Nebs No More After 24: Improving Use of Appropriate Respiratory
advertisement

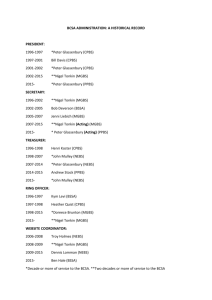
Nebs No More After 24: Improving Use of Appropriate Respiratory Services UCSF DIVISION OF HOSPITAL MEDICINE Supported by Caring Wisely, a project of the UCSF Center for Healthcare Value – Delivery Systems Initiative Christopher Moriates MD, Maria Novelero MA MPA, Matthew Cascino MD, Katie Quinn MPH, Theodore Omachi MD MBA, Sumant Ranji MD, Raman Khanna MD, Michelle Mourad MD BACKGROUND PILOT STUDY RESULTS: Nebulizer Utilization The delivery of a nebulized bronchodilator therapy (nebs) to hospitalized patients is a resource-intensive treatment involving direct care by a Respiratory Therapist (RT). 8.00 Administering unnecessary nebs is a missed opportunity to educate patients on the proper use of MDIs. Phase 2: Aug – Dec Phase 3: May-Jul •Removed neb treatments from the “admit order set” •Launched educational program, including prepared facilitator guides for attending physicians • Introduce CPOE intervention to link neb orders with automatic MDI transitions •Enlisted RTs and nurses to provide MDI teaching to inpatients Metered Dose Inhalers (MDIs) have been shown to be equally 1,2,3 effective as nebs when used correctly. A majority of patients misuse their prescribed MDI, but all are able to achieve mastery with teaching.4 Phase 1: Jun – Aug • •Created promotional campaign including posters, flyers, and pens • Expand project medical center-wide •Provided targeted feedback to physicians 7.00 1235 6.00 CONCLUSIONS A multifaceted intervention has been successful in simultaneously: •Decreasing neb treatments by approximately 50% •Enhancing MDI patient education 1400 •Improving evidence-based resident physician knowledge 1200 1113 1000 5.00 1017 800 4.00 600 At our 600-bed academic medical center, we spent over $1 million in direct costs for administration of nebs to nonintensive care unit patients on the Medicine Service during FY2012, averaging approximately 5 nebs for every admission to the high-acuity medicine ward. 3.00 To decrease neb usage in hospitalized patients on a highacuity medicine ward by at least 15%. To provide inpatient education on proper MDI selfadministration. To improve resident physician knowledge regarding the use of appropriate respiratory therapies. Nebs No More After 24! Help us improve transitions from nebulizers to MDIs and provide patient education about proper MDI use. Reducing utilization of these unnecessary treatments may provide an ideal target for improving healthcare value (quality / cost). 680 505 2.00 449 400 496 References: 1.00 200 0.00 0 May-12 Jun-12 Jul-12 Aug-12 Neb administrations per month GOALS •Saving direct costs for the medical center Sep-12 Oct-12 Nebs administrations per admission Pre- and post-intervention survey used to assess changes to resident physician knowledge and attitudes: Awareness that neb treatments are more expensive than MDIs: (p=0.11) Pre-Test Post-Test 82% 94% Misassumption that neb treatments are more efficacious than MDIs: (p<0.01) 26% WHAT CAN YOU DO? Use MDIs at admission unless there is a clinical indication for nebulizer therapy Transition your patients from nebs to MDIs after 24 hours, if appropriate, and write an order for RT to provide MDI teaching Help us spread the word: MDIs are as effective as nebulizer treatments! 3% Agreement with the statement that “patients receive adequate inpatient MDI teaching”: (p<0.01) Pre-Test Post-Test 2. Dolovich MB, et al. Chest. 2005;127(1):335–371. 4. Press VG, et al. JGIM. 2011;26(6):635–642. Nov-12 PILOT STUDY RESULTS: Knowledge and Attitudes Pre-Test Post-Test 1. Turner MO, et al. Arch Intern Med. 1997;157(15):1736–1744. 3. Mandelberg A, et al. Chest. 1997;112(6):1501–1505. 0% 16% MDIs provide high value, high quality patient care! We can teach and train our patients on correct MDI use while in the hospital!