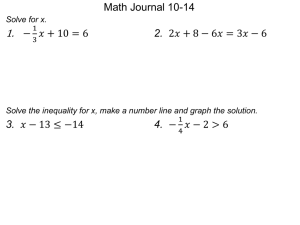
Here - Dani Rodrik`s weblog
advertisement

Distributive Politics and Economic Growth Alberto Alesina and Dani Rodrik (1994) Macroeconomic Theory Master in Economics 2010/11 Prof. José Tavares NOVA SBE Luís Fonseca – 425 Miguel Aguiar – 398 Distributive Politics and Economic Growth with Motivating Why is this issue important? What are the consequences of the initial wealth distributions? How does inequality affect the political process? How does inequality affect economic growth? Explain differences in growth between countries Ex: Asian and South American countries after World War II The Model Key features: Individuals differ in their endowments Growth is driven by expanding capital stock Long run growth is endogenous Growth Model Growth Model Growth Model Growth Model Growth Model Factors Capital Labor Perfect competition in factor markets Each factor is remunerated at its marginal productivity Factors Individuals 0 Pure Capitalist Worker Individuals MPL MPK - Tax Individuals MPL MPK -Tax Economic Growth Economic Growth What is the growth-maximizing tax rate then? We have to analyze what are the effects of the tax on capital on the growth rate! Ba-a-a-art, come here! Economic Growth Easy, Lisa! I’m here! Economic Growth With a 0% tax rate, there is no productive government spending and so, no production and no growth! Economic Growth When the government starts taxing capital, its spending on services raises the productivity of factors! Economic Growth But, there is a point at which we reach a maximum, because… Economic Growth … then, the tax becomes too high and after-tax return to capital decreases too much and disencourages capital accumulation, the main driver of growth! Economic Growth A very high tax rate can really harm economic growth. Economic Growth Economic Growth Very l-l-l-low! (Hic) High! Economic Growth Economic Growth Why does he want that? Well, Mr. Burns consumes exclusively out of his capital stock, so, his welfare is maximized when that capital stock grows at the maximum rate. Excellent!! Economic Growth Economic Growth Policy Choice What tax rate shall I set? Mr. Burns told me to set a low one… But everyone else told me to tax him more… Policy Choice My fellow citizens, thank you for electing me! I promise I will choose a tax rate that will maximize your welfare! For Mayor Quimby to follow on his promise, he needs to choose a tax-rate that is closest to the preferences of his voters. Policy Choice This implies that Mayor Quimby will not choose the tax rate that maximizes economic growth! Let us see why! Policy Choice Way to go, Homer! 0 Homer Simpson is the median voter! Inequality But what would happen in Springfield if we had different endowments? For example, what if we had more inequality? 0 Groundskeeper Willie is the new median voter! Inequality 0 Groundskeeper Willie is the new median voter! Inequality And what if we had a more equal Springfield? 0 Principal Skinner is the new median voter! Inequality He will prefer a lower tax rate than Mr. Simpson, leading to higher economic growth for Springfield than before! 0 Principal Skinner is the new median voter! Inequality We can now see how different initial factor endowments affect the political process and consequently, the growth rate of an economy! 0 Principal Skinner is the new median voter! Inequality Let us now start from a perfectly egalitarian society, where everyone has the same labor/capital share. Hey! That’s great! Homer would be as rich as Mr. Burns! 0 Conclusions So, the main conclusion of the model is: The more unequal is the distribution of income and wealth, the lower is the rate of growth of the economy. What can we do to have higher growth rates? It all depends on the capital endowment of the median voter! The more he has, the lower the tax, the higher the growth! Conclusions An interesting question is: can this majority voting rule lead to the maximum possible economic growth? No! Maximum growth is attained only if the median voter is equivalent to the pure capitalist, like Mr. Burns. But there are always workers with labor income which will prefer a tax rate higher than the growth-maximizing. Conclusions Alesina and Rodrik also stress that this model can be applied to democracies… …and also to dictatorships, because their decisions too are influenced by social demands and conflicts! Empirical Applications Alesina and Rodrik used land distribution and Gini index data Found significant negative relationship between these and subsequent growth Clarke (1993) has supported the robustness of these results With different inequality measures and specifications Democracies and non-democracies alike Persson and Tabellini (1991) argued that this inverse relationship does not hold for non-democracies Possible Extensions Allow for social mobility and stategic voting Effects of political pressure groups and elites Non-uniform endowments distributions