Chapter 5 Stratified Random Sampling
advertisement

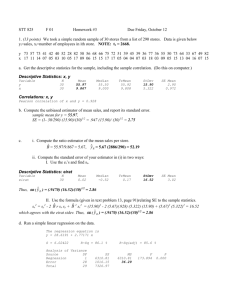
Chapter 5 Stratified Random Sampling Advantages of stratified random sampling How to select stratified random sample Estimating population mean and total Determining sample size, allocation Estimating population proportion; sample size and allocation Optimal rule for choosing strata Stratified Random Sampling The ultimate function of stratification is to organize the population into homogeneous subsets and to select a SRS of the appropriate size from each stratum. Stratified Random Sampling Often-used option – May produce smaller BOE than SRS of same size – Cost per observation may be reduced – Obtain estimates of population parameters for subgroups Useful when the population is heterogeneous and it is possible to establish strata which are reasonably homogeneous within each stratum Chapter 5 Stratified Random Sampling Improved Sampling Designs with Auxiliary Information Stratified Random Sampling Chapter 6 Ratio and Regression Estimators Stratified Random Sampling: Notation y i :sam ple m ean of data from stratum i, i 1, ,L n i :sam ple size for stratum i i : population m ean of stratum i i : population total of stratum i population total 1 2 L Stratified Random Sampling S R S w ithin each stratum , so: E ( yi ) i ˆi N i y i ; E (ˆi ) E ( N i y i ) N i E ( y i ) N i i i E stim ate population total by sum m ing estim ates of i ˆ ˆ1 ˆ2 N ˆ L y st Stratified Random Sampling: Estimate of Mean y st 1 N 1 N N 1 y1 N 2 y 2 N L yL L N i yi i 1 1 ˆ N 12Vˆ ( y1 ) N 22Vˆ ( y 2 ) V ( y st ) 2 N 1 2 N1 2 N 2 N L Vˆ ( y L ) 2 2 n 1 s1 n s 2 2 2 1 N 1 2 N 1 n1 N 2 n2 2 n s 2 L L N L 1 N L n L Stratified Random Sampling: Estimate of Mean , BOE Vˆ ( y st ) 1 N N 1 Vˆ ( y 1 ) N 2 Vˆ ( y 2 ) 2 2 1 2 2 N L Vˆ ( y L ) n1 s1 n2 s2 2 2 N1 1 N 2 1 2 N 1 n1 N 2 n2 N 2 2 nL sL 2 N L 1 N L nL 2 BOE 1.96 1 n1 s1 n2 s2 2 2 N1 1 N 2 1 2 N 1 n1 N 2 n2 N 2 2 nL sL 2 N L 1 N L nL 2 Stratified Random Sampling: Estimate of Population Total N y st N 1 y1 N 2 y 2 N L yL L N i yi i 1 2 Vˆ ( N y st ) N Vˆ ( y st ) 2 2 N 1 Vˆ ( y1 ) N 2 Vˆ ( y 2 ) 2 N1 2 N L Vˆ ( y L ) 2 2 n 1 s1 n s 2 2 2 1 N 1 2 N 1 n1 N 2 n2 2 n s 2 L L N L 1 N L n L Stratified Random Sampling: BOE for Mean and Total , t distribution When stratum sample sizes are small, can use t dist. L 2 2 ak sk k 1 S atterw aith e d f a L 2 sk k N k ( N k nk ) w h ere a k 2 nk nk 1 k 1 B O E fo r : N 1 1 t df 2 n 1 1 2 N N 1 2 s 1 n N 1 2 2 1 n N 2 2 2 s n 2 N 2 2 L 1 n N L L B O E fo r : N 1 2 t df n 1 1 N 1 2 s 1 n 1 N 2 2 1 n N 2 2 2 s n 2 2 N 2 L 1 n N L L 2 s n L L 2 s n L L Degrees of Freedom(worksheet cont.) S tratified R andom S am ple S um m ary: a k N (N k 1 k 155 , N 2 8 , n 12 3 k 2 62 , N a 1046.25 , a 1 df , n 20 , n 1 n N n ) k 2 3 93, 418.5 , a 1046.25 5.95 1046.25 5.95 2 19 21.09; t 21.09 2 2 3 627.75 2 418.5 15.25 627.75 9.36 418.5 15.25 2 2 2 2 627.75 9.36 2 7 2.08 (see E xcel w orksheet) 11 2 Compare BOE in Stratified Random Sample and SRS (worksheet cont.) S tratified R andom S am ple S um m ary: n 40, y 27.7; Vˆ ( y st ) 1.97. Strat. random sample has more precision If observations w ere from S R S : 2 40 11.31 s 11.31, Vˆ ( y ) 1 2.79 310 40 Approx. Sample Size to Estimate V ( y st ) B V ( y st ) 2 B 2 4 L et n i a i n , a i prop. of sam ple from stratum i 1 N a n s B N 1 N a n 4 2 L 2 2 i 2 i i i 1 i i L n 2 2 N i si ai i 1 w here D L N D 2 i 1 2 N i si B 2 4 Approx. Sample Size to Estimate B V ( N y st ) B V ( y st ) 2 2 4N 2 L et n i a i n , a i prop. of sam ple from