Clinical Listeriosis: What`s New?
advertisement

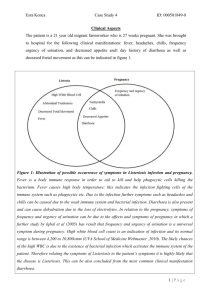
Clinical Listeriosis: What’s New? W F Schlech MD, FACP, FRCPC Listeria monocytogenes Organisms are widespread (ubiquitous)-- found in soil, food, water, sewage L. monocytogenes is a food-borne pathogen (LISTERIOSIS). Because of the organism’s exceptional abilities to cross three tight barriers, the mortality rate is high (~30%). (1) Intestinal barrier (2) Blood-brain barrier (meningitis) (3) Placental barrier (abortion) Individuals exceptionally vulnerable to death via. listeriosis (1) AIDS patients (2) Chemotherapy patients (3) Diabetics (4) Organ transplant recipients (5) Unborn Healthy adults do show transient fecal carriage of L. monocytogenes. Syndromes caused by Listeria monocytogenes • Neonatal sepsis • Neonatal meningitis – ‘Early’ – ‘Late’ • Adult meningitis – Rhombencephalitis • Peritonitis • Liver / spleen abscess • • • • • • • Cutaneous disease Pneumonia Septic arthritis Osteomyelitis Endocarditis Endopthalmitis Febrile gastroenteritis Most distinctive syndromes... • Neonatal sepsis and meningitis • Sepsis in the compromised host • Listeria rhombencephalitis** **see good review by Oevermann et al. Interdiscp Perspect Infect Dis, 2010 Suggestive features of Listeria meningitis/rhombencephalitis in adults • Presentation may be subacute • Nuchal rigidity less common (only 80% of adults) • Movement disorders more common (ataxia, tremors, myoclonus) (1520%) • Seizures more common (25%) • Fluctuating mental status common • Positive blood cultures more likely (75%) Suggestive features of Listeria meningitis/rhombencephalitis in adults • CSF findings: – Negative gram stain (60%) – Glucose level not low (normal in >60%) – Mononuclear cells predominate (30% cases) • Most importantly, less likely to be immunocompromised Recent Updates on Risk Factors Non-Pregnancy-Associated Human Listeriosis in England and Wales, 2001 to 2007 Increasing sepsis in elderly …Gillespie et al. J Clin Micro, 2009 Non-Pregnancy-Associated Human Listeriosis in England and Wales, 2001 to 2007 • 780 cases • Risk factors identified for sepsis vs CNS disease: – Presence of underlying disease (OR 3.1) – Malignancies (OR 1.8) – GI malignancy (OR 5.6) – Use of cytotoxic drugs (OR 2.1) – Rx to reduce acid secretion (OR 1.7) …Gillespie et al. J Clin Micro, 2009 Gastric acidity as protective factor …Gillespie et al. J Clin Micro, 2009 Gastric acidity as protective factor -Increasing use of PPIs vs H2 receptor antagonists possible association with increases of Listeria bacteremia? …Gillespie et al. J Clin Micro, 2009 Non-Pregnancy-Associated Human Listeriosis in England and Wales, 2001 to 2007 …Gillespie et al. J Clin Micro, 2009 Other papers at this meeting • Mook et al, XVII ISOPOL, CO 26 – UK update on risk factors • Hershko-Clement et al, XVII ISOPOL, CO 29 – Israeli experience • Goulet et al XVII ISOPOL, CO 31 Estimation of incubation period ( CNS median 10 days (2-19) vs perinatal 28 days (14-88). Has implications for investigation of outbreaks. Listeriosis in Scandinavia • 289 cases reported from Norway between 1977-2003 • 12 cases from 2 outbreaks • 39 perinatal cases • Perinatal cases stable 34/1,000,000) • Non-pregnancy cases increased from 1.1 to 3.7/1,000,000 …Antal et al, Scand J Infec Dis, 2007 Listeriosis in Scandinavia …Jensen et al, Eurosurveillance, 2010 “Quargel” Cheese Outbreak 2009-2010 • Sourmilk curd cheese • Multinational • Austria,Germany, and Czech Republic • Serotype 1/2a • 2 clones • 34 cases, adults …Fretz et al, Eurosurveillance, 2010 Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Listeriosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: • • • • Matched case-control study 30 cases in SOT (n=25,997) 15 transplant centers in Spain No outbreaks or clusters noted …Nuria et al. CID, 2009 Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Listeriosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: …Nuria et al. CID, 2009 Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Listeriosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: …Nuria et al. CID, 2009 Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Listeriosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: • Manifestations of Listeria infection – – – – – – Bacteremia Meningoencephalitis Spontaneous peritonitis Pleural empyema Liver abscesses Brain abscesses 26 (86.7) 10 (33.3) 2 (6.7) 1 (3.3) 1 (3.3) 1 (3.3) …Nuria et al. CID, 2009 Risk Factors, Clinical Features, and Outcomes of Listeriosis in Solid-Organ Transplant Recipients: • Antibiotic treatment – Ampicillin 28 (93.3) – Gentamicin 11 (36.7) – TMP-SMZ 11 (36.7) • Length of IV treatment, median days 21 (3–43) • Length of treatment, median days 21 (7–56) • Length of hospitalization, median days 30 (7–210) • 30-Day mortality 8 (26.7) …Nuria et al. CID, 2009 LM Meningitis in HIV • Review of ~300 pts with SBM at a Spanish hospital • 32 HIV (+) (RR for SBM = 19x) • Patients with HIV generally sicker with their SBM • LM a significant pathogen in this setting …Domingo et al. J AIDS, 2009 LM Meningitis in HIV HIV (+) N=32 HIV (-) N=267 …Domingo et al. J AIDS, 2009 Risk factors for perinatal infection • Review of 37 maternal-foetal cases from Denmark, 1995 – 2005 • Incidence 4.8/10,000 deliveries, higher then in previous 10 years • 24 survivors, 12 abortion/stillbirths • No differences in demographics between groups although abortion/stillbirths more common in mothers with previous miscarriage …Smith et al. Scand J Infec Dis, 2009 Risk factors for perinatal infection • 80% of children born to mothers with listeriosis developed neonatal listeriosis (early infection) • Typical skin rash was not noted in any cases • 23/24 infants discharged in good health • Only 4 women had known risk factors for non-pregnancy related infection …Smith et al. Scand J Infec Dis, 2009 Spontaneous abortion – the debate continues ! • Case-control study from Iran • 250 women with spontaneous abortion vs 200 with normal term deliveries from a single hospital 2002-2003 • Seropositivity using an IFA for antiListeria IgG (serotypes 1/2a and 4b) from Euroimmune AG …Jamshidi et al. Taiwan J Obs Gynec, 2009 Spontaneous abortion – the debate continues ! …Jamshidi et al. Taiwan J Obs Gynec, 2009 Spontaneous abortion – the debate continues ! …Jamshidi et al. Taiwan J Obs Gynec, 2009 Risk factors for mortality in non-perinatal listeriosis • 13 year retrospective cohort study from passive surveillance in LA County, California – 1992-2004 • 285 patients identified through LA County laboratories • Invasive isolates as well as stool isolates during an outbreak …Guevara et al. J Infec Dis, 2009 Risk factors for mortality in non-perinatal listeriosis …Guevara et al. J Infec Dis, 2009 Risk factors for mortality in non-perinatal listeriosis …Guevara et al. J Infec Dis, 2009 Risk factors for mortality in non-perinatal listeriosis -Risk of death higher at age >65 RR 1.85 (CI 1.09-3.14) …Guevara et al. J Infec Dis, 2009 Risk factors for mortality in non-perinatal listeriosis • Multivariant analysis of 29 factors for mortality was significant for: – Age >70 (OR 3.44) – Non-hematologic Ca (OR 5.92) – Use of corticosteroids (OR 3.34) – Alcoholism (OR 4.63) – Renal disease (OR 2.94) • All other CI’s overlap 1.0 …Guevara et al. J Infec Dis, 2009 Bacterial meningitis in the elderly • Review of 185 cases in Spain in patients >65 years between 1977-2006 • Most common organisms: – S. pneumoniae 74 – N. meningitidis 49 – L. monocytogenes 17 • Outcomes poor (31% mortality) • Neurologic presentations severe in comparison to younger patients …Cabellos et al. Medicine (Baltimore), 2009 TNF inhibitors are a new risk factor for listeriosis ….Slifman, A&R, 2003 Atopy a new risk factor? • Atopic mouse model v s outbred mice • LD50 much lower and bacterial counts in liver and spleen much higher in NC/Nga mice given an oral inoculum of LM • Associated with marked inc in IL-10levels • “Asthma” noted in other cohorts as risk …Kawamoto et al. XVII