LED3 3
button0 PIN4, button1 PIN5, button2 PIN6, button3 PIN7
DDRA = 0x0F (0b00001111) : PINA0 ~3= output, PIN4~7 = input
PORTA = 0xF0 (0b11110000) : pull up from PIN4 to 7 for input
PINA = 0xF0 (0b11110000) : initial status of PINA
All LEDs are off, all buttons are released
If LED2 is only need to be on PORTA = PORTA | 0x04 ( 0b00000100 )
PINA == 0xF4
( 0b11110100 )
Then, if only button2 is need to be read PINA & 0x04 ( 0b01000000 )
Button2 released:
PINA ( 0b11110100 )
& 0x40 ( 0b01000000 )
0x40 (0b01000000)
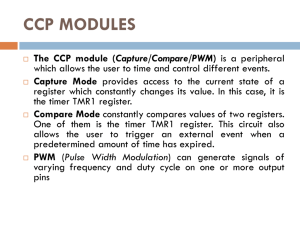
Pulse-width Modulation
◦
◦
◦
◦
What for
How it works
Applications
How to make it
Servo Motor Control
◦ What is servo motor
◦ How it works
◦ Set position of servo head
Simple Hexabot
◦ Walking
◦ Turning
◦ Control hexbot
What is it?
◦ Controlling power to inertial electrical devices
◦ Average voltage and current controlled by turning
switch
What for?
◦ Modern electronic power switches
◦ The main advantage of PWM is that power loss in
the switching devices is very low
◦ Relatively low cost
Applications
◦ Fans
◦ Pumps
◦ Robotic Servo
◦ Stepper Motor
◦ Telecommunication
How to make it?
◦ Digital Out (PINx)
◦ Special Function I/O Regiser (SFR/SFIOR)
◦ Using a main program
ns_spin( int delay_time ) ; TOGGLE_PIN(PINxx)
◦ Using interrupts
Timers
PORTB – PINB5 (OCA1), PINB6 (OC1B), PINB7 (OC2)
PORTE – PINE3 (OC3C), PINE4 (OC3B), PINE5 (OC3A)
How to set position of servo head
◦ /home/csc2700/csc2700/10-PWM-dimLight-01
ICR3 = 40000u;
// input capture register
// pulse cycle (every 40 milli-second)
TCNT3 = 0;
// interrupt flag register
// Set the WGM mode & prescalar
TCCR3A = ( 1 << WGM31 ) | ( 0 << WGM30 ) |
// timer control register
( 1 << COM3A1 ) | ( 1 << COM3B1 ) | ( 1 << COM3C1 );
TCCR3B = ( 1 << WGM33 ) | ( 1 << WGM32 ) |
// timer control register
TIMER3_CLOCK_SEL_DIV_8;
DDRE |= (( 1 << 3 ) | ( 1 << 4 ) | ( 1 << 5 ));
// I/O control register
uint16_t count = 0;
while (1){
OCR3A = count++;
us_spin(200);
}
// 0 ~ 65535 (pulse width), PINE3
What is it?
◦ Robotic Arms, RC-Airplane, etc.
◦ Mechanical position change
How does it work?
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Position Reader (Potentiometer)
DC-Motor
PWM DC-Motor Controller
Body Frame
Gears
Servo Head
How to set position of a servo head
◦ /home/csc2700/csc2700/10-PWM-Servo-01
int count = 0;
while (1){
switch (count++ % 4){
case(0):
OCR3A = 1000; break;
case(1):
OCR3A = 3000; break;
case(2):
OCR3A = 5000; break;
case(3):
OCR3A = 3000; break;
}
ms_spin(1000);
}
// OCR3A is PINE3 , 1000 is 1ms == left (0 degree)
// OCR3A is PINE3 , 3000 is 3ms == middle (90 degree)
// OCR3A is PINE3 , 5000 is 5ms == right (180 degree)
// OCR3A is PINE3
How to make it
◦
◦
◦
◦
ATmega128 Stamp Board
Three servo motors
3 wires (18 or 19 gauge, 12’ * 3)
Battery (V 5.0)
Let’s make it walk
◦ /home/csc2700/csc2700/10-PWM-HexaBot-01/
int count = 0;
while (1){
LED_OFF(COL0_3x3);LED_OFF(COL1_3x3);LED_OFF(COL2_3x3);
switch (count++ % 4){
case(0):
SetPWM( PWM_PINE3, RIGHT_FRONT); SetPWM( PWM_PINE4, LEFT_BACK); SetPWM( PWM_PINE5, MID_RIGHT); break;
case(1):
SetPWM( PWM_PINE3, RIGHT_BACK); SetPWM( PWM_PINE4, LEFT_FRONT); SetPWM( PWM_PINE5, MID_RIGHT); break;
case(2):
SetPWM( PWM_PINE3, RIGHT_BACK); SetPWM( PWM_PINE4, LEFT_FRONT); SetPWM( PWM_PINE5, MID_LEFT); break;
case(3):
SetPWM( PWM_PINE3, RIGHT_FRONT); SetPWM( PWM_PINE4, LEFT_BACK); SetPWM( PWM_PINE5, MID_LEFT); break;
}
ms_spin(100);
}
#define PWM_PINE3
#define PWM_PINE4
#define PWM_PINE5
0
1
2
#define MID_RIGHT
#define MID_LEFT
#define RIGHT_FRONT
#define RIGHT_BACK
#define LEFT_FRONT
#define LEFT_BACK
1300
1700
1700
1300
1300
1700
void SetPWM( uint8_t pwmNum, uint16_t pulseWidthUSec ){
uint16_t pulseWidthTicks = pulseWidthUSec * 2; // Convert to ticks;
switch ( pwmNum ){
case PWM_PINE3: OCR3A = pulseWidthTicks; break;
case PWM_PINE4: OCR3B = pulseWidthTicks; break;
case PWM_PINE5: OCR3C = pulseWidthTicks; break;
}
} // SetPWM
What is a motion in robotics?
◦ Sequence of specific poses with durationㄴ
What motions the simple hexabot can take?
◦
◦
◦
◦
◦
Forward
Backward
Left turn
Right turn
???
Create a LED brightness control program, which
has a plus button and a minus button
◦ The plus button is for increasing brightness of LEDs
◦ The minus button is for decreasing brightness of LEDs
(bonus) make a simple hexabot control program
using 4 buttons
◦ Forward button, backward button, left turn button right
turn button