The limbic system
The limbic system
Neuronal circuitry controls of emotional behavior and motivational drives
Composed of subcortical and cortical components
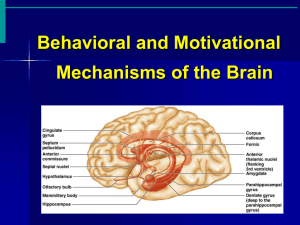
Limbic System
Figure 12.18
limbic
Subcortical group
Hypothalamus ,septum,paraolfactory area,epithalamus,ant.thalamic nuclei,hippocampus,amygdala,basal gangeli
Limbic cortex
Orbitofrontal coretx,subcallosal gyrous cingulate gyrus and parahippocamp gyrous
Limbic System: Emotion and
Cognition
The limbic system interacts with the prefrontal lobes, therefore:
One can react emotionally to conscious understandings
One is consciously aware of emotion in one’s life
Hippocampal structures – convert new information into long-term memories
The hypothalamus not only influences how you feel, it influences how you interpret the consequences of those feelings.
limbic
Visceral
Afferents
Hypothalamic Role in Emotion
Hypothalamic
Nuclei
Hormonal
Output
Nucleus of the
Solitary Tract
Autonomic
Output
Brain Stem
Nuclei
Autonomic
Preganglionic
Nuclei
Target
Organs
Hypothalamus
Pituitary
Releasing Factors
Autonomic
Nervous System
Adenohypophysis
(Anterior Pituitary)
Neurohypophysis
(Posterior Pituitary)
Sympathetic
Parasympathetic
“I feel fear!”
stria terminalis
Amygdala
Cortex, septum medial forebrain bundle
Hypothalamus mtt
Anterior Nucleus dorsal long.
Brainstem fasciculus
Amygdala ventral route ant.
parvo magno
(SO, PV) medial forebrain bundle post.
Brainstem spinal cord
Pituitary
Hypothalamus,Major
Hypothalamus is the most important output sorce
It communicate with brain stem by medial forebrain bundle ,bidirectionaly between forebrain and brain stem
Hypothalamus cont.
Controls:
1-vegetative and endocrine functions
2-behavior and motivation
vegetative and endocrine functions
Cardiovascular regulation involves
1-Post. And lateral hypothalamus area, increase
BP and HR.
2-preoptic area ,decrease BP and HR
*1and 2 mediated by cardiovascular centre in the pontile and medullary part of reticular formation
Body temperature regulation
Preoptic area
Thermo-regulation
(body temperature)
Involves autonomic nervous, endocrine, and skeletomotor systems
Body temperature detectors
Peripheral: skin, spinal cord, viscera
Central: anterior hypothalamus
Body temperature effectors
Heat retention or generation: posterior hypothalamus
Heat dissipation: anterior hypothalamus
Thermo-regulation
(body temperature)
Heat dissipating mechanisms
Dilation of blood vessels in the skin
Inhibition of shivering
Heat conserving mechanisms
Vasoconstriction of blood vessels in the skin
Shivering
Increased secretion of thyroxin
Response to Cold Response to Heat
Methods of thermo-regulation by the body
Regulation of body water intake
Thirst centre,lateral hypothalamus
Electrolyte concentrationmaking desire to drink
Supraopticx:urinary excrition due to ADH
Thirst
Function of serum osmolality and blood volume
Osmotic receptors in the hypothalamus
Volume receptors in the right atrium of the heart and great veins
Vasopressin release from hypothalamus
Increases water reabsorption from the kidney
Inhibited by ethanol
Circadian Rhythm
Oscillations during the course of the day
Corticosteriods
Feeding and drinking behavior
Growth hormone secretion
Lesions of the suprachiasmatic nuclei of the hypothalamus disrupts these oscillations
Control of Feeding
Feeding
Complex interaction of many systems
Regulation of energy metabolism by the
Ventromedial and Lateral nuclei of the hypothalamus
Physical Lesions produce hyperphagia and obesity or reduced attention to food.
Amygdala may also be involved indirectly
Lesions produce hyperphagia-like symptoms
Ventromedial hypothalamic lesions also cause increased insulin secretion Obesity.
Feedback Mechanisms Controlling
Feeding
Feedback from gut hormones
e.g. Cholecystokinin
Released from small intestine in response to feeding
Inhibits or suppresses feeding
Uterine contraction and milk ejection
Oxytocin stimulation by PARAVENTRICULAR
ز غم فلتخم يحآون اب ن آ طابترآ و لآدگيم آ هتسه
كيبميل متسيس يبصع تاطابترآ
لاوگنيس جنكش يلصآ تاطابترآ
تاعلاطآ شزآدرپ ياهريسم
Hippocampus circuit
Ent. cortex From perforant To dentate gyrous mossy fiber cA3 schaffer collaterals cA1 to subiculum to ento cortex