ISOPOL, BO 16 Genetic/gender predisposition? • In a humanized mouse model, a long variant mutation in caspase 12 inhibits immune response to listeriosis • Inhibited by estrogen, possibly conferring greater protection in innate immunity in females, especially African-Americans …Yeretssian et al. PNAS, 2009 New Syndromes NF due to LM: First report • 82yo man with hx of chronic lower extremity lymphedema, cirrhosis, and adrenal insufficiency • L Lower extremity erythema and swelling with progression • Rx with ceftriaxone but progressed • OR revealed NF and debrided …Sendi et al. CID, 2009 NF due to LM: First report • Treated with amox/clav, clindamycin , and gentamicin • Blood and tissue cultures grew LM only • Risk factors? – Prednisone 17.5 mg OD x 2 mo – Cirrhosis – Had consumed a lot of unpasteurized sheep’s milk cheese ! …Sendi et al. CID, 2009 Listeria sclerokeratitis • A 25-year-old non–contact lens–wearing male rugby player was referred with progressive infective sclerokeratitis unresponsive to topical antivirals and antibiotics. On examination, visual acuity was perception of light, and a large corneal abscess with overlying epithelial defect and hypopyon was present. The corneal lesion was cheesy white and raised with nasal scleritis. This raised the suspicion of a fungal keratitis. Empirical treatment with intensive topical antifungals was unsuccessful. A previous corneal scrape had been negative for bacteria and fungi. A corneal biopsy was performed, and Listeria monocytogenes was eventually isolated from enrichment culture. Antibiotic sensitivities showed it to be resistant to cefuroxime, methicillin, and ceftazidime but sensitive to all other antibiotics tested including ofloxacin. The treatment course was complicated by a corneal perforation that needed an emergency therapeutic penetrating Keratoplasty • 4 other case reports since 1988 …Tay et al. Cornea, 2006 Treatment Issues Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes to antibiotics • Fully susceptible – Penicillin, ampicillin, azlocillin, imipenem – All aminoglycosides – Vancomycin, teichoplanin – Cotrimoxazole, rifampin, tetracycline – Linezolid Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes to antibiotics • Intermediate susceptibility – Quinolones – Chloramphenicol – Clindamycin – Other macrolides Susceptibility of recent food isolates to antibiotics …Conter et al. Int J Food Microbiol, 2008 Susceptibility of recent food isolates to antibiotics …Conter et al. Int J Food Microbiol, 2008 Antibiotic susceptibility of LM Retail food isolates from Denmark …Aarestrup et al, Foodborne Pathog Dis, 2007 Antimicrobial resistance of Listeria monocytogenes human strains isolated in France. Abstract • Susceptibility to antibiotics of 4,816 clinical L. monocytogenes isolated since 1926 was studied and the temporal evolution of susceptibility to antibiotic was analyzed through several decades. The mechanisms of resistance were studied in each resistant strain. The prevalence of resistant strains was estimated at 1.27% among human isolates. Resistance to tetracyclines and fluoroquinolones was more common and has recently emerged. Although acquired-resistance in clinical L. monocytogenes did not implicate clinically-relevant antibiotics, the possibility of resistance gene transfers, the description of the first clinical isolate with high-level resistance to trimethroprim, and the recent increase in penicillin MICs with values up to 2 mug/mL reinforce the need for microbiological surveillance. …Morvan et al, AAC, 2010 Linezolid Anecdote • 76 yo man with recurrent fever and diagnosis of LM prosthetic valve endocarditis with splenic abscesses • Rx with vancomycin,gentamicin, ceftriaxone • PCR (+) at AVR surgery • CRF suggested change to linezolid with rx for 4 weeks • Successfully discharged • Previous rhombencephalitis case (Morosi et al 2006) …Munoz et al, Int J Microbial Agents 2006 Activity of Daptomycin against Listeria monocytogenes Isolates from Cerebrospinal Fluid • New