Mediastinal Tumors and Cysts
advertisement

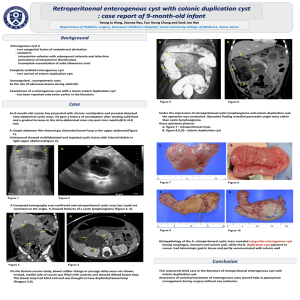
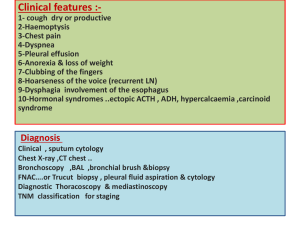
Mediastinal Tumors and Cysts Sung Chul Hwang, M.D. Dept. of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine Ajou University School of Medicine Introduction • • • • Silent in early phase Mainly cause pressure symptoms Incidentally discovered by routine x-rays Specific disease entities according to anatomical, and embryologic origin • 50% malignant in children where as 25% in adults • Metastatic tumor is the most common tumor Symptoms and Signs • • • • • • • Pain Cough Hemoptysis SVC syndrome Hoarseness Dyspnea Horner’s syndrome • • • • • • Dysphagia Pleural effusion Stridor Myathenia Gravis Phrenic nerve palsy Chylothorax Diagnosis • • • • • • Chest PA & Lateral Bucky film Chest CT Fluoroscopy Bronchoscopy Esophagogram • • • • • • NAB Isotope Scanning Angiography Thoracotomy VATS Medistinoscopy Common Diseases of the Mediastinum Thymoma • Anterior and Superior mediastinum • Most common (20%)of mediastinal tumor in adults but rarely seen in children • 2/3 is malignant • Equal frequency in males and females • 30 – 50 yrs • Various Classification : Lymphocytic, Epithelial, Spindle Cell • 50% are asymptomatic • Associated diseases : MG (35%), PRCA, DiGeroge SD, Carcinoid, Eaton-Lambert, agammaglobulinemia, myocarditis, thyrotoxicosis, etc Thymoma (Staging) • Stage I : contained within an intact capsule • Stage II: extension through the capsule to surrounding fat, pleura, pericardium • Stage III : Intrathoracic metastasis • Stage IV: Extrathoracic Metastasis Thymoma(Treatment) • Stage I : Surgical resection Recurrence 2-12% • Stage II & III : Surgery + Radiotherapy • Stage IV : Multimodality Induction chemotherapy, surgery + post op Radiotherapy • 5-year Survival 12 – 54 %, not affected by the presence of Myasthenia Gravis Thymoma Thymoma Ca++ mass Thymus Lymphoma • Metastatic is most common • 5-10% is mediastinal primary • Second moost common Anterior Mediastinal Mass in Adults • Malignant > Hodgkin’s • Dx: Mediastinoscopy, thoracotomy • NAB : Usually not confirmatory Hodgkin’s Lymphoma “mediastinal widening” Germ Cell Tumors • Anterior Mediastinal location • Mainly in late teens 15 %of Ant. Med. Tumors in Adults, 24 % in children • 1/5 is Malignant • Cystic Teratoma(Dermoid Cyst) vs. Solid tumor (Teratoma) • Solid tumor : 1/3 malignant • Radiosensitive • Teratoma, Malignant teratoma, Seminoma(dysgerminomas) Teratoma Teratoma Teratoma Teratoma Substernal Thyroid Tissues • Develops from cervical goiter or intrathoracic remnants • Can be diagnosed without biopsy by Radioactive iodine scan • No treatment unless symptomatic, usually pressure symptoms Rtrosternal Goiter Neurogenic Tumors • • • • Posterior mediastinal location 1/5 of mediastinal tumor Originate in neural crest Ganglioheuroma : most common in the textbook • Neurilemmoma – most common in Korea : “Dumb bell Tumor”, neural sheath origin Poosterior Mediastinal Tumor ( Neurillemmoma) ) “Dumb-bell” Tumor Neurilemmoma(Schwannoma) Para-ganglioma Mesenchymal Tumors • Lipoma, Fibroma, Mesothelioma • Superior or Anterior mediastinal location • Diagnosis with CT scan • May cause Hypoglycemia Mediastinitis • Acute : endoscopy complication, Boerhaave’s SD, operation, esophageal rupture, median sternotomy • Chronic : Tbc, histoplasmosis, silicosis, fibrosing mediastinitis Fibrosing Mediastinitis • 20- 40 years • Cough, Dyspnea, or Hemoptysis • Most common cause of Benign SVC syndrome • Almost always remote Histoplasmosis • Plain X-rays may be normal or only minimal changes • Partially calcified Mass on CT is diagnostic Fibrosing Mediastinitis F/29 with SVC Syndrome by Histoplasmosis Fibrosing Mediastinitis F/29 with SVC Syndrome by Histoplasmosis Pneumomediastinum • Spontaneous : mainly in young male adults • Hamman sign • Present along the Left sternal border • Substernal pain, cough, Dyspnea, Dysphagia Pneumomediastinum Benign Cysts • • • • • Most Common in Middle mediastinum 20% of mediastinal masses Less common in Korea Usually asymptomatic Bronchogenic cyst(32%), pericardial cyst(35%), enteric cyst(12%), thymic cyst, and thoracic duct cyst Pericardial Cyst • Thin-walled, mesothelial cell lining • most common in Right C-P angle • Simple cysts are almost always asymptomatic • Rare cardiac impingement Pericardial Cyst (1) Pericardial Cyst (2) Bronchogenic Cysts • • • • 30 - 60% of all mediastinal cysts Lined by ciliated respiratory epithelium May contain cartilages or mucous Communicate with tracheobronchial trees • May become infected • Wheezing, dyspnea, recurrent pulmonary infections Bronchogenic Cyst Bronchogenic Cyst Aortic Aneurysm Thymolipoma Paratracheal Lymphadenopathy Paratracheal Lymphadenopathy with Tracheal Compression Paratracheal Lymphadenopathy Paratracheal Malignant Lymphadenopathy