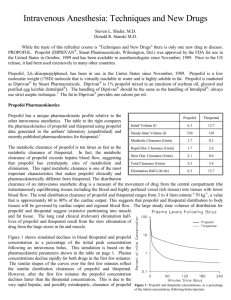
Excretion
advertisement
Total Intravenous Anesthesia อ.นพ.ธีรวัฒน์ ชลาชีวะ ภาควิชาวิสัญญีวิทยา โรงพยาบาลรามาธิบดี Beneficial of TIVA • Decrease global warming from N2O • Decrease pollution from volatile agents in OR • Decrease risk in patients or operation : – Suspected MH – Air embolism – Brain surgery • More suitable during operation that difficult or impossible to use inhalational anesthesia effectively – Laryngoscope, bronchoscopy – Thoracic surgery – Gastroscopy or colonoscopy • Decrease risk of PONV • Ambulatory surgery • Anesthesia in outside OR Balanced Anesthesia Unconscious - IV anesthetic agents Hypnosis - Inhalation agents Amnesia Reflex suppression Analgesia - Opioid Immobility - Muscle Muscle relaxants relaxation Is the Patient Anesthethetized? How do you gauge the depth of anesthesia when using TIVA? • Same skills are used as when administering volatile drugs. Pharmacokinetics and TIVA • Use of mathematics to describe How the body “handles” particular drug Open, three-compartment model Organ perfusion Tissue Group Vessel-rich Composition CO (%) Body Mass(%) 10 75 Brain, heart, liver, endocrine glands Muscle Muscle, skin 50 19 Fat Fat 20 6 Vessel-poor Bone, ligament, cartilage 20 0 Open, three-compartment model Context Sensitive Half Time • Time plasma concentrations take to reduce by 50% after discontinuing infusion. • Short CSHT drugs are desired for TIVA. Open, three-compartment model ke0: Describing drug delivery to the effect site the pharmacokinetic rate constant which describes the rate of equilibration between the plasma concentration and effect site. Effector Site Delay Effective Blood Concentration • Potency of – Volatile drugs : MAC (anesthetic required to prevent gross, purposeful movement in 50% of patients in response to a noxious stimulus) – Propofol : ED50 • propofol and N2O was 4.5 mcg/ml and the ED95 was 4.7 mcg ml. • propofol was 6.0 mcg/ml and the ED95 was 6.2 mcg/ml. Development of delivery systems AIM 1st maintenance of optimum & stable anesthetic condition iv. bolus injection : single, intermittent administration, iv. drip 2nd Infusion pump Syringe pump 3rd TCI TIVA-TCI : Target Controlled Infusion เป็ นเทคนิคที่นาเอาข้อมูลความสัมพันธ์ของอัตราการไหลของยาและ ระดับยาในกระแสเลือดมาคานวณโดยเครื่ องคอมพิวเตอร์เพื่อควบคุมระดับ ยาในแต่ละ Compartment ให้เป็ นไปตามต้องการ • TCI TIVA-TCI : Drugs suitable for Hypnosis Propofol Dexmedetomidine (Etomidate not suitable due to suppressant of adrenal steroidogenesis) Analgesics Alfentanil Remifentanil ? fentanyl not for long infusion (Morphine not suitable ) l Propofol • เป็ นยาในกลุ่ม alkylphenol ซึ่งเป็ นไขมันในอุณหภูมิหอ้ ง • ประกอบด้วย 1%propofol, 10%soybean oil as longchain triglycerides, 2.25%glycerol and 1.2%purified egg phosphatide มี 0.005% disodium edetate เพื่อ ป้ องกัน bacterial growth • Metabolism – Rapid metabolism in liver by conjugation and glucorodination – Renal excretion – Extrahepatic metabolism ; lung, small intestine, kidneys • CNS – Decrease CMRO2, CBF, ICP – Anticonvulsion – Myoclonic, hiccup • CVS – Venous dilatation, decrease PVR &CO --> hypotension – Greater CVS than thiopental • Respiration – may be transient apnea – decrease TV, rate Pharmacodynamic variability • Age – increased sensitivity of the elderly to the effects of propofol. ke0, hence plasma effect site equilibration has been reported not to be changed by age. – These properties suggest that induction in elderly patients should be achieved with lower plasma concentrations than in younger adults, however it should also be titrated more slowly to avoid side effects. Pharmacodynamic variability • Systemic disease – It has often been assumed – patients with significant disease would require less anaesthetic • increased central nervous system sensitivity to the drug • increased free fraction of drug secondary to reduced plasma protein binding (subtle pharmacokinetic changes) ในกรณี ไม่ใช้เครื่ อง TCI การนาสลบ ขนาดยานาสลบโดยปกติใช้ 1-2.5 มก./ กก. โดย - ในผู้ใหญ่ ไม่ ได้ รับยา opioid หรือ benzodiazepine เป็ นยา premedication ใช้ 2.25-2.5 มก./ กก. - คนแก่ อายุมากกว่ า 60 ปี ไม่ ได้ รับยา opioid หรือ benzodiazepine เป็ นยา premedication ใช้ 1.75 มก./ กก. - เด็กไม่ ได้ รับยา opioid หรือ benzodiazepine เป็ นยา premedication ใช้ 2-3 มก./ กก. การป้ องกัน hypotension ในผู้ป่วยทีป่ ่ วยเรื้อรัง หรือผู้ป่วยทีม่ ารับการผ่ าตัดหัวใจ ควรค่ อยๆให้ propofol 10-30 มก. จนกระทัง่ ผู้ป่วยสลบและควรให้ สารนา้ นาไปก่ อนให้ เพียงพอ ในกรณี ไม่ใช้เครื่ อง TCI Maintenance dose - ในกรณีฉีดยาเป็ นครั้งคราว(intermittent bolus) ให้ 10-40 มก. ทุกๆ 2-3 นาที - ในกรณีหยดยาอย่ างต่ อเนื่อง(continuous infusion) หลังให้ ยานาสลบ หยดยา 140 มคก./กก./นาที เป็ นเวลา 10 นาที ต่ อด้ วย 100 มคก./กก./นาที โดยให้ ร่วมกับ fentanyl 0.02 มคก./กก./นาที หรือ alfentanil 0.25 มคก./กก./นาที TIVA-MCI : manually-controlled infusion “ are used to designate manual adjustment of infusion rates for anaesthesia syringe pumps” Initial infusion rate 10 min Subsequence adjustment so as to maintain a stable level of anesthesia Less Pain With N2O Without N2O Start 8 10 12 >10 mins. 5 7 9 >2 hrs. 3 5 7 Not easy to control Time-consuming calculation No compensate for interrupted infusion Delayed emergence !!! Require skill & experience Propofol infusion rate (mg/kg/hr) 13 10 นาทีแรก 11 10 นาทีแรก 9 10 นาที-2 ชม 10 นาทีแรก 10 นาที-2 ชม 7 5 > 2 ชม 10 นาที-2 ชม 3 หัตถการที่ไม่ ปวด > 2 ชม > 2 ชม ผ่าตัดในช่ องท้ อง Opioid + N2O ผ่าตัดในช่ องท้ อง Opioid หยุดยาก่ อนเวลาทีต่ ้ องการให้ ผู้ป่วยตืน่ ระยะเวลาของการสลบ 15 นาที 30 นาที 1 ชม. 2 ชม. 3 ชม. 4 ชม. 5 ชม. 6 ชม. ควรหยุดยาก่ อนให้ ตนื่ 5 (3-8) นาที 7.5 (4-12) นาที 10 (4-15) นาที 12.5 (5-20) นาที 15 (6-23) นาที 20 (8-33) นาที 25 (9-43) นาที 30 (20-47) นาที TCI –propofol concentration Cet 2-3 µg/ml loss of eyelash reflex Cet 4-8 µg/ml for anesthetic procedure Intubation, LMA CP50 2.7 – 3.4 µg/ml loss of response to verbal or tactile stimuli* Target = ? Target concn based on •Level of stimulation •Drug interaction •Desired clinical endpoint •Decrement time •Intraindividual variability * : Vuyk J et al. Anesthesiology 1992; 77: 3. Crankshaw DP et al. Anaesth Intensive Care 1994; 22: 481. Smith C et al. Anesthesiology 1994; 81: 820. TCI for induction & Intubation •MO 5-10mg •Midazolam1-2mg Propofol TCI •Cet 2-3 µg/ml loss of response Check ventilation ↓Cet 2-3 µg/ml wait for next painful stimuli ↑Cet 4-6 µg/ml for skin incision Muscle relaxant Ventilate 1.0-1.5 min Cet 4-8 µg/ml for intubation Ventilate 1.0-1.5 min TTPE Propofol in different lipids • The standard propofol formulation contains 10%soybean oil as long-chain triglycerides. – Pain on injection 14.7% • Long- and medium-chain trigycerides reduced incidence of pain on injection to 2.7%. Propofol-related infusion syndrome High dose infusion >5 mg/kg/hr for > 48 hrs Abrupt onset of profound bradycardia, metabolic acidosis lipemic plasma, symptoms renal failure, fatty liver, rhabdomyolysis or myoglobinuria Risk factors : poor oxygen delivery, sepsis serious cerebral injury Monitor : acidosis, K+, renal function Thank you for your attention THIOBARBITURATE(THIOPENTAL) • • • • • Preparation 2.5% pale yellow solution pH 10 - 11 bacteriostatic Mechanism of action Interacts with GABA receptor-->membrane hyperpolarization • Terminal of action • Redistribution-->ultrashort acting • Metabolism --- liver • • • • • Excretion--renal excretion of water-soluble Dose 3-5 mg/kg IV depending on age, ASA : Onset = 60 seconds Recovery = 5-10 mins • Pharmacologic actions • CNS – Decrease ICP, CMRO2, CBF – Anticonvulsant 50-100 mg IV – Cerebral protection • Create electrical silence ;15-40 mg/kg then 2-4 mg/kg/hr • CVS – Venous dilatation--> CO, ABP – Baroreceptor reflex – Increase HR • CO may decrease markedly – Hypovolemia – Beta blocker – Previous heart disease • Respiratory – – – – Depression medullary center--> RR, TV Apnea Upper airway obstruction Airway reflex • Bronchospasm • Laryngospasm Side Effects • • • • • Thrombophlebitis Intraarterial injection-->spasm Allergic reaction( histamine release ) Hypotension Subcutaneous injection-->necrosis Contraindication *PORPHYRIA* BENZODIAZEPINES • • • • • Minor tranquilizer Antianxiety, sedation Amnesia Control convulsion Relax skeletal muscle DIAZEPAM (Valium) • • • • • • • Highly lipid soluble Insoluble in water Mechanism of action Modifies GABA receptor activity Metabolism--> hepatic Excretion--> renal Indication – – – – Premedication : 0.05-0.1 mg/kg Induction of anesthesia :0.3-0.5 mg/kg Intravenous sedation : 1-2 mg p.r.n. IV Treatment of seizure MIDAZOLAM (Dormicum) • • • • • • • • pH<4-->Water soluble Physiologic pH--> lipid soluble Mechanism of action Modifies GABA receptor activity t 1/2 = 1 - 4 hr. Metabolism--> hepatic Excretion--> renal Indication – Premedication : 0.07-0.15 mg/kg – induction of anesthesia : 0.15-0.3 mg/kg – intravenous sedation : 0.5-1 mg repeat to effect BENZODIAZEPINES • CNS – – – – Decrease CMRO2, CBF HR increase due to drug induce vagolysis Anxiolysis, amnesia (dose related) Anticonvulsant properties • CVS – Slight decrease SVR, BP • Respiratory – – – – Dose related respiratory depression Respiratory response to CO2 decrease Lower incidence of apnea Careful titration FLUMAZENIL (Anexate) • Central acting benzodiazepine antagonist • Dose 0.25 - 0.5 mg. • Onset in 30 - 60 sec. • Duration 1 hr. • Liver metabolized • Side effects • dizziness, anxiety, nausea, vomiting, agitation KETAMINE • • • • • • • • • Preparation Water soluble, racemic mixture Mechanism of action Act on