lipopeptide antibiotic for treatment of Gram (+) infections • 76 isolates from CSF in Netherlands tested • MIC’s and E-tests showed unacceptably high values • Daptomycin not likely to be useful in LM meningitis …Spanjaard and Vandenbroucke-Grauls, AAC, 2008 Levofloxacin Anecdote • 74 yo woman with acute LM meningitis • Alcoholism a risk factor • Treated with cefotaxime and levofloxacin empirically • Switch to meropenem + levo on ID of LM in CSF • LP 1 hr post-infusion yielded levofloxacin levels 7.79 and 5.28 mg/L in blood and CSF respectively • Meropenem D/C’d day 8, switch to po levofloxacin • Would levo be a good addition to regimen of a beta-lactam? …Viali et al, DiagMicrobiolInfDis 2007 Predictors of mortality and impact of aminoglycosides on outcome • Retrospective mortality study in a large tertiary care hospital in Barcelona 1983-2006 • Adult, non-pregnant cases • 118 episodes (16 excluded as died in <48hrs) • 69 had beta-lactam monotherapy, 33 had combination therapy with Ags …Mitja et al. J Antimicrob Chemo, 2009 Predictors of mortality and impact of aminoglycosides on outcome • Evenly matched except > corticosteroid exposure (p =<.001) and > number presented with coma (p=.027) in combination rx group • Overall mortality 33% in combination group vs 14.5% in monotherapy (p=.03) • Early mortality 8 x greater in combination rx group (OR = 2-33) …Mitja et al. J Antimicrob Chemo, 2009 Antibiotic therapy of LM meningitis • Comparison of moxifloxacin vs ampicillin + gentamicin • Experimental infection in NZ rabbits • LM injected in cisterna magna • 16 hrs later antibiotics started • Comparisons to controls without ATBs …Sipahi et al, JAC, 2008 Antibiotic therapy of LM meningitis •Persistant infection in all groups – no advantage to moxifloxacin use …Sipahi et al, JAC, 2008 Predictors of mortality and impact of aminoglycosides on outcome • 57% of combination group received “inadequate therapy” including a cephalosporin (42%) • Multivariate analyses demonstrated age, corticosteroids, and renal failure as significant predictors of early mortality and neoplastic disease and coma as late predictors …Mitja et al. J Antimicrob Chemo, 2009 Predictors of mortality and impact of aminoglycosides on outcome • Conclusions – aminoglycosides are not beneficial and may be harmful in treatment of listeriosis but noncephalosporin beta-lactams are key to effective treatment …Mitja et al. J Antimicrob Chemo, 2009 Use of steroids in LM meningitis/encephalitis? • Corticosteroids have become a standard adjunct to antibiotics in bacterial meningitis (S. pneumoniae) • Anecdotal case reports continue to suggest a potential role in LM infection – Kayaaslan et al, Int J Infec Dis, 2009 – Orton-Castano et al, Rev Neurol, 2002 – Popescu et al, J Clin Path, 2004 Probiotics for protection? • Guinea pig model • Yogurt with Bifidobacteria and Lactobacilli reduced invasion and number of stillbirths in pre-treated animals given 10 9 oral LM • Implications for advice to pregnant women? …Smith et al. XVII ISOPOL, BO 14 Summary • Recent reviews suggest an upswing in non-perinatal listeriosis, especially sepsis • Risk factors include age and immunosuppression, including use of newer agents such as monoclonals and TNF-alpha inhibitors • NF has now been reported with LM • Recent data suggests that aminoglycosides may be harmful but more data required before altering standard beta-lactam + Ag treatment • Newer agents such as linezolid and moxifloxacin may not be as useful as expected • Use of adjunctive corticosteroid treatment continues to be anecdotal – perhaps best reserved for abscess or severe illness Obrigado! Listeriosis in Scandinavia …Antal et al, Scand J Infec Dis, 2007 Listeriosis in Scandinavia …Antal et al, Scand J Infec Dis, 2007 Listeriosis in Scandinavia …Jensen et al, Eurosurveillance, 2010 MRI vs SPECT scan in rhombencephalitis • This report describes a case of brain-stem listeriosis in a previously healthy 51-year-old woman. The diagnosis was based on clinical findings, the