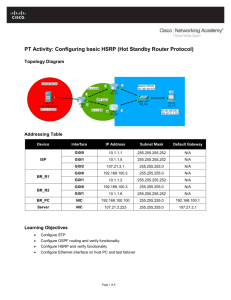
Configuring Layer 3
Redundancy with
HSRP
Implementing Layer 3 High Availability
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-1
Routing Issues: Using Proxy ARP
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-2
Routing Issues: Using Default Gateways
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-3
Router Redundancy
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-4
Router Redundancy Failover
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-5
HSRP Configuration
Standby group
Set of HSRP devices emulating a virtual router
Enabling HSRP on an interface automatically disables
ICMP redirects.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-6
Virtual Router MAC Address
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-7
Forwarding Through Active Router
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-8
Active and Standby Routers
Active router
Responds to ARP requests of
the default gateway with the
MAC address of the virtual router
Assumes the active forwarding of
packets for the virtual router
Sends hello messages
Knows the virtual router IP
address
Standby router
Listens for periodic hello
messages
Assumes the active forwarding of
packets if no messages heard
from active router
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-9
HSRP States
An HSRP router can be in one of
five states.
State
Definition
Initial
The state at the start. State after configuration change or when an
interface first comes up.
Listen
The router knows the virtual IP address. It listens for hello messages
from other routers.
Speak
The router sends periodic hello messages and actively participates in
the election of the active or standby router.
Standby
The router is a candidate to become the next active router and sends
periodic hello messages.
Active
The router currently forwards packets that are sent to the group virtual
MAC address. The router sends periodic hello messages.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-10
HSRP State Transition
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-11
HSRP Priority and Preemption
The device with the highest
priority in an HSRP group
becomes the active router.
The default priority is 100.
In the case of a tie, the router
with the highest configured IP
address will become active.
Preemption enables the
higher priority device to
become active.
switch(config)# interface vlan 10
switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
switch(config-if)# standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1
switch(config-if)# standby 10 priority 110
switch(config-if)# standby 10 preempt
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-12
HSRP and STP
Configured active
router should be the
same as STP root
bridge.
Blocked uplink caused
traffic to take less-thanoptimal path.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-13
HSRP Authentication
Configure authentication string (maximum of eight characters,
default cisco) for standby group.
switch(config)# interface vlan 10
switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
switch(config-if)# standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1
switch(config-if)# standby 10 priority 110
switch(config-if)# standby 10 preempt
switch(config-if)# standby 10 authentication xyz123
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-14
HSRP and Timers
When active HSRP
fails, timers can
determine how fast
standby should become
active.
Failover delay
configuration should
also take into account
IGP convergence delay.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-15
HSRP Timer Configuration
Configure hello time and hold time to millisecond values.
The hold time parameter value should be at least three times the
value of the hello time parameter.
Configure the preempt delay timer so that preemption occurs after
the switch has fully rebooted and has established full connectivity
to the network.
switch(config)# interface vlan 10
switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
switch(config-if)# standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1
switch(config-if)# standby 10 priority 110
switch(config-if)# standby 10 preempt
switch(config-if)# standby 10 timers msec 200 msec 750
switch(config-if)# standby 10 preempt delay minimum 300
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-16
HSRP Versions
HSRPv1 (default).
Group number from 0 to 255.
Virtual MAC address 0000.0C07.ACXX (XX = HSRP group).
Hello packets sent to multicast address 224.0.0.2.
HSRPv2 (Cisco IOS Release 12.2(46)SE and later).
Group number from 0 to 4095.
Virtual MAC address 0000.0C9F.FXXX (XXX = HSRP group).
Hello packets sent to multicast address 224.0.0.102.
HSRPv2 and HSRPv1 have different packet formats.
Configure same version on all devices of HSRP group.
switch(config-if)# standby 10 version 2
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-17
Displaying the Standby Status
switch# show standby brief
P indicates configured to preempt.
|
Interface
Grp Pri P State
Active
Standby
Virtual IP
Vl10
10
110 P Active local
10.1.10.3
10.1.10.1
switch# show standby
Vlan10 - Group 10
State is Active
1 state change, last state change 00:00:43
Virtual IP address is 10.1.10.1
Active virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a
Local virtual MAC address is 0000.0c07.ac0a (v1 default)
Hello time 3 sec, hold time 10 sec
Next hello sent in 0.016 secs
Preemption enabled
Active router is local
Standby router is 10.1.10.3, priority 90 (expires in 11.328 sec)
Priority 110 (configured 110)
Group name is "hsrp-Vl10-10" (default)
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-18
HSRP Interface Tracking
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-19
HSRP Interface Tracking
Configure the standby group.
Configure priority (default is 100).
Configure preempt on all devices within the HSRP group.
Configure the tracked interfaces and decrement (default
decrement is 10).
switch(config)# interface vlan 10
switch(config-if)# ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0
switch(config-if)# standby 10 ip 10.1.1.1
switch(config-if)# standby 10 priority 110
switch(config-if)# standby 10 preempt
switch(config-if)# standby 10 track fastethernet0/23 20
switch(config-if)# standby 10 track fastethernet0/24
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-20
Tracking Options
switch(config)# track 1 ?
interface Select an interface to track
ip
IP protocol
list
Group objects in a list
rtr
Response Time Reporter (RTR) entry
Standby command can track interface or object.
Tracked objects are defined with track object_number.
Track number interface can verify line protocol or IP routing
capability.
Track number ip route can verify network reachability.
Track number list can define complex conditions.
Track number rtr can verify parameters such as IP SLA.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-21
HSRP and IP SLA Tracking
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-22
Multiple HSRP Groups
To load-balance links between access and distribution, configure
the HSRP active router and the spanning-tree root for each VLAN
to be on the same multilayer switch.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-23
Multiple HSRP Group Configuration
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-24
Monitoring HSRP
SW1#show standby brief
P
|
Interface
Grp Pri P
Vl63
63
120 P
Vl64
64
90 P
indicates configured to preempt.
State
Active
Standby
Active local
10.1.63.2
Standby 10.1.64.1 local
Virtual IP
10.1.63.254
10.1.64.254
SW1#show standby neighbor vlan64
HSRP neighbors on Vlan64
10.1.64.1
Active groups: 64
No standby groups
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-25
Summary
A single default gateway or proxy ARP does not provide the
redundancy that is required in a campus network.
HSRP provides router redundancy to end devices.
HSRP is configured using the standby command for each
interface.
Preemption, timers, and interface tracking are options that can be
configured to optimize HSRP and reduce failover time.
Specific debug commands are used to view the HSRP state
changes.
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-26
© 2009 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
SWITCH v1.0—6-27