Analysing Training Sessions
advertisement

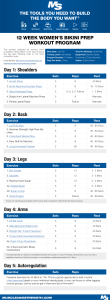
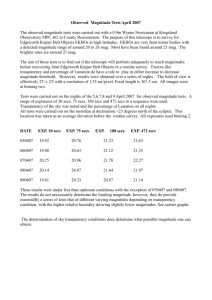
Heart rate Resting Heart Rate Working Heart Rate Maximum Heart Rate Target Heart Rate/Target zone Recovery Rate ◦ Pg 78-79 Event Predicted time if we Current World Record could work at the same (to nearest second) pace throughout the event 100m 10 secs 10 secs 200m 19 secs 19 secs 400m 40 secs 43 secs 800m 1 min 20 secs 1 min 41 secs 1500m 2 mins 30 secs 3 mins 26 secs 3000m 5 mins 7 mins 21 secs Aerobic Activity ◦ Working with oxygen ◦ If exercise is not too fast and is steady, the heart can supply all the oxygen muscles need Anaerobic Activity ◦ Working without oxygen ◦ If exercise is done in short, fast bursts, the heart cannot supply the muscles with the blood and oxygen they need to release energy for exercise. ◦ Muscles work without oxygen and repay the oxygen debt once the exercise has been completed. Glucose (from Carbohydrates) is broken down in our tissues in the presence of Oxygen to release energy. Glucose Oxygen Carbon Dioxide Water Energy If the level of exercise is too intense, oxygen cannot be supplied quickly enough to release energy aerobically. Glucose Energy Lactic Acid During recovery from anaerobic exercise the performer will still be breathing heavily even if they are not working hard. This is so that they can pay back the oxygen debt that they have developed. ‘The amount of oxygen consumed during recovery, above that which would normally have been used at rest. It results from a shortfall in availability of oxygen during exercise.’ 200 180 Heart Rate (bpm) 160 140 120 100 Session 1 80 Session 2 60 40 20 0 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 Time (mins) 16 18 20 180 Upper threshold 160 TARGET ZONE Heart Rate (bpm) 140 120 Lower threshold 100 80 60 40 20 0 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 Time (mins) 7 8 9 10 11 12 Heart rate Resting Heart Rate Working Heart Rate Maximum Heart Rate Target Heart Rate/Target zone Recovery Rate Aerobic Anaerobic