Low EF Sticker
advertisement

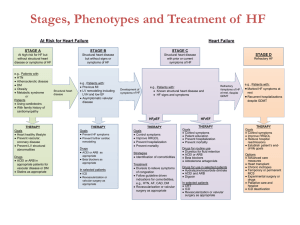
Primary Prevention ICD Therapy: Tools to Enhance Guideline Compliance By: Margaret S. Thomas, RN,CVRN Michael J. Mirro, MD Alicia S. Floor, AS,RN, Rob L.Plant, PharmD Parkview Health Fort Wayne, Indiana Background 1) Data from NCDR- ICD Registry indicates ICD guideline non-compliance is a significant issue (JAMA 2010;305:91-92) a) Analysis of 111,707 primary prevention ICD implants at 1,227 centers(2006-2009) b) 25,145 (22.5%) implants performed did not meet evidenced-based implant criteria c) 9,257 (37%)implants occurred <40 days post-AMI d) 15,604 (62%)implants occurred in new CHF (<90 days) e) 3,022 (12%) implants occurred in CHF Class IV (NYHA) f ) 814 (3%) implants occurred <90 days post-CAB 2) The Department of Justice (DOJ) has launched an investigation of 100 centers nationally to assess inappropriate use of ICD therapy in CMS patients (claims data 2003-2009) Objectives 1) Review of ICD Registry data from PHI can enhance guideline compliance for primary prevention ICD therapy 2) Critical source documentation in the outpatient record is subject to wide variation thus a standardized electronic pre-implant form will assist in documentation of key data fields 3) Capture of potential new primary prevention ICD patients should occur through the use of EF alerts in the in-patient/out-patient imaging departments (Echo/Nuclear/Angio) 4) Use of Wearable Cardiac Defibrillator (WCD) useful in protecting patient during waiting periods (<90 days new CHF or revascularization) 5) Computerized Decision Support (CDS) can enhance guideline compliance at point of care 6) Documentation of use or non-use of ICD therapy should occur electronically in the medical record. Methods 1) Educate Staff (Posters/Lectures) 2) Review ICD Registry Data with CV-EP monthly 3) Implementation of pre-implant ICD form that collects key clinical data elements electronically 4) Deploy EF stickers on inpatient charts through imaging departments 5) Deploy electronic CDS tools 6) Tract WCD use and patient outcomes SCD Prevention Program • • • • • • Patient Safety Issue : Hospital and Office Educate All Staff : EF Documentation Hospital : New CHF and AMI Patients EF Stickers on Charts HIT : EF Alerts and Drug Therapy (CDS) LifeVest Policy : Prevent Patient Loss • • HIT= Health Information Technology CDS= Computer Decision Support SCD:Primary Prevention • • • • Beta-Blockers ACE-Inhibitors Aldosterone Antagonists Implantable CardioverterDefibrillator(ICD) • SCD= Sudden Cardiac Death Tools to Enhance SCA Prophylaxis • Cardiac Imaging (Echo/Nuclear/Cath Lab) • EF Stickers on All Charts (EF<36%) • Electronic EF Alerts for CHF • HIT : Clinical Decision Support (CDS) • HIT : Data Mining Capability for ICD use • CDS= Computer Decision Support • • HIT= Health Information Technology SCA= Sudden Cardiac Arrest Low EF Sticker HIT Tools Embedded in EHR • Clinical Decision Support EF Alerts • PINNACLE Registry EF Data Entry • • HIT= Health Information Technology EHR= Electronic Health Record SCA Prophylaxis Plan : Documentation • ICD Implant Candidate • ICD not Indicated (Life expectancy <1 year) • ICD Indicated but needs 90 day wait • ICD Implant Refusal • SCA= Sudden Cardiac Arrest Patient Treatment Algorithm •Patient Identification LifeVest Optimal Medical EF<36% • Office • Hospital • Education Repeat EF<36%: ICD Indicated EP referral & ICD Therapy Follow-up 90 days Repeat EF>35% Non-ICD indicated MTWA & Holter guided drug therapy & ILR placement Conclusions • Implement Pre-Implant Form in ICD implants (including generator changes) • Implement EF Sticker plan and follow-up • Implement HIT-CDS tools • Implement Primary Prevention CDS tool with electronic documentation of ICD use/non-use