Transcription and Translation
advertisement

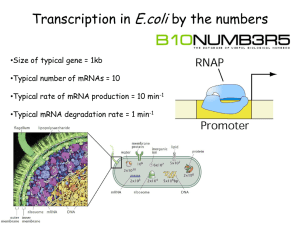
Transcription and Translation GENE EXPRESSION - How the genes are expressed is a function of the protein produced. DNA (gene) Ribosome tRNA & rRNA Protein m RNA Trait (expression) There are two processes that make this happen… Transcription • mRNA strand is built from the code on the DNA strand (gene) Translation • mRNA strand is used at the ribosome to help join amino acids to form a protein. TRANSCRIPTION Let’s watch a video of transcription… Requirements for Transcription a gene segment on the DNA many free floating RNA nucleotides the enzyme RNA polymerase PREDICT: What do you think the RNA polymerase will do? located Free floating RNA nucleotides bond with complimentary DNA nucleotides to form a strand of mRNA 4 Weak hydrogen bonds break between the 2 DNA strands 3 DNA double helix unwinds at the area of the DNA where the gene is 2 1 Steps in transcription When the mRNA is completely formed, it breaks away from the DNA. The DNA strands reconnect and the mRNA is free to travel to the cytoplasm These stages are catalyzed by the enzyme RNA polymerase Each triplet code on a DNA molecule is transcribed into a triplet codon on the mRNA molecule. • If the DNA codes for a polypeptide is T-A-C—C-C-G—T-A-G—C-T-T—A-C-T • What would the codons on the complimentary strand of mRNA codons look like? A-U-G – G-G-C – A-U-C – G-A-A – U-G-A • DNA codes: T-A-C—C-A-T—C-C-C—A-A-A—A-C-T • mRNA codons: A-U-G – G-U-A – G-G-G – U-U-U – U-G-A Think…think…..think…. • What does each letter in the code or codon stand for represent? That’s right….a nucleotide • What do the particular codes and codons represent? Amino Acids….good job! • Because each base triplet on the mRNA stands for an amino acid, each mRNA molecule must contain how many times the number of nucleotides as the number of amino acids making up the protein product. 3X….Wow! You guys are on a roll! Engage your BRAIN….The intersection of science and math • An mRNA strand with 66 nucleotides codes for a polypeptide how many amino acids in length? 22…you all are Math whizzes • A protein 300 amino acid units in length was synthesized from an mRNA strand how many nucleotides in length? 900…Woo Hoo! • A DNA strand 700 nucleotides in length will be transcribed into an mRNA strand how many nucleotides in length. 700…Ah! This one is tricky! How do we read mRNA codons? • • • • There are 4 different bases in DNA (A, C, G, T) which can combine in different triplets to form 64 possible triplet codes (43). When these codes are transcribed into mRNA, there are 64 triplet codons which can be formed. Only 20 amino acids are used so sometimes more than one codon represents an amino acid. We can use the chart to the right to determine the exact sequence of amino acids that will make up a protein. • How many different mRNA codons are there on the chart? 43 = 4 x 4 x 4 = 64 different codons (using A, G, C and U in triplets) • How many different amino acids are there? Only 20 • Which amino acids only have ONE triplet code assigned to them? Methionine and Trytophan • With the exception of Methionine and Tryptophan, more than one nucleotide triplet codes for each amino acid. • Give an example of an amino acid which has more than one codon. valine, alanine, isoleucine, threonine, and many more • What do you notice about the codons that code for the same amino acid? They are very similar and usually only the last nitrogen base is different. Special Codons Start Codon • AUG-codes for the amino acid methionine. It signals the ribosome that it is the beginning of the mRNA sequence. Stop Codons • UAA, UAG, UGA- Don’t code for an amino acid!!!! Signal the ribosome that it is the end of the mRNA sequence and triggers the release of the mRNA from the ribosome. • What is the DNA code for the mRNA start codon, methionine? TAC • What are the DNA codes for the stop codons UAA, UAG and UGA? ATT, ATC, ACT • After transcription has taken place, the mRNA moves out of the nucleus to link with a ribosome in the cytoplasm. Translation will take place here….. TRANSLATION Let’s Watch a video on Translation… Requirements for Translation Steps in Translation mRNA joins with the ribosome (in cytoplasm or near the Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum the mRNA slides through the ribosome to expose the next codon the next tRNA with amino acid joins the mRNA tRNA (with an amino acid attached) joins the mRNA codon to ANTI-codon (The anticodon on the tRNA is complimentary to the codon on the mRNA.) the first tRNA is released from the mRNA amino acids stay bonded to each other Sequence is repeated Repeat steps 4-8 until a stop codon is reached a second tRNA with attached amino acid joins the mRNA a peptide bond forms between the first two amino acids mRNA and protein is released from the ribosome The Final Products of Protein Synthesis Let’s Watch a video to sum up Transcription and Translation…