results of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) analysis, CSF culture, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) findings. MRI demonstrated upper brain stem and cerebellar peduncle involvement. In addition, Tc-99m exametazime (HMPAO)-labeled single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) of the brain revealed bilateral cerebellar hypoperfusion. Antibiotic therapy resulted in partial clinical recovery after 3 weeks. At the end of 6 months, brain-stem findings had nearly resolved. However, although minimal residual findings were observed on MRI at 6 months, bilateral diffuse cerebellar hypoperfusion remained on Tc-99m HMPAO brain SPECT. …Sahin et al, MedGenMed, 2007 Czech LM Outbreak 2006 • 75 cases • Mixed adult and perinatal cases, primarily in elderly • Serotype 1/2b, 26/30 isolates pulse type A • Same type found in cheese and salad …Vit et al, Eurosurveillance, 2007 Czech LM Outbreak 2006 …Vit et al, Eurosurveillance, 2007 Czech LM Outbreak 2006 …Vit et al, Eurosurveillance, 2007 Listeriosis in UK 2001-2004 Outbreaks …Gillespie et al, Emerg Infec Dis, 2006 Listeriosis in UK 2001-2004 Increases in non-perinatal cases …Gillespie et al, Emerg Infec Dis, 2006 Listeriosis in UK 2001-2004 Age of Cases …Gillespie et al, Emerg Infec Dis, 2006 Listeriosis in UK 2001-2004 Bacteremia accounts for increase in age >60 …Gillespie et al, Emerg Infec Dis, 2006 Listeriosis in Portugal 1994-2003 • 10 year retrospective study • All cases identified in 23 hospital labs and Portuguese NIH Porto • Most blood/CSF isolates • 35 cases, 5 perinatal • CFR ~17-36% • Increases in 2003 (reporting bias?) – incidence at least 1.4/1,000,000 • Minimal clinical information was available …Almeida et al, BMC Infect Dis, 2006 Age Distribution with and without Comorbidities, 1990-2001 Without Underlying Condition Without Underlying Condition (n=248) (n=248) With Underlying Condition (n=2207) With Underlying Condition (n=2207) …Fontanet, Martin, Schreiber, Inst Pasteur, 2005 Incidence in Males vs. Females (Including Pregnancy-Associated Cases) Males (n=2520) Mean: 52yrs 52yrs Median: 62yrs Median: 62yrs Mean: Females Females(n=2463) (n=2463) Mean: 41yrs Mean: 41yrs Median: 35yrs Median: 35yrs …Fontanet, Martin, Schreiber, Inst Pasteur, 2005 Clinical Presentation, 1996-2001 • 87% had an underlying condition • 8.6% (94) presented with other clinical presentations, most commonly ascites & peritonitis, infected aortic aneurysm, abscess, gastroenteritis, lung infection, and UTI • Sepsis more common in patients with comorbidities, EXCEPT alcoholism, which was more commonly associated with CNSI (p<0.0001) …Fontanet, Martin, Schreiber, Inst Pasteur, 2005 Susceptibility of Listeria monocytogenes to antibiotics • Resistant – Cephalosporins • Only aminoglcosides and glycopeptides are bactericidal • In vitro synergism with ampicillin and gentamicin • In vitro indifference and antagonism with some other combinations …adapted from Hansen, Gerner-Smidt, Bruun, APMIS, 2005 Treatment of CNS LM CNS Penetration Good Diffusion Penicillins 3rd & 4th Gen Cephs Chloramphenicol Rifampin TMP-SFX Poor Diffusion Early Gen Cephs Clindamycin AMGs Tetracyclines Macrolides Linezolid- the newest kid on the block? • Leiti, CID, 2005 reported a case treated with oral linezolid/rifampin for 107 days after a 40 day course of ampicillin • Morosi, J Infection, 2006 reported successful rx of rhombencephalitis after “failure” of amp/gent, followed by TMPSFX/vanco. TMP-SFX was continued • Munoz, Int J Antimicrob Agents, 2006 reported a case of culture (-) endocarditis (16S (+) for LM!) treated with 2 wks of vanco followed by 4 weeks of linezolid Treatment Listeria monocytogenes infections • Ampicillin and gentamicin remains the best studied regimen • Cephalosporins are uniformly inactive • Moxifloxacin active (Grayo, XVI ISOPOL) • Linezolid active • Length of treatment should be 3 weeks for sepsis and meningitis and 6 weeks for brain abscess or endocarditis (Lorber, CID, 1997)