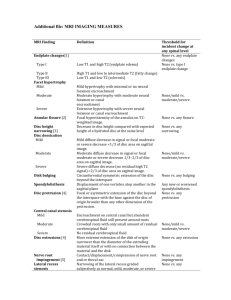
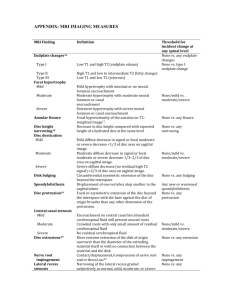
Document
advertisement

ั ื่ ม โรคกระดูกสนหล ังเสอ ั MD, PhD, LLB กิตติ จิระรัตนโพธิช ์ ย ว ัตถุประสงค์ ั หลังปกติ กระดูกสน ั หลังตามวัย การเปลีย ่ นแปลงของกระดูกสน ั หลังเสอ ื่ ม โรคกระดูกสน พยาธิกาเนิด กลุม ่ อาการทางคลินก ิ แนวทางการวินจ ิ ฉั ย แนวทางการรักษา 2 ั กระดูกสนหล ังปกติ กายวิภาค 26 Vertebra 23 Disc 24x2 facet joints 23x2 endplates (29)x2 nerve roots Ligaments หน้าที่ แกนกลางโครงร่าง รับโหลด เคลือ ่ นไหว ั หลังและ ป้ องกันไขสน รากประสาท 3 ั ื่ ม กระดูกสนหล ังเสอ มีการเปลีย ่ นแปลงด ้าน ั หลัง ทีเ่ กิดขึน ้ กับโครงสร ้างกระดูกสน Disc, body, endplate, facet, ligament & capsule โดยอาจไม่สง่ ผลให ้เกิดกลุม ่ อาการทางคลินก ิ Morphology, anatomy, histology, physiology, biochemistry, neurology, pathology, biomechanics, & functions Aging spine หรือเกิดกลุม ่ อาการทางคลินก ิ Degenerative spine diseases Degenerative disc diseases 4 Intervertebral disc degeneration Changes in NP • proteoglycan, water, collagen II, • cell density • cell death, collagen I Genetic factors Age, Nutrition Environmental factors Changes in AF & endplate • vascular & neural invasion • endplate vascularity, fracture Disc morphology changes Inappropriate response to load 5 Disc degeneration Loss of disc height & abnormal load distribution Spondylotic changes of the body & facet joint Facet joint hypertrophy & Capsular laxity instability Hypertrophy of ligamentum flavum, ossification Ossification of posterior longitudinal ligament Facet Kirkkaldy_Willis (1982) Dysfunction Three stages of spinal degeneration Disc Synovitis Dysfunction Circumferential tears Continuing degeneration Herniation Radial tears Intermittent axial pain Instability Capsular laxity Subluxation Instability Lateral nerve entrapment Internal disruption Disc resorption Persistent back & leg pain One level stenosis Osteophytes Stabilization Enlargement of articular processes Multilevel spondylosis and stenosis Leg pain ± neurological deficit 7 โครงสร้าง Morphology Physiology Function Disc ความสูงลดลง Content changes Osteoporotic changes Motion & load vascularity Marrow changes Load function Vertebral body ความสูงลดลง Endplate Facet & capsule Ligament Spinal cord & root Sclerosis osteophyte Hypertrophy Subluxation Load function Cartilage content Motion & load change Hypertrophy Content elasticity changes changes changes Motion & load Function changes 8 Imaging of spine degeneration Spondylotic changes Vacuum disc 9 Osteophyte Marginal syndesmophyte พบ ใน spondyloarthropathy Traction spur พบใน instability Non-marginal syndesmophyte พบใน diffuse idiopathic skeletal hyperostosis 10 Internuclear cleft Endplate & marrow changes Schmorl’ node OPLL Cord signal changes in T1 & T2-weighted 11 อาการทางคลินก ิ •Axial pain •Radicular pain •Referred pain Abnormal load Abnormal motion of spinal segment Neuro deficit •Radiculopathy •Myelopathy •Spondylolisthesis •Scoliosis •Kyphosis Pain Insta Defor bility mity 12 SInstability 13 Degenerative disc diseases กลุม ่ โรคซงึ่ เป็นผลจากหมอนรองกระดูก ั ื่ ม สนหล ังเสอ Axial pain / radiculopathy / myelopathy caused by , disc degeneration, disc herniation or spondylotic changes Facet joint arthritis Spinal stenosis Spondylolisthesis, scoliosis, kyphosis