Serotonin Syndrome Case Debrief
advertisement

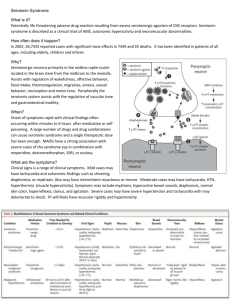
Serotonin Syndrome Case Debrief Case Debriefing • How do you think that the case went overall? • What was done well by the team leader? by the participants? • How did you come to a concrete diagnosis? • What factors played a role in the patient’s disposition? • What could have been done better? Serotonin Syndrome • First described in 1959 in TB patients. • Named in 1982 to describe the symptoms that occur when >2 drugs that increase serotonin concentrations are given. Serotonin Syndrome • Pathophysiology – Hyperserotonergic state caused by excessive stimulation of the serotonin 5HT1A receptors – Different types of serotonin receptors are found throughout the organ systems in the body. Serotonin Syndrome • Drugs that increase serotonin – Precursor – L-tryptophan – Inhibit serotonin metabolism – MAOIs – Increase serotonin release – amphetamines, lithium, MDMA – Inhibit serotonin reuptake – cocaine, dextromephoraphan, meperidine, SSRIs, TCAs, trazadone, venlafaxine – Serotonin receptor agonists – buspirone, LSD – Dopamine agonists – l-dopa Serotonin Syndrome • Signs and symptoms vary by patient (1-2 in each category) – Cognitive-Behavioral – Neuromuscular – Autonomic Serotonin Syndrome • Cognitive-Behavioral Signs and Symptoms – – – – – – – – – – Confusion/disorientation Agitation/irritability Unresponsiveness Anxiety Insomnia Lethargy Seizures Hypomania Hallucinations dizziness Serotonin Syndrome • Neuromuscular signs and symptoms – Myoclonus – Hyperreflexia – Muscle rigidity – Tremor – Ataxia – Shivering/chills – Nystagmus – Babinski’s sign bilaterally Serotonin Syndrome • Autonomic signs and symptoms – – – – – – – – – – – – Hyperthermia Diaphoresis Sinus tachycardia Hypertension Tachypnea Dilated pupils Non-reactive pupils Flushed skin Hypotension Diarrhea Abdominal cramps salivation Serotonin syndrome • Clinically – Vital signs abnormally high – Temperature, Pulse, Respiratory Rate, Blood Pressure – Symptoms as previously discussed • Treatment – Supportive with aggressive cooling measures – Benzodiazepines for seizures, rigidity, agitation – Cyproheptadine for severe cases (PO form only) • Precautions – Cardiovascular collapse – Seizures Serotonin Syndrome • Differential diagnosis – Serotonin syndrome – Neuroleptic malignant syndrome – Sepsis – Heat stroke – Anticholinergic toxidrome – Thyroid storm References • Tintinelli, et al. Emergency Medicine: A Comprehensive Guide. 6th Edition. • http://uuhsc.utah.edu/poison/healthpros/ut ox/vol4_no4.pdf • Emedicine.com