File
advertisement

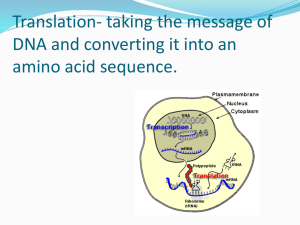
Materials: worksheet *Turn in Central Dogma HW and Gizmo to Front Tray by 2 min. Catalyst (5 min): 1. What are the 3 processes included in the Central Dogma? 2. What is happening in each process? Elite Eight Trait Check-Up 1. Respect the Threshold 1. Everyone on time? 2. Silent for First Five? 2. Be Prepared (2 min) 1. Seated 2. Have materials 3. Working on catalyst Announcements • Need a binder by: –Thursday: Periods 1, 2, 4, 6 –Friday: Periods 5, 7 • Know your Gizmo username and password for Thursday/Friday • Quiz over the Central Dogma on Thursday/Friday Objectives • I can explain what is happening in transcription and translation. • I can explain the function of the 3 types of RNA. • I can read a codon chart and create a protein for a certain DNA strand. THINK: • What do you use your phone for? • How can deaf people call to set up a doctors appointment? (If you had to invent a product/service for this to be possible, what would you need?) DNA proteins mRNA transcription translation The Central Dogma of Biology!!!! Dogma: a set of principles Transcription Where is DNA? The nucleus What is the end product? Proteins What organelle makes proteins? Ribosomes (outside of the nucleus) Label the DNA and where the proteins are made in the cell DNA Ribosomes: make proteins Why do we need RNA? DNA needs to get ‘the message’ out of the nucleus It needs a messenger Think/Pair/Share: • Where does the message need to go? •What is the ‘message’? mRNA (messenger RNA): carries information from DNA to the ribosomes (in the cytoplasm or on the Rough ER) Transcription: making mRNA from DNA DNA mRNA Transcription happens in the nucleus Steps during Transcription • DNA unzips, exposing the strand that will code for the message • Free-floating nucleotides match up with the appropriate exposed base creating a strand of mRNA – what protein do you think brings the mRNA nucleotides to DNA? • mRNA detaches and leaves the nucleus • DNA zips back up DNA: G C G T A T C G mRNA: C G C A U A G C Partner work (5 min): Transcribe DNA Strands into mRNA strands Answer one per pair on a half sheet of paper. 1. ATCGAA 2. GGCATA 3. CTAGCG 4.What process did this represent? 5. What is being made and where? Translation Translation Translation is the process of using mRNA to build a protein. mRNA protein Translation happens in the ribosome Translation Translation needs 3 types of RNA: • mRNA (messenger RNA) • rRNA (ribosomal RNA): makes up the ribosome • tRNA (transfer RNA): carries amino acids (the monomer of proteins) to the ribosome so they can make a protein But HOW does mRNA code for proteins? PROTEINS are long strings of Amino acids ____________ The order of the amino acids determines the shape of the protein mRNA uses a code to tell the ribosome what proteins to make Codon: 3 letters of mRNA together code for a specific amino acid (there are 22!) Think: • • • • • • 3 “letters” = 1 codon How many codons would be in a strand of.... 6? 2 codons (2 amino acids) 18? codons!(6 amino acids) 6 codons 450????? 150 Proteins are often HUNDREDS of amino acids long. You can start to see why we have such long strands of DNA. The MESSAGE is LONG! tRNA reads the codon and brings the specific amino acid to the ribosome Anticodon: The sequence of 3 bases on tRNA that is complementary to a codon on mRNA Codon Summary • Triples of mRNA that code for a specific amino acid Translation Steps: • 1) Make sure you have the transcribed strand. Remember: it MUST be RNA! (Translation is RNAprotein, NOT DNA protein) • 2) Divide up strand into codons (sets of 3) • 3) Use the Codon Chart to identify the amino acid coded for by the codon (*This chart will be GIVEN, you DON’T need to memorize it!) Start and Stop Codons • Just like journalists use quotation marks (“__”) to indicate the beginning and end of a quote.... • The ribosome needs a start and stop codon to know when to start and stop ‘reading’ the mRNA Codon charts show the amino acid that an mRNA codon calls for Codon Practice • Strand of DNA: A T G G T C A T C • Strand of RNA: U A C C A G U A G • Codons U A C Tyrosine C A G Glutamine U A G STOP AGG TCT ACA ACT mRNA codon tRNA anticodon amino acid UCC AGG ser AGA UCU arg UGU ACA cys UGA ACU stop DNA: mRNA: TTACGTATC AAUGCAUAG Codons: AAU GCA UAG Amino acids:asp ala stop Panther Pass 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. What is happening in transcription? What is happening in translation? Why do we need mRNA? What is the function of tRNA? DNA: A C G T C G G A T mRNA: amino acid sequence: