CH-5 Lecture - Horizon Medical Institute
advertisement

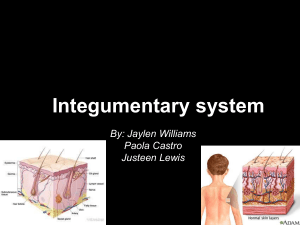
Lecture Notes Classroom Activity to Accompany Medical Terminology Systems, Sixth Edition Barbara A. Gylys ∙ Mary Ellen Wedding 5 Integumentary System 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Structure • Epidermis • Dermis • Subcutaneous tissue • Accessory organs • Glands • Hair • Nails 2 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Function • Covers and shields outer body surfaces • Sweat and oil glands produce secretions • Contains an intricate network of sensory receptors • Regulates body temperature, pain, and pressure • Melanocytes produced in basal layer gives color to the skin 3 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Structure and Function Exercise Q: What does the term integument mean? A: Refers to the skin. Q: What are the accessory structures of the skin? A: Hair, nails, and glands (sweat and oil) Q: What are the functions of the subcutaneous layer of tissue? A: Binds the dermis to underlying structures; stores fats, insulates and cushions the body, and regulates temperature. Q: In the basal layer, what specialized cells protect the skin from damaging effects of the sun? A: Melanocytes, which produce melanin. Q: Which accessory organs produce oil? A: Sebaceous glands. 4 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs and Symptoms • Malignancy of basal layer is commonly caused by repeated overexposure to the sun. 5 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Basal Cell Carcinoma Signs and Symptoms (continued) • Locally invasive tumor, but rarely metastasizes. • Tumors grow slowly, but commonly ulcerate. • Tumors usually occur on the face. • Predominant in fair-skinned men older than 60 years. 6 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Basal Cell Carcinoma Treatment • Size, shape, location, and invasiveness of the carcinoma determine type of treatment. • Curettage and electrodessication. • Cryotherapy and laser therapy. • Chemotherapeutic drugs. • Surgical excision (used in 90% of the cases). • Irradiation or chemosurgery. 7 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise Q: Mr. T is advised that the basal cell carcinoma on his face will not spread but will remain local. Nevertheless, it will destroy underlying and adjacent tissue. The term for spread of CA from one part of the body to another site is called _____________. A: metastasis. Q: A 70-year-old male is diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma due to overexposure to the sun. He is advised that the most common site of this skin cancer is the _____________. A: face. Q: After closely examining a growth on Ann’s arm, she is informed that it is noncancerous. The dermatologist charts the noncancerous growth as (benign, cancerous, malignant). A: benign Q: Mr. J is diagnosed with basal cell carcinoma and asks the nurse to explain this type of cancer. A: She explains it is a malignancy of the basal layer of skin, commonly caused by repeated overexposure to the sun. 8 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Abscess Signs and Symptoms • Localized collection of pus at infection site (characteristically a staphylococcal infection). • A furuncle, or boil, is an abscess in a hair follicle and adjacent subcutaneous tissue. 9 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Abscess Signs and Symptoms (continued) • A carbuncle is a cluster of furuncles in the subcutaneous tissue. • Affected portion of skin may be extremely tender, painful, and swollen. • Abscess may enlarge, soften, and open, discharging pus and necrotic material. • Erythema and edema may persist at the site for days or weeks. • Mild fever may accompany this condition. 10 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Abscess Treatment • Cleaning infected area thoroughly with soap and water. • Applying hot, wet compresses to promote vasodilation and drainage from lesions. • Administering topical antibiotics. • Incision and drainage (I&D) may be necessary after lesion has matured. 11 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise Q: Mrs. K presents with redness and edema on the neck. The term to describe reddening of the skin is ____________. A: erythema, erythamatous Q: Upon diagnosis of a furuncle, the nurse explains that this is an infection caused by a/an (bacterium, injury, virus). A: bacterium Q: The physician charts a cluster of furuncles in the subcutaneous tissue as a ________________. A: carbuncle Q: Sue is diagnosed with an abscess on her knee. She asks the nurse to explain this condition. A: She explains it is a localized collection of pus at the infection site, characteristically caused by the bacterium known as staphylococcus. 12 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Psoriasis Signs and Symptoms • Circumscribed red patches covered by thick, dry, silvery, adherent scales. 13 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Psoriasis Signs and Symptoms (continued) • Excessive development of the basal layer • of the skin. • Affected areas typically appear dry, cracked, and encrusted. • Buildup of skin is composed of living and dead tissue. • Common sites include scalp, knees, elbows, umbilicus, and genitalia. 14 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Psoriasis Treatment • Depends on the type of psoriasis, extent of the disease, and the effect of the disease on the patient. • No cure; treatment is only palliative. • Topical application of various medications, such as coal tar, vitamin D, corticosteroid drugs, and wet dressings. 15 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Psoriasis Treatment (continued) • Photochemotherapy called PUVA with exposure to ultraviolet-A (UVA) light to slow hyperkeratosis. • Ultraviolet-B (UVB) light therapy or natural sunlight to retard cell production. • Excrimer laser, a more powerful form of UVB light therapy, is directed to the plaques to control scaling and inflammation. 16 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise Q: Joan K is diagnosed with psoriasis. The physician explains that the most common sites of psoriasis are the ________________. A: scalp, knees, elbows, umbilicus, and genitalia Q: Mr. M presents for treatment of psoriasis with ultraviolet (UV) light therapy. The doctor explains that UV therapy retards cell production and slows horny growths on the skin. Overgrowth of the horny layer of the epidermis is a condition called (keratoid, keratolysis, hyperkeratosis). A: hyperkeratosis Q: For chronic psoriasis, a powerful form of UVB light therapy directed to the plaques is effective in controlling scaling and inflammation. This type of laser is called _____________ ___________. A: excrimer laser 17 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Medical Vocabulary • acne • allograft • alopecia • autograft • contusion • debridement • dermatomycosis • diaphoresis 18 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Medical Vocabulary (continued) • gangrene • hematoma • hirsutism • impetigo • macule • petechia • pilonidal 19 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Medical Vocabulary (continued) • pyoderma • scabies • sebaceous • steatoma • subcutaneous • vulgaris • xenograft 20 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Diagnostic Procedures • Biopsy • Skin test • Intradermal allergy test reactions. 21 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Word Building Exercise Q: Inflammation of skin: A: dermatitis Q: Instrument to cut skin: A: dermatome, dermatotome Q: Tumor (consisting) of fat: A: adipoma, lipoma, steatoma Q: Excision or removal of a nail: A: onychectomy Q: Skin that is blue (in color): A: cyanoderma 22 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Medical and Surgical Procedures • Debridement • I&D • Mohs surgery • Skin graft • allograft • autograft • synthetic • xenograft 23 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise Q: Mr. Y presents to have foreign material removed from his wound and avoid the development of an infection. The therapeutic procedure is charted as (allograft, cryotherapy, debridement). A: debridement Q: Joan F presents to the clinic to remove a basal cell carcinoma from her face. The doctor freezes and destroys the lesion with nitrogen. This therapeutic procedure is known as (cryotherapy, debridement, UV). A: cryotherapy. Q: Patient X is informed that pus will be removed from her abscess by incising and draining it. The procedure is abbreviated as ______. A: I&D 24 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise (continued) Q: The surgeon informs Lydia T that layer by layer her tumor will be excised until it is removed. What type of surgery is this called? A: Mohs surgery Q: Mr X, a burn patient, is given a transplant of healthy tissue from his son. What type of transplant is this known as? A: allograft Q: John, a fireman who suffers from chemical burns, is having healthy tissue transplanted from a pig. What type of transplant is this called? A: xenograft 25 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Pharmacology • Antibiotics • Antifungals • Antipruritics • Corticosteroids 26 5 INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Clinically Related Exercise Q: To treat a skin infection, the physician prescribes a/an (antifungal, antibiotic, corticosteroid). A: antibiotic Q: Mary broke out with a poison ivy rash after a camping trip. A topical drug is prescribed to decrease inflammation and itching. This drug is called a/an (antifungal, antibiotic, corticosteroid). A: corticosteroid Q: Mrs. K is diagnosed with ringworm and is treated with a/an (antifungal, antibiotic, corticosteroid). A: antifungal 27