2010 Evacuation Awareness Training
advertisement

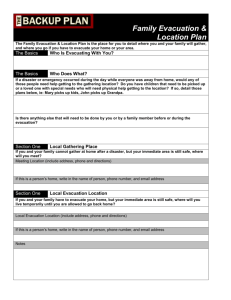
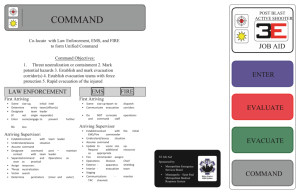
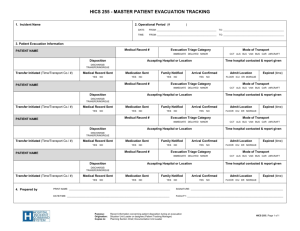
Hospital Evacuation Plan Managing the Worst-Case Scenario Why Do We Need a Plan? Joint Commission Requirements Safety of our patients When the environment cannot support care, treatment, and services Continuity of care Element of preparation Activation Levels Level 1 – Alert for potential evacuation Level 2 – Limited area / horizontal Level 3 – Limited area / vertical Level 4A – Large area / building Level 4B – Entire single campus – East or West Level 4C – Entire Longwood Area Evacuation – Both East and West Campuses Types of Evacuation Emergency Evacuation-Fire, Explosion – Immediate departure due to life or safety threat Urgent Evacuation-Flood, Utility Failure – Commence within four hours Planned Evacuation – At least 48 hours to prepare 4 4 GO Kits Unit / Team Leader vests Clipboards / checklists Mobility triage tape GO pouches Re-sealable medication bags Chemical light sticks Chalk / tape for evacuation marking Pens / markers Job Job Action Job Action Job Sheet Action Sheet Action Sheet Sheet GO Pouch Patient Form Patient Movement Flow Horizontal movement Unit – From unit to Patient Holding Area – Horizontal Movement Team Vertical movement – From Holding Area to Patient Loading Area – Vertical Movement Team Patient loading Movement to onward destination Placement at onward destination Horizontal Movement Team Holding Area Vertical Movement Team Loading Area Transport To Onward Destination Patient Mobility Levels Ambulatory Wheelchair Non-Ambulatory – – – – – Lowest acuity Moderate acuity Critical care Interrupted procedure Arm-carry Behavioral Health Patient Movement Sequencing By mobility level Focus on efficiency First, move the ambulatory – Ambulatory elderly and behavioral health may be moved faster as wheelchair patients Discharge-eligible patients Wheelchair patients Non-ambulatory patients – From lowest to highest acuity Evacuation Sleds NO LIFTING. Uses roll and drag method only. – Stairwell braking system for safe mobilization of lightweight or heavier patients by any staff member. Allows for all staff to be utilized in an evacuation. Regular sled (36x87 in), holds 800lbs Bariatric sled (48x87 in), holds 800lbs Compact and durable -- efficient storage options. helps protect person while transporting. holds IV bags, oxygen and other small devices. Stored on each floor and in distribution MedSled Special Situations & Critical Care Mothers and babies together Specialty care patients Airborne infectious isolation patients Morbidly obese patients Ventilated patients Orthopedic w/equipment Patients undergoing procedures Staff Assignments On-duty personnel remain until released Manpower is allocated by the Command Center What is Your Role? Evacuation Management Incident Command -Personnel Staging Team -Vehicle Staging Team -Equipment/Supply Staging Team -Medication Staging Team Operations Section Chief Staging Manager Medical Care Branch Director Security Branch Director Evacuation Branch Director Inpatient UL Access Control UL Horizontal Movement UL Patient Tracking UL Crowd Control UL Patient Holding UL Traffic Control UL Vertical Movement UL Law Enforcement Interface Patient Loading UL Tracking/Accountability UL Maintaining Continuity of Care Clinical staff Equipment and supplies – – – – – Surge Area Supply Cart Oxygen Biomedical equipment Supplies, linen, portable lighting Patient comfort and privacy items Emergency Response Manual Now On-line Emergency Response Manual now on the portal in PPGD Emergency Response Manual