Substance Abuse - Mother Baby University
advertisement

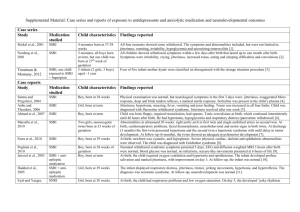
Perinatal Substance Abuse Denice Gardner, MSN, NNP-BC Objectives • Discuss Perinatal Substance Abuse and its affect on the newborn Pictures used in this presentation were obtained from the Mosby’s Nursing Consult web site Categories of Drugs Tobacco/Nicotine Alcohol Stimulants Narcotics & Opioids Sedatives/Hypnotics Antidepressants Effects of Drugs on Pregnancy Spontaneous abortion Placenta previa Placental abruption Preterm labor Premature rupture of membranes C-Section delivery Precipitous delivery Hypertension Tobacco & Nicotine Tobacco is a CNS stimulant Active components of cigarette smoke Nicotine Tar Carbon monoxide Cyanide Plus, thousands of other compounds Tobacco & Nicotine Nicotine-water & fat soluble; cross the placenta Carbon Monoxide- combines with hemoglobin & impairs oxygenation for mother & fetus; causes placental vasoconstriction & vasospasm Dose/Response relationship- the higher the number of cigarettes smoked – the greater the effect on the fetus Tobacco & Nicotine Fetal/ Newborn Effects Intrauterine growth restriction Slight increase in risk for congenital malformations Neurobehavioral effects Sudden Infant Death Syndrome Increased cost of hospitalization & medical care Increased perinatal mortality Tobacco & Nicotine Nursing Considerations EDUCATION Follow infant’s growth Provide information regarding smoking cessation programs & encourage participation Alcohol CNS depressant Absorbed rapidly through the stomach & intestines; metabolized by the liver; excreted through the kidneys & lungs Fetal alcohol is eliminated only after being broken down in the maternal liver Diffuses across the placenta & impairs flow of nutrients to the fetus Alcohol Broken down into acetaldehyde & acetate. (Acetaldehyde is MORE toxic than alcohol). Is a known teratogen Fetal effects are directly related to dose, chronicity of use, gestational age, & duration of exposure Alcohol Fetal Alcohol Spectrum Disorder (FASD) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome (FAS) Partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Alcohol-Related Birth Defects (ARBD) Alcohol-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder (ARND) Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Most severe form of FASD Most common identifiable cause of mental retardation (also is a preventable cause) Abnormalities in 3 domains Poor growth CNS abnormalities (developmental delays, impaired brain growth, abnormal structure, etc.) Dysmorphic facial features (thin, upper lip; smooth philtrum; short palpebral fissures, etc.) Alcohol exposure may or may not be confirmed Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Partial Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Typical dysmorphic facial features Abnormality in one of the domains CNS abnormality Growth Behavioral or cognitive ability Confirmed prenatal alcohol exposure Alcohol-Related Birth Defects (ARBD) Typical dysmorphic facial features Normal growth and brain function/structure Congenital anomalies in other organs (cardiac, skeletal, renal, eyes, ears) Confirmed prenatal alcohol exposure Alcohol-Related Neurodevelopmental Disorder (ARND) Absence of typical dysmorphic facial features Normal Growth CNS abnormalities: Decreased cranial size at birth Structural brain abnormalities Impairment of neurologic status in relation to age Behavioral or cognitive abnormalities inconsistent with age/developmental level Confirmed prenatal alcohol exposure Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Withdrawal from Alcohol Begins anytime between birth & 12 hours after birth Symptoms Tremors Hypertonia Opisthotonos Weak suck & poor feeding Sleeplessness Excessive crying Excessive mouthing behavior Stimulants Cocaine Amphetamines Cannabinoids Cocaine One of most powerful addictive substances Is fat-soluble with low molecular weight so readily crosses blood-brain barrier & placenta Rarely used alone Long half-life (can be present in infant’s urine for up to 7 days of age) Cocaine Fetal/Newborn Effects No increase in congenital malformations Multi-organ dysfunction CNS: abnormal sleep pattern, EEG, & cry; seizures/tremors; cerebral infarctions Sensory organs: increased auditory startle response; abnormal ABR Cardiac: arrhythmias; hypertension; decreased cardiac output Cocaine Fetal/Newborn Effects Multi-organ dysfunction (cont.) Respiratory: apnea; periodic breathing Renal: ectopia GI: intestinal perforation; early-onset NEC Eye: vascular, disruptive lesions; retinal hemorrhage Withdrawal from Cocaine Felt to be due to CNS irritability from effects of cocaine rather than from withdrawal Initial period of hyperirritability followed by drowsiness &/or lethargy Changes in behavioral state Difficulty responding to human voice/face, comforting, &/or environmental stimuli Difficulty maintaining alert states or rapid change is states Hyperactive startle Amphetamines Used medically for treatment of narcolepsy, depression, weight loss, hyperactivity Neurotoxic Fetal/Newborn effects: IUGR Withdrawal from Amphetamines Abnormal sleep patterns Diaphoresis Vomiting after birth Agitation alternating with lethargy Constriction of pupils High-pitched cry Loose stools Yawning Fever Hyperreflexia Cannabinoids CNS- both depressant & mild hallucinogenic effects High