Ossification of PLL, OYL 14 Symptom/sign Pain Axial Radicular Referred Radiculopathy Myelopathy Deformity Instability กลุม ่ โรค วินจ ิ ฉ ัย ประวัต ิ Spondylosis, facet ตรวจร่างกาย Nerve root Radiology Enthesitis, visceral X-ray F/E views HNP, stenosis Oblique view CSM, OPLL, OYL CT Scoliosis, MRI listhesis, EMG kyphosis LAB Abnormal spinal motion segment 15 HNP CSM OPLL OYL 16 sspondylosis SNormal Sspondylolytic spondylolisthesis SHNP Spars defect Sdegen. scoliosis SStenosis SOYL 17 Treatment of degenerative spine Neuro deficit Pain Insta- Defor- bility mity 18 Back or neck pain Non-radicular back or neck pain Back or neck pain with radiculopathy Acute (4 wk), subacute & chronic Acute, subacute & chronic (>12 wk) Another specific spinal causes 19 Treatment options Medications Non-medications Acute, subacute, chronic Intervention techniques Acute, subacute, chronic Subacute, chronic Surgery Chronic 20 Surgical treatment Indications Cauda equina syndrome Progressive myelopathy or radiculopathy Severe myelopathy or radiculopathy Correct deformity Unstable spine Failure conservative treatment at least 3 months for mechanical pain 21 SDecompression SDecompression + fusion + stabilization SDecompression + reduction +fusion + stabilization 22 Evidence summary Treatment of back pain Acute Chronic nonradicular Chronic radicular Medications Acetaminophen NSAIDs Muscle relaxant Acetaminophen , NSAIDs, Opioids, Antidepressants , Anticonvulsants Non medications Superficial heat, Stay active Education Multidisciplinary Rx., exercise, manipulation, massage, acupuncture Intervention techniques Medial branch block (±) Chemonucleolysis Epidural steroid (HNP) Spinal cord stimulation (failed back) Surgery Total disc replacement Discectomy Decompression Fusion Interspinous spacer 23 สรุป ั หลังเสอ ื่ มเกิดขึน กระดูกสน ้ เสมอถ ้ามีอายุ ยาวนานพอ แต่มบ ี างคนเท่านัน ้ ทีเ่ กิดอาการ ั หลังเสอ ื่ มอาจทาให ้เกิดอาการ ผลจากกระดูกสน ั หลังและรากประสาททางานผิดปกติ ปวด ไขสน ั หลังไม่มั่นคง กระดูกสน ั หลังผิดรูป กระดูกสน วิธก ี ารรักษาขึน ้ กับอาการของผู ้ป่ วย (รักษา อาการปวด คลายการกดเบียดรากประสาท ั หลัง ทาให ้กระดูกสน ั หลังมั่นคงและจัด ไขสน แนวกระดูกให ้ดีขน ึ้ ) 24 Case Hx. A 60-year-old male presented with progressive difficulty on walking and hand using for 6 months. PE. Spastic gait, Lhermitte’s sign +, Grip release +, Finger escape+, scapulohumeral reflex + 3+ 3+ Hoffman’s sign+, Babinski -, clonus – 3+ 3+ 3+ 3+ Decreased pinprick L5 Rt 1+ 1+ EHL gr IV Rt 25 26 27 (a-b)/b X 100 = 15% (b-c)/c X 100 = 15% a (a-c)/a X 100 = 25% After Sx. b 4 Mo c 4 Yr 28 แหล่งความรูเ้ พิม ่ เติม ั หลังเสอ ื่ ม ตาราโรคกระดูกสน ั 2553 โดยรองศาสตราจารย์ กิตติ จิระรัตนโพธิช ์ ย ตาราทีเ่ กีย ่ วข ้องในห ้องสมุดคณะแพทย์ 29 Schmorl’s nodes 30 Level of evidence Level Study (Systematic reviews ;SR) I 1. High quality RCTs; Narrow confidence interval 2. SRs of Level I study with consistent results II 1. Lesser quality RCT 2. Prospective comparative study 3. SRs of Level II or Level I study with inconsistent results III 1. Case control study 2. Retrospective comparative study 3. SRs of Level III IV Case series V Expert opinion Center for evidence-based medicine, Oxford, UK 31 Overall strength of evidence Strength of evidence Finding from