avfistula - Pilgrims Hospital
advertisement

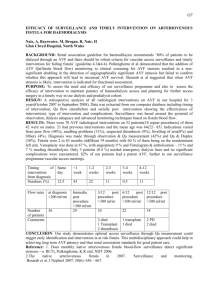
Bzzz…. Bzzz…. Bzzz…. Bzzz…. Dr. Maha Al Marashi KM. 60 Female Elective admission on into Beaumont Hospital under the care of nephrology service with poor flow through left femoral perma-cath which was inserted. KM. 60 Female BGHx: IDDM 1982 Diabetic retinopathy Diabetic neuropathy ESRF on haemodialysis alternate days HTN Left subclavian vein stenosis KM. 60 Female Left brachio-cephalic AVF Right brachio-basilic AVF Left subclavian stenosis Fistuloplasty Superficialisation Right upper limb graft Venoplasty right brachio-basilic AVF Right femoral permacath KM. 60 Female Doppler lower limbs: Patent veins which may be suitable for fistula/ graft. KM. 60 Female Left SFA-SFV groin PTFE graft loop AVF Sartorious muscle mobilised medially and laterally to expose SFV + SFA respectively Venaflo graft tunneled in loop to lower thigh. KM. 60 Female Parachute anastamosis to SFV and SFA. Heparin flushing. Haemostasis. Closure in layers. KM. 60 Female Post-operatively: Good bruit Good signals Left foot pink No haematoma No pain Arterio-Venous Fistula History Many advances in the treatment of kidney failure have been seen since the first attempts at dialysis treatments were made in the 1920s. The first breakthrough came in 1965 with the development of the AV fistula at the Bronx Veteran's Administration Hospital in New York by Kenneth Charles Appell. The development of the AV fistula has marked an important advance, allowing effective treatment for longer periods of time. Pathophysiology Normal blood flow in the brachial artery is 85 to 110 mL/min. After the creation of a fistula, the blood flow increases to 400 to 500 mL/min immediately, and 700 to 1,000 mL/min within 1 month. A bracheocephalic fistula above the elbow has a greater flow rate than a radiocephalic fistula at the wrist. Both the artery and the vein dilate and elongate in response to the greater blood flow and shear stress, but the vein dilates more and becomes "arterialized". When the vein is large enough to allow cannulation, the fistula is defined as "mature." An arteriovenous fistula can increase preload. Venous Access for Haemodialysis AV Fistula AV Graft Venous catheter (permacath) AV Fistula “Gold Standard” It has a lower risk of infection than grafts or catheters It has a lower tendency to clot than grafts or catheters It allows for greater blood flow, increasing the effectiveness of hemodialysis as well as reducing treatment time It stays functional for longer than other access types; in some cases a well-formed fistula can last for decades Fistulas are usually less expensive to maintain than synthetic accesses Pre-op Diagnostic Tests Duplex arteries and superficial veins Venogram MRA/MRV Surgical Techniques: Native A, Normal anatomy of the right antecubital fossa, showing the cephalic vein (CV), median antecubital vein (MACV), basilic vein (BV), brachial artery (BA), radial artery (RA), and ulnar artery (UA). B, Brachiocephalic arteriovenous fistula. C, Brachiobasilic arteriovenous fistula. D, Brachial artery–to– median antecubital vein arteriovenous fistula Surgical Techniques: Graft Radial graft – formed in the wrist (radio-cephalic) Brachial graft – formed near the elbow (brachiocephalic) Leg graft – formed in the thigh Neck graft – ‘necklace graft’ Complications Infection Thrombosis Stenosis Aneurysm/ pseudo-aneurysm Steel syndrome Limb ischaemia Intervention Angioplasty Stenting Thrombectomy Tie-off Removal of infected graft. Aftercare Making sure the access is checked before each treatment. Not allowing blood pressure to be taken on the access arm. Checking the pulse in the access every day. Keeping the access clean at all times. Using the access site only for dialysis. Being careful not to bump or cut the access. Not wearing tight jewelry or clothing near or over the access site. Not lifting heavy objects or putting pressure on the access arm. Sleeping with the access arm free, not under the head or body. Conclusion AV fistula ‘gold standard’ for venous access for haemodialysis. Commonly radio-cephalic in nondominant arm Approximately 6/52 to ‘mature’ May use graft material: mature faster but higher rate of infection Palpate for thrill and auscultate for bruit/ bzzz…