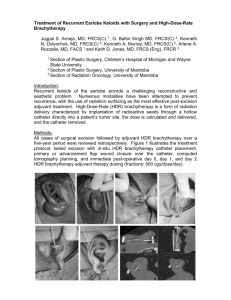
brachygeneral
advertisement

Introduction to Brachytherapy Presentation Overview What is Cancer? Principles of Radiation Oncology Introduction to Brachytherapy Typical Treatment Process Q&A What is Cancer ? Cancer is related to: • Growth • Differentiation • Tissue integrity TUMORcells CARCINOMA TRANSPORT INVASIE AANHECHTING HYPERPLASIE EXTRAVASATIE INTERVASATIE DYSPLASIE Metastasis IN SITU Healthy cells organ 2 TUMORcells Blood vessel organ 1 Capillary Cancer Treatment Options SURGERY CHEMOTHERAPY BRACHYTHERAPY HORMONE-THERAPY IMMUNOTHERAPY RADIOTHERAPY Principles of Radiation Oncology Damaging cells with radiation until cell repair is not possible anymore Repair possibility of “normal” tissue is higher than of tumor cells Cell Sterilization with Ionizing Radiation Particle Cell Nucleus Electron microscope image of multiplying cells Chromosome cell Why Brachytherapy? Cancer Alternative: Surgery Brachytherapy End result What is Brachytherapy with Remote Afterloading? Brachytherapy is Greek for: Brachy = short distance, close-in Therapy = treatment Remote Afterloading is: Cancer treatment with radioactive sources controlled from a distance Why Brachytherapy? 3-Fields External Beam AP-PA External Beam Brachytherapy Highly conformal Conformal Brachytherapy Treat only tumor tissue Spare healthy tissue Dose is determined by: Source Strength Exposure Time Source Position Brachytherapy: Advantages Higher local control, due to higher dose to target volume Less dose to surrounding tissue due to sharp fall-off of radiation dose Higher treatment dose delivered to the center of the tumor which is more radiation resistant More conformal treatment due to stepping source technique Brachytherapy: Disadvantages Hazard of radiation exposure Potential patient hospitalization Only local treatment Special skills and training are needed Licensing and credentialing needed Complete coverage of target volume is essential Surgical trauma in the case of interstitial techniques Brachytherapy Delivery Methods Liquids Phosphorous (blood disorders) Strontium (bone cancer) Iodine (thyroid) Implants Permanent (Au-198 or I-125 seeds for prostate) Temporary (wires or afterloading techniques) Treatments by Type of Loading Manual “hot” loading Manual Afterloading Remote Afterloading Brachytherapy Remote Afterloading Methods Low Dose Rate Cesium pellets or Iridium wires, treatment 1-3 days High Dose Rate Cobalt-60 pellets, Iridium-192 10 Ci source, treatment in minutes Pulsed Dose Rate Iridium-192 1 Ci source, treatment 1-3 days Afterloader: Low Dose Rate (LDR) Cesium spheres and Iridium wires no real optimization possible long treatment times (days) well known radiobiological and late effects 1978 Afterloader: High Dose Rate (HDR) Stepping Iridium-192 source (10 Ci) 200+ applicators for body site specific treatments Programmable variable source positioning via steps and dwell times Short treatment times (minutes) 1986 - present Afterloader: Pulsed Dose Rate (PDR) stepping Iridium source (0.5 - 2Ci) no limitation to body sites and curvatures optimization possible short radiation times (minutes) long treatment times (days) requires less shielding 1986 - present Brachytherapy Components Planning Systems Imaging devices Remote Afterloaders Body-site Specific Applicators Treatments by Location Intracavitary techniques (i.e. Vaginal, Rectum) Intraluminal techniques (i.e. Lung) Interstitial techniques (i.e. Breast, Prostate) Surface applications (i.e. Skin) Synergy with Brachytherapy Brachytherapy – External beam Brachytherapy – Surgery Per-operative Pre-operative (improves surgical outcome) Brachytherapy – Chemotherapy Brachytherapy - Hyperthermia Nucletron is the Solution microSelectron Digital Afterloader for HDR & PDR Body-site Specific Solutions PLATO & Oncentra Treatment Planning Systems Training Leadership Technical Support Licensing Support Reimbursement Support Service History of Radiation Oncology & Brachytherapy Question & Answers