Klinefelter Syndrome
advertisement

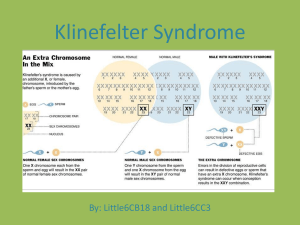
Tall Stature with Arrested Puberty M. Hashemipour Professor of Pediatric Endocrinology Isfahan University of Medical Sciences Case 1 15.5 year-old boy • Referred for gynaecomastia. • Tall stature, does not want to grow taller. What do you ask him? Case 1 o o o o Tall since early childhood, but more excessively at 12 years Pubic hair started at age 12 sense of smell School performance Forgetful, Poor academic performance Family history The only child. Mother: one miscarriage, healthy, height 145 cm Father: type 2 diabetes, height 163 cm What's important in Physical examination? 145 163 What's important in Physical examination? Auxology Height 179.1 cm; Arm span 186cm Weight 87.0 kg BMI 27.2 voice did not change Gynaecomastia noted at the age of 12 years old Pubertal exam Pubertal Staging Pubertal exam Testes 4/4 mls Pubic hair TS 4 Eunuchoid body habitus Gynaecomastia Abdominal striae BP 12/7 what's Eunuchoid body habitués Arm span _ Height The arm span is the distance between the tips of the middle fingers when the arms are raised to a horizontal position . Arm span - Height 1 – 7 yr 8 – 12 yr > 12 yr : Boys Girls 17 _3 0 +1 +4 Upper to lower segment The upper segment to lower segment ratio Birth : 1.7 3 years: 1.33 5 years : 1.17 10 years : 1.0 Upper to lower segment pre-puberty During ratio puberty Adult men Adult woman ≥1 ≤1 o.92 0.95 Eunuchoid proportions Lower segment 2-5cm >upper segment Arm span – Height> + 5 cm What's your investigation Bone age Bone age: 14 years at chronological age 15 years 6 months Investigations LH: 35.6 mIU/ml (prepubertal <1.0) FSH 51.8 mIU/ml (prepubertal <1.0) Testosterone 4.5 nmol/L (pubertal 8.4-28.7) FBS, lipid profile and liver enzymes: normal Chromosomal Study Chromosomal study 47 XXY Father: 46 XY Mother: 46 XX what is the most likely diagnosis? Diagnosis Klinefelter syndrome with Gynaecomastia Obesity Treatment Testosterone 100mg 4-weekly, and to achieve 250mg 4-weekly by 6 months. Obesity: Weight reduction: healthy diet, behavioural changes, exercise Gynaecomastia Monitor for regression after starting testosterone and weight reduction May need surgery if fails to regress Discussions Klinefelter Syndrome (1942) Prevalence 1 in 500-1000 males Increased incidence with advanced maternal age Classical KS: 47 XXY (80-90%) Variants: 46 XY/47 XXY mosaicism 48 XXXY; 48 XXYY Phenotypic males with 46 XX, Y to X translocation Klinefelter Syndrome Mutation causes: Hyalinization and fibrosis of seminiferous tubules and aggregation of Leydig cells Azoospermia Variable testosterone deficiency Elevated gonadotropin Klinefelter Syndrome Clinical features: diagnosis rarely made before puberty Height: above average, disproportionately long legs Small penile size Low IQ learning disabilities Features of Klinefelter’s syndrome Taller than average height Reduced libido Reduced facial and body hair Gynaecomastia Small testes Fatigue Depression Osteoporosis Fat accumulation (abdomen, hips) Poor erections Infertility Handelsman DJ, Zajac JD. Med J Aust 2004; 180: 529–35. Klinefelter Syndrome At risk of: Low bone mineral density Type 2 DM Varicose veins, venous thrombosis, pulmonary embolism Early tooth decay Klinefelter Syndrome At risk of Infertility Breast carcinoma Extra-gonadal germ cell mediastinal Increased incidence of autoimmune disease: SLE, RA and Sjogren synd. Klinefelter Syndrome Treatment: Androgen replacement Surgery for severe gynaecomastia.