shoulder - Radiology
advertisement

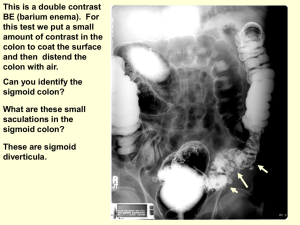
Abdomen case #1 Patient came to the ER with new onset of abdominal pain. Diagnosis: Free air under hemidiaphragm bilaterally Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Upright abdomen CLINICAL INDICATION: Abdominal pain HEART REPORT The patient has free air under both sides of the diaphragm. The possibility of a GI tract perforation has to be considered most likely. FREE AIR L1 VERTEBRA COLON GAS CONCLUSION: Pneumoperitoneum – likely GI perforation Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. •Air under hemidiaphragm bilaterally could be caused by many conditions such as perforated peptic ulcer, perforated diverticulum, or abdominal trauma. •This condition may require surgery to treat the condition that caused the free air to be under the diaphragm. • The longer treatment (generally surgery) is delayed the more serious the patient’s health status may become with peritonitis and sepsis. Abdominal case #2 Abdomen pain increasing over past 4days. History of previous abdominal surgery 6yrs ago. Diagnosis: Small bowel obstruction Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Abdominal X-ray -Supine DISTENDED SMALL BOWEL CLINICAL INDICATION: Increasing abdominal pain over past 4 days—prior surgery ILIAC CREST REPORT: There is distended small bowel filling of the mid abdomen with no significant colon gas. This is likely due to post of adhesions from prior surgery. LUMBAR VERTEBRAE LT. PUBIC RAMUS CONCLUSION: Small bowel obstruction • GI suction tube inserted nasally may be used to clear the obstruction; patient put on restricted NPO diet •Surgical intervention to lyse t post-operative adhesion •Electrolytes, fluids, and nutrients should be administered intravenously to replace fluids & compensate for malabsorption Abdomen case #3 Complaints of decreasing caliber stool and straining. Diagnosis: Large bowel obstruction Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Supine abdomen radiograph TRANSVERSE COLON CLINICAL INDICATION: Complaints of decreasing caliber stool and straining DISTENDED/ OBSTRUCTED RIGHT COLON REPORT: The right colon, Transverse colon and Lt. colon are distended. The femoral head, symphysis pubis and inferior pubic ramus are unremarkable. FEMORAL HEAD SYMPHYSIS PUBIS CONCLUSION: Distal colon obstruction possibly due to malignancy. Colonoscopy is suggested. Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. Management of Large Bowel Obstruction: •IV fluids and medicine to manage symptoms •If obstruction persists, colonoscopy and surgical may be necessary. Antibiotics and IV fluids given to avoid infection. •Other nonsurgical treatments such as enemas may be used to clear large bowel obstruction due to fecal impaction. Abdomen case #4 Patient with positive hem occult and incomplete colonoscopy Diagnosis: Colon cancer Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Your Interpretation here. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Barium Enema DESTINED DESCENDING COLON CLINICAL INDICATION: Positive hem occult and incomplete colonoscopy. 12TH RIB LUMBAR VERTEBRAE COLON STRICTURE REPORT: Distended descending colon with short segment stricture indicated by the narrowing of contrast in the column. Distally there is a normal sized sigmoid colon and rectum. CONCLUSION: Partial obstruction of the Lt. colon most typical for colon cancer. Recommend colonoscopy for evaluation. HIP JOINT Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. Suggestions for management: • Surgical resection of the cancerous portion of the colon •Biopsy of sentinel lymph nodes to determine if metastasis has occurred. • Chemotherapy for possible tumor reduction and treatment of residual microscopic tumor. •Annual colonoscopies to monitor for recurrent of new colon malignancy developing. Abdomen case # 5 Abdomen pain and weight loss Diagnosis: Metastatic cancer of the liver. Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal Your Interpretation here. structures. RADIOLOGY EXAM: CT scan 2 LOW DENSITY MASSES IN THE LIVER STOMACH CLINICAL INDICATION: Abdomen pain and weight loss. REPORT: Abnormal low density masses present in the Rt. & Lt. lobes of the liver are seen on this IV contrast enhanced CT scan. CONCLUSION: Multiple hepatic masses most typical for metastatic disease probably from a GI source. Colon evaluation may be helpful. AORTA LT. KIDNEY Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. -A Liver biopsy should be taken to get histologic diagnosis -treatment will vary depending on extent and nature of cancer - A portion of the liver may be surgically excised in patients who have a single isolated metastatic lesion in addition to surgical resection of the primary lesion. Abdomen case #6 Recumbent film of the abdomen for patient with acute abdomen pain. Diagnosis: Gall stones Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: AP abdomen x-ray CLINICAL INDICATION: Acute abdominal pain GALL STONES COLON GAS ILIAC CREST REPORT: Multiple radiopaque densities in the patient right upper quadrant. These are rounded and are less than 1cm in diameter. Most typical for calcified gallstones. CONCLUSION: Cholelithiasis FEMORAL HEAD Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. • A gallstone is a concretion in the gallbladder, cystic duct or bile duct composed chiefly of cholesterol crystals. • Gallstones are more common in women and their incidence increases with age. •For gallstones to cause clinical symptoms, they must obtain a size sufficient to produce mechanical injury to the gallbladder or obstruction of the biliary tract. Abdomen case #7 Ultrasound for right upper quadrant pain. Diagnosis: Gall stones Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. Your Interpretation here. Gallstone RADIOLOGY EXAM: • Ultrasound of liver and gallbladder Shadow CLINICAL INDICATION: •Acute pain in the RUQ LIVER GALL BLADDER REPORT: •Liver ultrasound shows echogenic mass in gallbladder typical for cholelithiasis •Prominent acoustic shadow displayed deep to the calculi CONCLUSION: •Cholelithiasis KIDNEY Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. •Some risk factors for gallstones include obesity, advanced age (over forty), being female, having a family history, diabetes, and using cholesterol lowering drugs •Symptoms include: intense pain to right upper quadrant and referred pain to shoulder and/or between should blades •Gallstones are caused by too much bilirubin or cholesterol in bile •Gallstones can block the hepatic, common bile, or cystic ducts Sources: http://www.mayoclinic.com/health/gallstone s/DS00165/DSECTION=causes http://digestive.niddk.nih.gov/ddiseases/pu bs/gallstones/ Abdomen case #8 Contrast enhanced CT scan performed for abdominal mass palpated at physical exam. Diagnosis: AAA Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Your Interpretation here. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Contrast enhanced CT scan of the abdomen. AORTIC ANEURYSM BLOOD CLOT REPORT: The CT indicates an enlarged abdominal aorta with low density clot at the margin of the aneurysm. RT. PSOAS MUSCLE LUMBAR VERTEBRAL BODY CLINICAL INDICATION: An abdominal mass was detected during physical exam palpations. A CT was ordered to determine the origin. LT. FACET JOINT CONCLUSION: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. Risk factors include smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol, male gender, advanced age (60+), emphysema, genetic factors, and obesity. Surgery is only recommended to repair the unruptured aneurysm if it is larger than 5 cm and if the risk of surgery is less than the risk of the aneurysm rupturing. The two surgical options are a traditional (open) repair and an endovascular stent grafting. Abdomen case # 9 Arteriogram of abdominal aorta performed due to abnormal renal nuclear medicine study. Diagnosis: Stenosis of the Lt. Renal Artery Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Arteriogram of the Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal abdomen. structures. CLINICAL INDICATION: Abnormal nuclear medicine renal scan. ABDOMINAL AORTA RIGHT RENAL ARTERY CATHETER LEFT RENAL ARTERY. STENOSIS REPORT: The image shows the aorta and Rt. & Lt. renal arteries. The aorta demonstrates normal filling with the contrast material. The Rt. renal artery also shows normal filling and configuration. The Left renal artery shows a high grade stenosis at it’s junction with the aorta. CONCLUSION: Left Renal Artery Stenosis Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. Patients with stenosis of a renal artery can exhibit the following symptoms: • High blood pressure • Mild to moderate renal failure • Heart failure Abdomen case #10 Horse stepped on patient Diagnosis: Fracture of the Rt. Kidney Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: CT of Abdomen @ the level of the kidney Liver CLINICAL INDICATION: Trauma- Horse stepped on the patient. REPORT: CT through the kidney shows a normal left kidney with a low density laceration extending though the mid portion of the right kidney,. Fluid in peritoneum is likely blood or unopacified urine. CONCLUSION: Fractured Rt. Kidney Rt. Kidney IVC Erector Spinae mm. . Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. The patient will need evaluation by trauma surgery with fluid replacement and likely surgery to repair or remove the damaged kidney. The CT scan has evolved into a critical trauma imaging tool as the entire body can be evaluated rapidly to aid in management decisions. Abdomen case #11 Abdominal distention and shifting dullness on exam. CT scan with oral contrast and abdomen x-ray after CT scan. Diagnosis: ASCITES Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. L1 VERTEBRAE FLUID & SHIFT RADIOLOGY EXAM: CT scan CLINICAL INDICATION: Abdominal distension and shifting dullness CONTRAST IN COLON REPORT: Fluid filled areas indicated by red arrows causing shift in abdominal viscera most notably in ascending colon shifted AIR IN SMALL BOWEL medially. CONCLUSION: Radiological exam and clinical indications (shifting dullness, abdominal distension) confirm classical signs of ascites (fluid in peritoneal space). FLUID Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. 1.) By definition, ascites is excess fluid in the peritoneal cavity. 2.) Causes of ascites include portal hypertension due to liver disease, CHF, portal vein thrombosis. 3.) Treatment of ascites includes decrease sodium in diet, decrease alcohol consumption, diuretics, and antibiotics if infection develops. Abdomen case #12 Ultrasound exam performed at FAST exam for patient in a MVC. Diagnosis: Hemoperitoneum Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. RADIOLOGY EXAM: Ultrasound FAST exam for MVC patient. LIVER FLUID IN MORISON’S POUCH KIDNEY DIAPHRAGM CLINICAL INDICATION: Abdominal pain, recent trauma REPORT: Liver and right kidney are seen with anechoic fluid separating the structures and extending into Morrison’s pouch. CONCLUSION: Fluid in Morrison’s Pouch (Hemoperitoneum) Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process 50 words or less. Evaluation of volume status- IV fluid replacement as necessary. Emergent laparotomy •Surgical ligation or repair of bleeding vessel. Interventional Radiology can embolize bleeding vessel for hemostasis Abdomen case #13 Left upper quadrant palpable mass and fullness. Diagnosis: Splenomegaly Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. Your Interpretation here. RADIOLOGY EXAM: AP Abdomen CLINICAL INDICATION: Lt upper quadrant palpable mass & fullness LIVER BOWEL GAS ENLARGED SPLEEN REPORT: A markedly enlarged spleen is prominent in the patient’s upper left quadrant. Inage shows a normal amount of diffuse gas in the distal small bowel as well as the colon. CONCLUSION: Splenomegaly Hematology evaluation is indicated as initial step. BLADDER Three bullet points about pathology identified OR Management of the identified process •Splenic enlargement can be caused by infections, abnormal blood cell counts, cancer, and lymphatic problems. • Symptoms may include: • Inability to eat a large meal due to discomfort and fullness. • Pain in upper left quadrant of abdomen • Fatigue, weight loss, infections, easy bleeding. Abdomen case #14 Pt. with jaundice with CT scan and ERCP Diagnosis: Stone in the Common bile duct Add red arrows & captions that confirm the diagnosis and /or other abnormalities. Use blue arrows to indicate 3 normal structures. LIVER RADIOLOGY EXAM: DILATED BILE DUCTS AORTA CT (computed tomography) and ERCP (endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography) CLINICAL INDICATION: Patient with jaundice and CT scan and ERCP. REPORT: Low density dilated bile ducts are seen on the CT scan. ERCP indicated gallstone that obstructs bilirubin flow to the intestines through the common bile duct, causing jaundice. RT. KIDNEY ` ` ` ` ` BLOCKAGE ` IN THE ` COMMON ` BILE DUCT ` ` ` CONCLUSION: Intraluminal calculus causing Biliary dilation. Jaundice in patient was due to blockage causing dilation of the duct. Choledocholithiasis. Management of the identified process Treatment of jaundice in this patient requires the removal of the gallstone. Laparoscopic surgery to remove the bile duct obstruction could be performed. The patient could also be given medications that would dissolve the gallstone. This may be useful in patients who can not tolerate surgery.