Nose and paranasal sinuses
advertisement
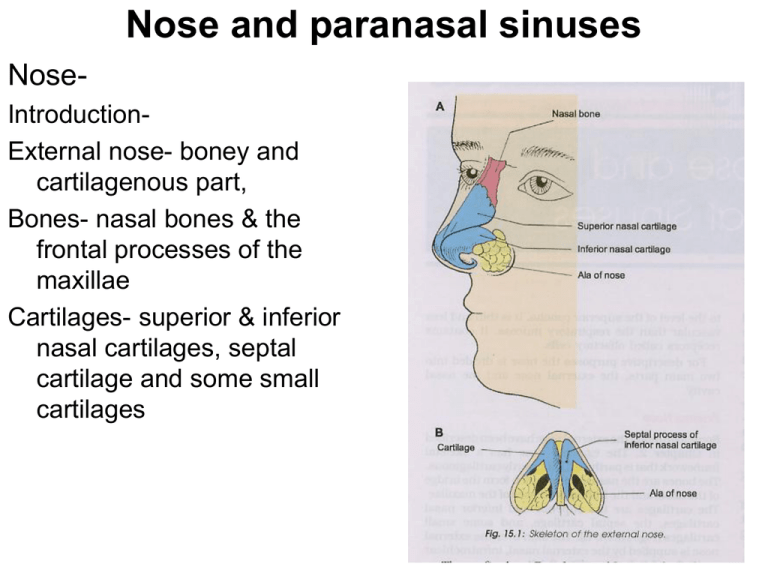
Nose and paranasal sinuses NoseIntroductionExternal nose- boney and cartilagenous part, Bones- nasal bones & the frontal processes of the maxillae Cartilages- superior & inferior nasal cartilages, septal cartilage and some small cartilages Nose and paranasal sinuses Nasal cavity• Extent-external nares to the posterior nasal apertures. • Rt and lt halves by nasal septum • Each half- roof, floor, medial & lateral walls • Measurement-5cm height, 5-7cm length & 1.5cm wider near the floor and near the roof is 1-2mm Nose and paranasal sinuses Nasal septum• Osseocartilaginous partition betw the 2halves of the nasal cavity • Mucous membrane & forms the medial wall of both the nasal cavities • Boney part- vomer & perpendicular plate of the ethmoid. Nasal spine of the frontal bone, the rostrum of the sphenoid & the nasal crests of nasal, palatine and maxillary bones • Cartilaginous part- septal cartilage & the septal processes of the inferior nasal cartilages • Cuticular part- fibrofatty tissue covered by the skin • Borders- sup, inf, ant and post & rt and lt surfaces Nose and paranasal sinuses Arterial supply• Anterosuperior- ant ethmoidal artery • Posteroinferior-sphenopalatine artery • Anteroinferior- superior labial branch of facial artery • Posterosuperior- post ethmoidal artery • Kiesselbach’s plexus- common site of bleeding from the nose or epistaxis and know as “Little’s Area” Venous drainage• From little’s area there are venous plexus which drains into the facial vein, posteriorly through the sphenopalatine vein to the pteryoid venous plexus Nose and paranasal sinuses Nerve supplyGeneral sensory• Anterosuperior-internal nasal branch of the anterior ethmoidal nerve • Posteroinferior-nasopalatine branch of the pterygopalatine ganglion • Posterosuperiormedial,posterior, superior nasal branches of the pterygopalatine ganglion Special sensory or olfactory nerves are confined to the upper part or olfactory area Nose and paranasal sinuses Lymphatic drainage• Anterior halfsubmandibular nodes • Posterior halfretropharyngeal & deep cervical nodes Nose and paranasal sinuses Clinical anatomy• Little’s area on the septum is the common site of bleeding from the nose or epistaxis • Pathological deviation of the nasal septum is often responsible for the repeated attacks of common cold, allergic rhinitis, sinusitis. Nose and paranasal sinuses Lateral wall of nose• Irregular and having presence of 3 shelflike bone projectionsconchae • Lateral wall separates the nose: orbit above, with the ethmoidal air sinuses & maxillary sinus below, from lacrimal groove and nasolacrimal canal in front Nose and paranasal sinuses Lateral wall3parts • Vestibule- small depression area in the anterior part • Middle part-atrium of the middle meatus • Posterior partconchae Nose and paranasal sinuses Skeleton of the lateral wall Boney- nasal, frontal process of the maxilla, labyrinth of the ethmoid with superior and middle conchae, inferior nasal conchae, perpendicular plate of the palatine bone together with its orbit and sphenoidal processes and medial pteyroid plate Cartilaginous- superior nasal cartilage, inferior nasal cartilage and 3-4 small cartilages of ala Cuticular lower part- fibrofatty tissue covered with skin Nose and paranasal sinuses Conchae and meatuses • inferior concha is independent bone • Middle concha- projection from the medial surface of the ethmoidal labyrinth • Superior concha- projection from the medial surface of the ethmoidal labyrinth • Inferior meatus- nasolacrimal duct • Middle meatus- ethmoidal bulla is a rounded elevation produced by the underlying middle ethmoidal sinus; hiatus semilunaris is a deep semicircular sulcus below the bulla; infundulum is a short passage at the anterior end of hiatus; opening of the frontal sinus, maxillary air sinus and middle ethmoidal air sinus • Superior meatus- opening of the posterior ethmoidal air sinuses • Sphenoethmoidal recess- opening of the sphenoidal air sinus Nose and paranasal sinuses Nose and paranasal sinuses Arterial supply of the lateral wall • Anterosuperior quadrant- ant ethmoidal artery assisted by the post ethmoidal and facial arteries • Anteroinferior quadrant- branches from the facial artery and greater palatine arteries • Posterosuperior quadrantsphenopalatine artery • Posteroinferior quadrant- branches from the greater palatine artery Venous drainageVeins forms plexus which drains anteriorly into the facial vein, posteriorly into the pharyngeal plexus of veins and from the middle part to the pterygoid plexus of the vein Nose and paranasal sinuses Nerve supply1. a) General sensory nerves Anterosuperior quadrantant ethmoidal nerve branch of ophthalamic nerve b) Anteroinferior quadrant-ant superior alveolar nerve branch of maxillary nerve c) Posterosuperior quadrantpost superior lateral nasal branches from the pterygopalatine ganglion suspended by the maxillary nerve d) Posteroinferior quadrantant or greater palatine branch from the pterygopalatine ganglion suspended by the maxillary nerve 2. Special sensory or olfactory nerve- Nose and paranasal sinuses Lymphatic drainageAnterior half- submandibular nodes Posterior half- retropharygeal and upper deep cervical nodes Nose and paranasal sinuses Clinical anatomy1. Common cold or rhinitis 2. Paranasal air sinuses may get infected from the nose. Maxillary sinusitis is the commonest of such infections 3. Hypertrophy of the mucosa over the inferior nasal concha is the common feature of allergic, rhinitis, which is characterized by sneezing, nasal blockage and excessive watery discharge from the nose Nose and paranasal sinuses 1. Frontal sinus 2. Maxillary sinus 3. Sphenoidal sinus 4. Ethmoidal sinus Nose and paranasal sinuses