Removable Partial Dentures: Clasp Design & Components
advertisement

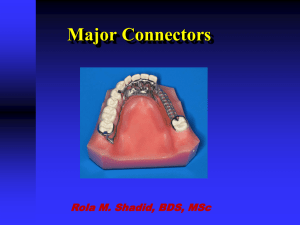
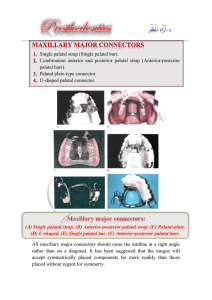
CLASP RETAINED REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURES COMPONENT PARTS OF A REMOVABLE PARTIAL DENTURE • Retentive Arm • Bracing or Reciprocal Arm or Plate • Rest • Minor Connector • Major Connector • • • • • Grid Retention Areas Tissue Stop Indirect Retainer Denture Base Denture Teeth Cast RPD Framework Components • • • • Major Connector Minor Connectors Clasp Assembly Retention for Replacement Teeth Cast RPD Framework Components • MAJOR CONNECTOR • A major connector is the part of a RPD that connects the components on one side of the arch to the components on the opposite of the arch. Major Connector Requirements • • • • Rigidity Should be contoured Should avoid circumjacent structures Minimum bulk Maxillary Major Connectors • • • • • Palatal Strap Anterior Posterior (A-P) Palatal Strap Palatal Plate Palatal Bar U-Shaped (Horseshoe) Palatal Connector Palatal Strap Palatal Strap A-P Bar • Palatal bar is defined as being 8mm or less in width. • A palatal strap is greater than 8mm in width • OBVIOUSLY,THIS IS NOT BRAIN SURGERY Palatal Plate Strap or Bar ? Anterior edge should follow contour of rugae A-P Strap or Bars ???? Maxillary framework should be 6mm from free marginal gingiva, if this is not possible than the framework should end on teeth. Maxillary Major Connectors • • • • • • Palatal Strap Anterior Posterior (A-P) Palatal Strap Anterior Posterior (A-P) Palatal Bar Palatal Plate Palatal Bar U-Shaped (Horseshoe) Palatal Connector Mandibular Major Connectors Mandibular Major Connectors • • • • • Lingual Bar Lingual Plate Double Ling Bar (Kennedy Bar) Labial Bar Swinglock Mandibular Major Connectors Lingual Plate Lingual Bar • The superior border of a lingual bar should be at LEAST 4 mm below the free marginal gingiva. Lingual Bar and Lingual Plate Indications For Use Of A Lingual Plate • For stabilization of periodontally involved teeth. • In Class I situations in which residual ridges have undergone excessive vertical resorption. • When the lingual frenum is high or the space available between the gingival margin and the floor of the mouth is <8 mm. • Lingual bar approximately 4mm + 4mm clearance from free marginal gingiva = 8mm and want no impingement of lingual frenum. Indications for use of a Lingual Plate, continued • When the patient has found a lingual bar objectionable in the past • When the future replacement of one or more incisor teeth will be facilitated by the addition to the lingual plate. Lingual plates must always terminate in a prepared rest seat and never on an inclined surface. Labial Bar Double Lingual Bar or Kennedy Bar Palatal torus U Shaped Swing Lock Major Connector Or Clasp??? Mandibular Major Connectors • • • • • Lingual Bar Lingual Plate Double Ling Bar (Kennedy Bar) Labial Bar Swinglock Cast RPD Framework Components • MAJOR CONNECTOR • MINOR CONNECTORS • Minor connectors are those components that serve as the connecting link between the major connector and the other components. • Many times a minor connector will be continuous with a lingual or palatal plate rather than a distinct element. Reciprocal Arm Retentive Arm APPLICATION OF CLASP ASSEMBLY TO TOOTH • Minor connectors may play a critical role by serving as a connector for indirect retainers that minimize the rotation of free end saddles. • An indirect retainer is that part of an RPD that assists the direct retainer in preventing displacement of distal extension denture bases by resisting lever action from the opposite side of the fulcrum line. It is the rest within the rest seat that prevents the displacement. Indirect retention • The ideal position for an indirect retainer is at a right angle to the fulcrum and located on the strongest tooth. Cast RPD Framework Components • MAJOR CONNECTOR • MINOR CONNECTORS Cast RPD Framework Components • Major Connector • Minor Connectors • Clasp Assembly • A clasp assembly is the part of a RPD that acts as a direct retainer and/or stabilizer for a prosthesis by partially encompassing or contacting an abutment tooth. • Clasps are made up of a retentive arm, a reciprocal or bracing arm, and a rest. CLASP ASSEMBLY Clasp • • • • Retentive Arm Bracing or Reciprocal Arm or Plate Rest Minor Connector Clasps • Retentive Arm (Direct Retainer)-that component of an RPD used to retain or prevent dislodgement. The terminal third of which is the ONLY portion of the casting that touches the tooth BELOW the height of contour therefore, it must move over the height of contour for the RPD to go to place. It must flex or the tooth move. Clasps • Reciprocal Arm-stabilizes the tooth by being in contact with the opposing side of the tooth during the entire period of the retentive arm deformation. (Its movement over the height of contour during insertion and removal.) BRACING 2o Bracing: – Cross arch bracing • location of retentive arms on the same side of the teeth on opposite sides of the arch. RETENTION (pp84-93) • Angle of convergence-THE UNDERCUT Size and Distance • Length of the clasp arm • Diameter of the clasp arm • Cross sectional form of clasp arm • Material used for clasp arm-CrCo vs Gold • Uniformity of retention-across the arch Dental Retainers •Clasps –Cast •Suprabulge •Infrabulge –Wrought wire •Attachments •Intracoronal •Extracoronal Stress breaking • Aim - reduce torquing force on distal abutment teeth Stress breaking Mesial Rest - Wrought Wire RPI REST PLATE I-BAR • Don’t get hung up on names of clasps; learn the principles, the names will change. MADDEN CLASP Failure to cover the retromolar pad