the studies Good evidence Level I studies Fair evidence Level II studies Poor evidence Level III, IV studies Inconsistent/insufficient 32 Grading of recommendation Grading Definition A • Strongly recommends • Good evidence that intervention improves health outcomes; Benefits > harm B • Recommend for some eligible patients • At least fair evidence; benefit > harm; low cost C D I • Not recommend or against • At least fair evidence; benefit ~ harm • Against interventions • At least fair evidence that intervention is ineffective; harm > benefit • Insufficient evidence to recommend or against US Preventive Task Force for Grading strength of evidence 33 Effect size of treatment No effect, small, moderate, large effect Small Moderate Large Decrease VAS (0-100) 5-10 10-20 >20 Improve ODI (0-100) 5-10 10-20 >20 0.2-0.5 0.5-0.8 >0.8 Standard mean difference US Preventive Task Force for Grading strength of evidence 34 Acute LBP Level of evidence Effect size Grading of Recom. Good Smallmoderate B Fair Smallmoderate B-C Bed rest, exercise Good No effect D Deep heat, , TENS, Acupuncture, support, Back school, ultrasound, Traction Poor No-Small I Treatment Acetaminophen NSAIDs Muscle relaxants Stay active, education Manipulation, herbal Superficial heat Chou et al., Spine 2009 35 Subacute & Chronic LBP Treatment Level of evidence Effect size Grading of Recom. Multidisciplinary, Exercise, manipulation massage, acupuncture Good-fair Moderate B Good-fair SmallModerate B Antidepressants Anticonvulsants Benzodiazepines Acupuncture, back school Fair SmallModerate B-C Traction, mattress Fair No benefit D Laser, Lumbar support TENS, ultrasound, short wave, biofeedback, traction Poor Unable to estimate I NSAIDs ,Acetaminophen opioids Chou et al., Spine 2009 36 Interventional techniques for non-radicular back pain Treatment Level of evidence Effect size Grading of Recom. Medial branch block Fair Smallmoderate B-C Epidural adhesiolysis (failed back) Fair Smallmoderate C Facet joint injection Fair No benefit D Intradiscal steriod injection Fair No benefit D Local, botulinum, epidural injection Poor Unable to estimate I SI joint injection Radiofrequency denervation Poor Unable to estimate I No trials Unable to estimate I Spinal cord stimulation Intrathecal therapy Coblation nucleoplasty 37 Interventional techniques for discogenic & radicular back pain Treatment Level of evidence Effect size Grading of Recom. Good Moderate B Fair Moderate B Spinal cord stimulation (for failed back surgery) Fair Moderate B Intradiscal steriod inj. Fair No effect C Epidural steriod injection (for spinal stenosis) IDET, Radiofrequency denervation Poor Unable to estimate I No trials Unable to estimate I Chemonucleolysis Epidural steriod injection (caudal>interlaminar>transfo raminal) Coblation nucleoplasty Spinal cord stimulation 38 Surgery Treatment Level of evidence Effect size Grading of Recom. Micro / open discectomy Good Moderate B Stenosis decompression Good Moderate B Interspinous spacer (X-STOP) Fair Moderate B Full endoscopic disc surgery Fair Moderate B Fair-poor Unable to estimate I Fusion Fair Moderate B Total disc replacement Fair Moderate B Nucleus replacement Poor Unable to estimate I Other minimally invasive disc surgery 39