affinity for lipids & accumulates in fatty tissue of body Placental transfer is greatest during first trimester of pregnancy Results in increased carbon monoxide levels in blood causing hypoxia Narcotics & Opioids Natural Opioids Morphine & Opium Semi-synthetic Opioids Heroin & methadone Synthetic Opioids Oxycodone, hydromorphone, oxycodone, Fentanyl, etc. Narcotics & Opioids Fetal/Newborn Effects Readily crosses placenta Lower Apgar Scores Do NOT use naloxone for with known/suspected narcotic & opioid dependence due to creation of rapid withdrawal & seizures Meconium aspiration IUGR Lower incidence of RDS Narcotics & Opioids Congenital infections Increased incidence of SIDS Low birth weight Microcephaly Increased chromosomal abnormalities in heroine-exposed infants Sedatives/Hypnotics Barbiturates Benzodiazepines Sedative/Hypnotics Readily crosses placenta Fetal blood levels are similar to maternal blood levels Accumulate in adipose tissue High concentration also present in brain, lungs, & heart Fetuses exposed to long-term benzodiazepines may have hypotonia, feeding difficulty, & withdrawal symptoms Antidepressants Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs) Sertaline (Zoloft), Fluoxetine (Prozac), Escitalopram (Lexapro), Paroxetine (Paxil), etc. Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) Amitriptyline (Elavil), Nortriptyline, etc. Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs) Phenelzine (Nardil), Isocarboxazid (Marplan), etc. Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Onset may vary from shortly after birth to 2 weeks Duration may range from 8 to 16 weeks Severity of presentation varies Infants of chronic drug abusers usually have more severe withdrawal The closer to delivery the drug is taken, the later the signs of withdrawal appear & the more severe the symptoms will be Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Multiorgan/System Disorder Most common symptoms Neurologic Increased tone Tremors Exaggerated reflexes Irritability/restlessness High-pitched cry Difficulty sleeping Seizures Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Most common Symptoms Autonomic Yawning Nasal stuffiness Sweating Sneezing Low-grade fever Mottling Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Most Common Symptoms GI Loose stools Vomiting/regurgitation Poor feeding Difficulty swallowing Excessive sucking Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Most Common Symptoms Respiratory Tachypnea Others Skin excoriation Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Onset of withdrawal symptoms Alcohol- usually 3-12 hours after delivery Narcotics- usually 48-72 hours after delivery, but may be as long as 4 weeks Barbiturates- usually 4-7 days after delivery but can occur 1-14 days after delivery Cocaine- usually 48-72 hours after delivery Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Severity of NAS depends on The type of drug used Half-life of the drug Time of last exposure before delivery Dose taken Quality of labor Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Severity of NAS depends on Type of analgesia/anesthesia used during labor Maturity & status of infant Gestational age Nutritional status of mother Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Scoring Systems Modified Finnegan Scoring Tool Gold Standard*** Neonatal Drug Withdrawal Scoring System Neonatal Withdrawal Inventory Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Screening Tools Maternal Thorough history & assessment Drug testing (urine is most commonly used) Infant Thorough assessment Urine Drug screen Meconium Drug Screen Newer testing: hair and umbilical cord testing Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Nursing Management Accurate assessment, evaluation, & use if institution’s screening tool Comfort measures (swaddling, holding, cuddling, response to stress cues, etc.) Assessment & encouragement of mother/infant interaction Maternal/family support Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Pharmacologic management Tincture of opium Camphorated Tincture of Opium (Paregoric) Morphine (most common) Methadone Clonidine Chlorpromazine (Thorazine) Phenobarbital Diazepam Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Breastfeeding Cigarettes: not contraindicated encourage decreasing numbers of cigarettes smoked & smoking cessation Smoke after breast feeding Alcohol: use should be discouraged Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome Breastfeeding Cocaine: contraindicated during active use Marijuana: contraindicated Heroin: contraindicated Methadone: not contraindicated; should not be stopped abruptly Sedatives/Hypnotics: dose-dependent; discontinue with signs of lethargy &/or weight loss References Chang, G., Lockwood, C.J., & Barss. (2012). Substance Use In Pregnancy. Retrieved from www.uptodate.com on 8/17/2012. Sielski, L.A., Garcia-Prats, J.A., & Kim, M.S. (2012). Infants of Mothers with Substance Abuse. Retrieved from www.uptodate.com on 8/17/2012. References Sielski, L.A., Garcia-Prats, J.A., & Kim, M.S. (2012). Neonatal Opioid Withdrawal (Neonatal Abstinence Syndrome). ` Retrieved from www.uptodate.com on 8/17/2012. Verklan, M.T. & Walden, M. (2009). Core Curriculum for Neonatal Intensive Care Nursing (4rd Edition). Elseiver Saunders: St. Louis. Retrieved from Mosby’s Nursing Consult web site on 6/16/2012.