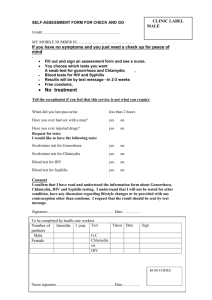
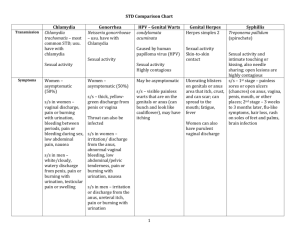
Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Chlamydia, Gonorrhea

Sexually Transmitted Diseases:
Chlamydia, Gonorrhea,
Trichomoniasis, Syphilis, HIV
Dr. Nicholas Viyuoh, MD
Board Certified OB/GYN
Lock Haven Hospital-Haven Health Care for Women
Presentation contains graphic pictures of diseases
Chlamydia
What is it?
A vaginal infection of the bacteria
Chlamydia trachomatis
Normal Cervix
Image from the Practitioner’s
Handbook for the Management of
STDs
Mucopurulet cervix with inflammation, discharge, and ectopy (abnormal cells) due to infection with Chlamydia
Image from The Practitioner’s Handbook for the
Management of STDs
Chlamydia
How is it transmitted?
Oral, anal, vaginally, and during childbirth
Chlamydia may be cultured from the throats of those who have had oral exposure from an infected individual
Symptoms — usually present within 2 weeks of exposure
Female: Vaginal discharge, burning with urination, painful intercourse, bleeding between menses
Male: Penile discharge, burning with urination
Chlamydial infection within the lymphatic system of an infected male www.mc3.edu/sa/hpnc/nurstd/std.htm
Chlamydia
Rates of Chlamydia by
Age
• Note: almost all cases of
Chlamydia are college-aged
• MOST FREQUENTLY
REPORTED BACTERIAL
STD!
Clinton County Rates
(2004) from the PA dept of Health
• 61 reported cases in
2004 in Clinton County
• 21,385 reported in PA in 2004, exclusive of
Philadelphia
• Rate increasing
8.84%/year
From the Center of Disease Control
Chlamydia
The bacteria that causes Chlamydia:
Chlamydia trachomatis microbewiki.kenyon.edu/index.php/Chlamydia
Complications:
Females: PID, infertility
Males: epididymitis
Prevention:
Abstinence
Limit sexual partners
Condoms
Treatment:
Antibiotics
Doxycycline,
Azithromycin,
Erythromycin
Gonorrhea
What is it?
STD cause by bacteria
Neisseria gonorrhoeae
Very common STD
Signs/Symptoms — usually present within 10 days of exposure
Males: Burning with urination, yellow/green/white discharge from penis, swollen or tender testicles
Females: often asymptomatic, painful urination, increased discharge
Penile discharge in individual infected with Gonorrhea www.mc3.edu/sa/hpnc/nurstd/std.htm
Gonorrhea
Cervical discharge in female infected with
Gonorrhea http://medinfo.ufl.edu/year2/mmid/bms53
00/images/b2.jpg
Complications
Females: PID, infertility
Males: epididymitis
Treatment: Antibiotics, although we are now seeing more resistance to antibiotics
Prevention: abstinence, limit number, condoms
Trichomoniasis
What is it?
STD caused by protozoan parasite
Trichomonas vaginalis
Signs/Symptoms
Females: frothy yellowgreen discharge with a strong odor, pain with intercourse and urination, vaginal itching
Males: irritation in penis, discharge
“Strawberry Cervix” from T. vaginalis www.fpnotebook.com/ID211.htm
Trichomoniasis
T. vaginalis, protozoa that causes Trichomoniasis isolated from culture http://www.tulane.edu/~wiser/protozoology/not es/intes.html
Complications
More susceptibility to other STDs and HIV
Prevention
Abstinence
Limit Sexual Partners
Condoms
Treatment
Vaginal or oral medication: Flagyl
Syphilis
What is it?
Bacterial STD caused by Treponema pallidum
Transmission
Have to have a sore to transmit, but sores may be hidden
Transmitted vaginally, anally, orally www.wales.nhs.uk
Syphilis
pathmicro.med.sc.edu
Signs/Symptoms
May be asymptomatic for years
Primary stage: painless ulcer
(chancre) lasting 3-6 weeks
Secondary stage: rash (not itchy), on palms of hands and soles of feet, swollen gland, weight loss, headaches.
Tertiary stage: internal organ
(brain, heart, eye, nerves) damage,
End stage: paralysis, numbness, blindness, dementia, death
From the Practitioner’s Handbook of
Management of STDs
Syphilis
Diagnosis:
One of the 2 STDs that is diagnosed with a blood test (other is HIV)
The test is called an
RPR.
Treatment:
Antibiotics in the primary or secondary stages
Prevention:
Abstinence
Condoms
Limit Partners http://www.anaisdedermatologia.org.br/_img/figuras_en/200604201
93906.jpg
HIV
HIV: what is it?
HIV: Human
Immunodeficiency
Virus
AIDS is Acquired
Immunodeficiency
Syndrome (AIDS)
Having HIV does
NOT mean you have AIDS http://www.wellesley.edu/Chemistry/Chem101/hiv/HIV-
1.html
References
http://www.cdc.gov/std/stats/trends2005.
htm