ppt
advertisement

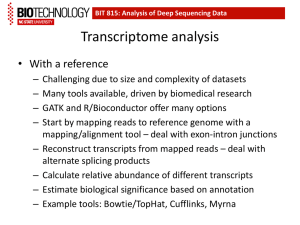
Transcriptome Assembly and Quantification from Ion Torrent RNA-Seq Data Alex Zelikovsky Department of Computer Science Georgia State University Joint work with Serghei Mangul, Sahar Al Seesi, Adrian Caciula, Dumitru Brinza, Ion Mandoiu Advances in Next Generation Sequencing Illumina HiSeq 2000 Up to 6 billion PE reads/run 35-100bp read length Roche/454 FLX Titanium 400-600 million reads/run 400bp avg. length http://www.economist.com/node/16349358 Ion Proton Sequencer SOLiD 4/5500 1.4-2.4 billion PE reads/run 35-50bp read length 2 RNA-Seq Make cDNA & shatter into fragments Sequence fragment ends Map reads A Gene Expression B C D Transcriptome Reconstruction A B A C D E E Isoform Expression C 3 Transcriptome Assembly • Given partial or incomplete information about something, use that information to make an informed guess about the missing or unknown data. 4 Transcriptome Assembly Types • Genome-independent reconstruction (de novo) – de Brujin k-mer graph • Genome-guided reconstruction (ab initio) – Spliced read mapping – Exon identification – Splice graph • Annotation-guided reconstruction – Use existing annotation (known transcripts) – Focus on discovering novel transcripts 5 Previous approaches • Genome-independent reconstruction – Trinity(2011), Velvet(2008), TransABySS(2008) • Genome-guided reconstruction – Scripture(2010) • Reports “all” transcripts – Cufflinks(2010), IsoLasso(2011), SLIDE(2012), CLIIQ(2012), TRIP(2012), Traph (2013) • Minimizes set of transcripts explaining reads • Annotation-guided reconstruction – RABT(2011), DRUT(2011) 6 Gene representation Tr1: e1 Tr2: e1 Tr3: Pseudoexons: e5 e3 e2 pse1 Spse1 e4 pse2 Epse1 Spse2 e5 pse3 Epse2 Spse3 pse4 Epse3 Spse4 e6 pse5 Epse4 Spse5 pse6 Epse5 Spse6 pse7 Epse6 Spse7 Epse7 • Pseudo-exons - regions of a gene between consecutive transcriptional or splicing events • Gene - set of non-overlapping pseudo-exons 7 pseudo-exons Splice Graph TSS TES Genome 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 8 MaLTA Maximum Likelihood Transcriptome Assembly • Map the RNA-Seq reads to genome • Construct Splice Graph G(V,E) Genome – V : exons – E: splicing events • Candidate transcripts – depth-first-search (DFS) • Select candidate transcripts – IsoEM – greedy algorithm 9 How to select? • Select the smallest set of candidate transcripts • covering all transcript variants Transcript : set of transcript variants alternative first exon alternative last exon alternative 5' splice junction exon skipping alternative 5' splice junction intron retention splice junction Sharmistha Pal, Ravi Gupta, Hyunsoo Kim, et al., Alternative transcription exceeds alternative splicing in generating the transcriptome 10 diversity of cerebellar development, Genome Res. 2011 21: 1260-1272 IsoEM: Isoform Expression Level Estimation • Expectation-Maximization algorithm • Unified probabilistic model incorporating – – – – – Single and/or paired reads Fragment length distribution Strand information Base quality scores Repeat and hexamer bias correction Read-isoform compatibility graph wr ,i wr ,i OaQa Fa a Fragment length distribution i A B j A C C Fa(i) Fa (j) Greedy algorithm 1. Sort transcripts by inferred IsoEM expression levels in decreasing order 2. Traverse transcripts – Select transcripts if it contains novel transcript variant – Continue traversing until all transcript variant are covered 14 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 15 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 16 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 17 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 18 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 19 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 20 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 21 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 22 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 23 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: 24 Greedy algorithm Transcripts sorted by expression levels Transcript Variants: STOP. All transcript variant are covered. 25 MaLTA results on GOG-350 dataset • 4.5M single Ion reads with average read length 121 bp, aligned using TopHat2 • Number of assembled transcripts – MaLTA : 15385 – Cufflinks : 17378 • Number of transcripts matching annotations – MaLTA : 4555(26%) – Cufflinks : 2031(13%) 26 Expression Estimation on Ion Torrent reads • Squared correlation – IsoEM / Cufflinks FPKMs vs qPCR values for 800 genes – 2 MAQC samples : Human Brain and Universal 0.8 R2 for IsoEM/Cufflinks Estimates vs qPCR 0.7 0.6 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0 IsoEM HBR Cufflinks HBR IsoEM UHR Cufflinks UHR Conclusions • Novel method for transcriptome assembly • Validated on Ion Torrent RNA-Seq Data • Comparing with Cufflinks: – similar number of assembled transcripts – 2x more previously annotated transcripts • Transcript quantification is useful for transcript assembly better quantification? 28 29