NMDA receptor Act on opioid and cholinergic receptor Causes dissociation Metabolism-- hepatic Norketamine--1/5 potency of ketamine Excretion--renal • Indications – induction of anesthesia – sole anesthesia – premedication • DOSE – 1-2 mg/kg IV induction – 3-5 mg/kg IM induction – 0.2-0.8 mg/kg IV sedation-->5-20 mcg/kg/min – 15-45 mcg/kg/min with O2/N2O maintenance • CNS – Increase CMRO2, CBF, ICP – Amnesia, analgesia • CVS – Increase MAP, CO, HR – If cathecholamine depletion or autonomic – block--> depress myocardium • Respiration – Bronchodilation--sym mediated – Relative preservation of laryngeal reflexs PROPOFOL (Dripivan) • • • • • • 2,6 di-isopropylphenol; 1% solution in egg white lecithin emulsion Mechanism May be at GABA receptor Metabilism--liver Excretion--renal • CNS – Decrease CMRO2, CBF, ICP – Anticonvulsion – Myoclonic, hiccup • CVS – Venous dilatation, decrease PVR &cardiac – depression--> hypotension – Greater CVS than thiopental • Respiration – may be transient apnea – decrease TV, rate • Indication – Induction of anesthesia – Sole anesthetic for short procedure – Treatment of seizures • Dose – 2-2.5 mg/kg IV induction – 100-200 mcg/kg/min maintenance – 25-100 mcg/kg/min sedation ETOMIDATE • Mechanism – May act at GABA receptor at reticular activating system • Metabolism--hepatic • Excretion--renal • Dose – 0.2-0.4 mg/kg IV induction – onset 30-60 sec. – Recovery = 5 mins • CNS – – – – – – may increase EEG activity in those with epilepsy Myoclonic movement (pretreat c opioid ) CBF, ICP, CMRO2 decrease CPP maintained Enhance SSEP response • CVS-- STABLE • Respiration – Transient apnea – Decrease rate and TV • Disadvantage ; Adrenocortical suppression OPIOIDS • Agonist • Partial agonist • Agonist -antagonist • Antagonist • Agonist Morphine Codeine Pethidine Sufentanyl Fentanyl Alfentanyl • Partial agonist • Agonist - antagonist Buprenorphine Pentazocine, Nalbuphine, Nalorphine • Antagonist Naloxone • Benefits – Good analgesia (dull pain) – Sedation, euphoria – Antitussive • Indications – Premedication – Supplement anesthesia – Sole anesthesia – Analgesia • Acute postoperative pain • Cancer pain Side effects • Nausea and vomiting • Pruritus • Visceral smooth muscle – Constipation – Biliary spasm – Ureteral spasm • CVS – Hypotension – Bradycardia • • • • • RR and response to PaCO2 Chest wall rigidity Urinary retension Histamine release MORPHINE • • • • • • • • Supraspinal analgesia Increase pain threshold Sedation, euphoria Pruritus, urinary difficulty Histamine release Spasm of sphincter of oddi Anti - tussive Dose related resp. depression PETHIDINE • Potency 1/10 of MOSO4 • Equianalgesic dose : same effect of resp. depression • Shorter duration of action • Atropine - like effects : HR,bronchodilatation, mydriasis • Active metabolites Norpethidine • CNS excitement, agitation seizures FENTANYL • • • • • Potency = 100 times MOSO4 Rapid onset, short duration No histamine release Bradycardia Truncal rigidity NALOXONE • • • • Pure opioid antagonis Dose 1 - 4 mcg/kg Duration 30 - 45 min Caution > close observe for – recurrent sedation/depression – increase sympathetic outflow – reverse analgesia + resp. depression