stratum i 1 N a n s B N 1 2 N a n 4N 2 L 2 2 i 2 i i i 1 i i L n 2 2 N i si ai i 1 w here D L N D 2 i 1 2 N i si B 2 4N 2 Summary: Approx. Sample Size to Estimate , L N 2 i s 2 i ai i 1 n L N D 2 N i s 2 i i 1 D B 2 w hen estim ating 4 D B 2 4N 2 w hen estim ating Example: Sample Size to Estimate (worksheet cont.) L N n 2 i 2 si a i i 1 N D 2 N i 1 P rio r su rvey: 1 5, 2 1 5, 3 1 0 . E stim ate to w ith in 2 h rs w ith 9 5 % co n f. allo catio n p ro p o rtio n s are a1 a 2 a 3 1 3 . B 2 D B 4 3 N 2 i s 2 i ai 1; N D 3 1 0 9 6,1 0 0 2 2 2 155 ( 25 ) 1 3 2 62 ( 225 ) 1 3 2 2 93 (100 ) 1 3 6, 9 9 1, 2 7 5 i 1 3 N i s i 1 5 5(2 5) 6 2 (2 2 5) 9 3(1 0 0 ) 2 7 ,1 2 5 2 i 1 n 6, 9 9 1, 2 7 5 9 6,1 0 0 2 7 ,1 2 5 so n1 n 2 n 3 1 3 5 6 .7 5 7 (5 7 ) 1 9 D L i s 2 i B 2 4 Example: Sample Size to Estimate (worksheet cont.) L N 2 i 2 si a i i 1 n N D 2 N i 1 P rio r su rvey: 1 5, 2 1 5, 3 1 0 . E stim ate to w ith in 4 0 0 h rs w ith 9 5 % co n f. allo catio n p ro p o rtio n s are a1 a 2 a 3 1 3 . D B 2 4N 2 400 2 4N 2 160 , 00 2 3 N 2 i s 2 i ai 4N 155 ( 25 ) 1 3 2 40 , 000 N 2 2 62 ( 225 ) 1 3 ; N D 4 0, 0 0 0 2 2 93 (10 0 ) 1 3 6, 9 9 1, 2 7 5 i 1 3 N i s i 1 5 5(2 5) 6 2 (2 2 5) 9 3(1 0 0 ) 2 7 ,1 2 5 2 i 1 n 6, 9 9 1, 2 7 5 4 0, 0 0 0 2 7 ,1 2 5 so n1 n 2 n 3 1 3 1 0 4 .2 1 0 5 (1 0 5) 3 5 D L i s 2 i B 2 4N 2 5.5 Allocation of the Sample Objective: obtain estimators with small variance at lowest cost. Allocation affected by 3 factors: 1. Total number of elements in each stratum 2. Variability in each stratum 3. Cost per observation in each stratum 5.5 Allocation of the Sample: Proportional Allocation If don’t have variability and cost information for the strata, can use proportional allocation. S am ple size for stratum h : nh n Nh N In general this is not the optimum choice for the stratum sample sizes. 5.5 O ptim al (m in V ( y st ) allocation Vˆ ( y st ) of the sam ple: sam e cost/obs L 1 N 2 i 1 2 n s 2 N i 1 i i N i ni in each stratum m in Vˆ ( y st ), subject to g ( n1 , n 2 , , n L ) 0, , n L ) n1 n 2 nL n n1 , n 2 , , nL w here g ( n1 , n 2 , Directly proportional to stratum size and stratum variability U se L agrange m ultipliers: Vˆ ( y st ) ni g ni 0, i 1, , L ni n N i si N k 1 T his m ethod of choosing n1 , n 2 , called N eym an allocation , i 1, L , nL k sk ,L 5.5 O ptim al (m in V ( y st ) allocation L of the sam ple: sam e cost/obs n in each stratum ni n , i 1, L N D k ,L sk k 1 substitute ni n for a i above gives N i si i 1 L n 2 L N D 2 i 1 2 N i si ai L i 1 N i si N 2 i 1 2 F rom previous slide 2 N i si 2 N i si 5 .5 O p tim al (m in V ( y st ) allo catio n o f th e sa m p le: sam e co st/o b s in each stratu m Worksheet 11 5.5 O ptim al (m in V ( y st ) allocation Vˆ ( y st ) of the sam ple for fixed cost C : c i = cost/ob s L 1 2 N i 1 in stratum i. m in Vˆ ( y st ), subject to g ( n1 , n 2 , n1 , n 2 , , nL w here g ( n1 , n 2 , Vˆ ( y st ) ni g ni , n L ) 0, , n L ) c1 n1 c 2 n 2 U se L agrange m ultipliers: 0, i 1, 2 n s 2 N i 1 i i N i ni cL nL C Directly proportional to stratum size and stratum variability , L ni n N i si ci , i 1, L N k sk ,L ck k 1 Inversely proportional to stratum cost/obs 5.5 O ptim al (m in V ( y st ) allocation L of the sam ple: sam e cost/obs n in each stratum 2 L N D i 1 ni n N i si ci , i 1, L N k sk ,L ck k 1 substitute ni n n for a i above gives L N k sk k 1 L c k N i si i 1 L N D 2 i 1 2 N i si ci ai i 1 2 From previous slide 2 N i si 2 N i si 5 .5 O p tim al (m in V ( y st ) allo catio n o f th e sa m p le: c i = co st/o b s in each stratu m Worksheet 12